包覆BST陶瓷的制备工艺与储能性能研究毕业论文
2020-04-05 10:46:15
摘 要
高功率脉冲系统小型化的发展要求储能介质材料具有更高的储能密度和耐压强度。Ba1-xSrxTiO3陶瓷因具有较高的介电常数等优点,成为理想的第三代脉冲形成线介质材料之一,但较低的耐压强度限制了其在储能领域的应用。因此,脉冲功率技术的发展要求相关科研工作者制备出具有高介电击穿强度的储能陶瓷。本文主要阐述通过化学包覆SiO2方法,制备具有“核-壳”结构SiO2包覆纳米Ba0.4Sr0.6TiO3粉体,以及使用常规固相烧结和微波烧结两种烧结方式,对陶瓷显微结构以及介电性能的影响。
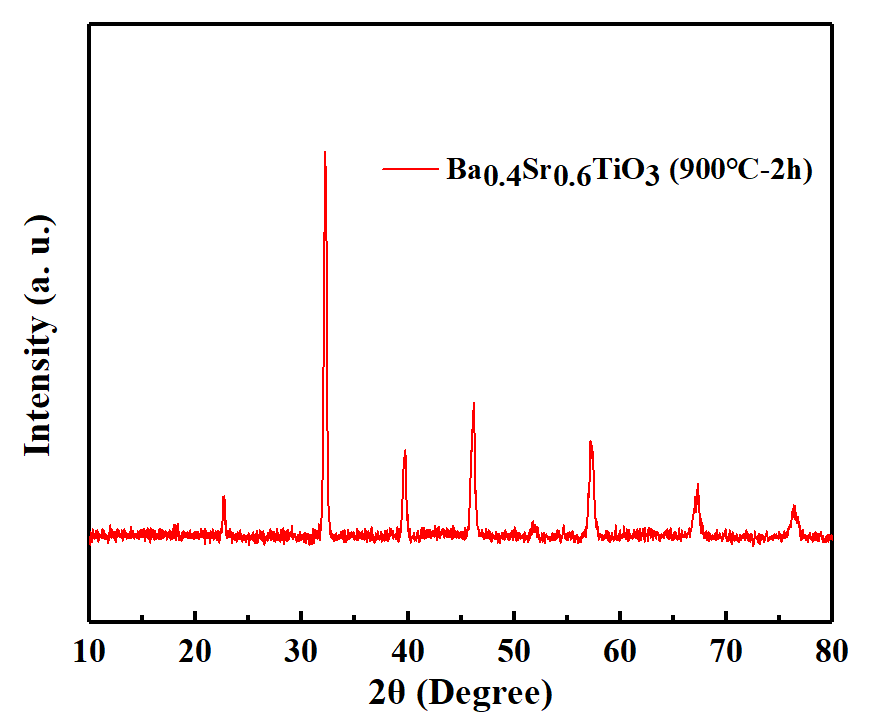
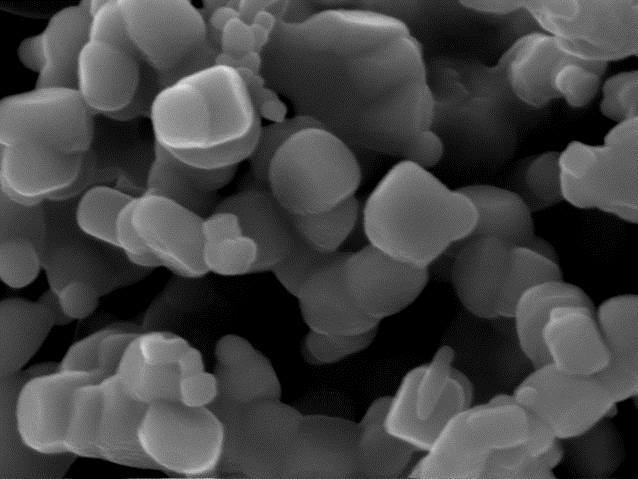
(1)以乙酸钡、乙酸锶为钡、锶源,钛酸四丁酯为钛源,聚乙二醇为分散剂,采用草酸盐共沉淀法可制备出纯度高的纳米级Ba0.4Sr0.6TiO3粉体。制得的粉体为钙钛矿结构; 900℃下煅烧得到的粉体晶粒发育完好,粒径分布均匀,平均粒径为130nm左右且分散良好
(2)采用Stöber方法制备出具有“核-壳”结构的SiO2包覆纳米Ba0.4Sr0.6TiO3粉体,研究表明SiO2可以较均匀的包覆在纳米粉体的表面,制备出包覆有不同“核-壳”的粉体;通过改变加入正硅酸四乙酯的量可以改变“壳”层的厚度,制备出具有不同“壳”层厚度的“核-壳”结构包覆纳米Ba0.4Sr0.6TiO3粉体。
(3)包覆后烧结得到的陶瓷材料表现出立方相结构,一部分SiO2与Ba0.4Sr0.6TiO3发生反应,形成了第二相Ba2TiSi2O8。未包覆SiO2的Ba0.4Sr0.6TiO3陶瓷的晶粒尺寸较大,而二氧化硅的加入可以抑制晶体的生长且在陶瓷中会以液相形式存在。且相对于常规烧结,微波烧结的陶瓷晶粒尺寸明显减小且大小更均匀。
(4)在相同温度下,随着SiO2包覆量的增大,材料的介电常数逐渐降低,且微波烧结的介电常数低于常规烧结,这可归因于微波烧结具有更小的晶粒尺寸。对于相同烧结方式的样品,包覆SiO2的Ba0.4Sr0.6TiO3陶瓷的击穿场强明显增大,这是由于SiO2玻璃相具有良好的抗击穿性能。随着顺电相二氧化硅含量的增大,Ba0.4Sr0.6TiO3@xwt%SiO2陶瓷的饱和极化强度(Ps)降低。微波烧结得到的陶瓷材料达到了最大的充电储能密度2.30J/cm2、最大的有效储能密度1.83J/cm2以及最大的击穿场强30.78 kV/mm。
关键字:Ba0.4Sr0.6TiO3陶瓷;草酸盐共沉淀法;SiO2包覆;微波烧结;储能性能
Abstract
The development of miniaturization of high-power pulse systems requires energy storage media materials with higher energy storage density and higher breakdown strength. Ba1-xSrxTiO3 ceramics have become ideal third-generation pulse-forming dielectric materials because of their high dielectric constant. However, their lower breakdown strength limits their applications in energy storage field. Therefore, the development of pulsed power technology requires relevant researchers to prepare energy storage ceramics with higher dielectric breakdown strength. This thesis mainly describes the preparation of SiO2-coated nanoparticles of Ba0.4Sr0.6TiO3 with "core-shell" structure through chemical coating of SiO2, as well as the impact of using conventional solid-state sintering and microwave sintering, to the ceramic microstructure and the electrical properties.
(1) Barium acetate, barium strontium, strontium source, tetrabutyl titanate as titanium source, polyethylene glycol as dispersant, oxalate co-precipitation method could be prepared with high purity nano-scale Ba0.4Sr0 .6TiO3 powder. The prepared powder was in perovskite structure; the powder crystal grains obtained by calcining at 900℃ developed well and the particle size distribution was even, the average particle size was about 130 nm and the dispersion was good.
(2) SiO2-coated nano-Ba0.4Sr0.6TiO3 powders with "core-shell" structure were prepared by Stöber method. The results show that SiO2 can be uniformly coated on the surface of nano-sized powders into "Core-shell" powder. By changing the amount of tetraethyl orthosilicate added, the thickness of the "shell" layer can be changed to prepare the "core-shell" structured coated nano-Ba0. 4Sr0.6TiO3 powder with different "shell" thickness.
(3) After sintering, the obtained ceramic material showed a cubic phase structure, and part of SiO2 reacts with Ba0.4Sr0.6TiO3 to form the second phase Ba2TiSi2O8. The grain size of Ba0.4Sr0.6TiO3 uncoated with SiO2 is larger, while the addition of silica can suppress the crystal growth and exist in liquid phase in ceramic. Compared with the conventional sintering, the size of the ceramic grains of microwave sintering is significantly reduced and becomes more uniform.
(4) At the same temperature, with the increase of SiO2 coating, the dielectric constant of the material gradually decreases, and the dielectric constant of microwave sintering is lower than that of conventional sintering, which can be attributed to the smaller grain size. SiO2 coating makes the material more obvious electro-conductivity. As the silica content increases, the saturation polarization (Ps) of xwt% SiO2 @ Ba0.4Sr0.6TiO3 ceramics decreased. The breakdown field strength of Ba0.4Sr0.6TiO3 coated with SiO2 was obviously higher the samples with the same sintering method because of the good anti-breakdown property of SiO2. The ceramic material obtained by microwave sintering achieved the maximum charge storage density of 2.30J/cm2, the maximum effective energy storage density of 1.83 J/cm2 and the maximum breakdown field strength of 30.78 kV/mm.
Keywords: Ba0.4Sr0.6TiO3 ceramics; oxalate co-precipitation method; SiO2 coating; microwave sintering; energy storage performance
目 录
摘要……………………………….………………………………………………………………I Abstract……………..…………………………………………………………………………….II
1 绪论 1
1.1 脉冲形成线储能介质材料的现状 1
1.2 储能介质陶瓷材料的性能表征 3
1.2.1 介电常数 3
1.2.2 介质损耗 4
1.2.3 击穿强度 4
1.2.4 介电非线性 5
1.2.5 储能密度 6
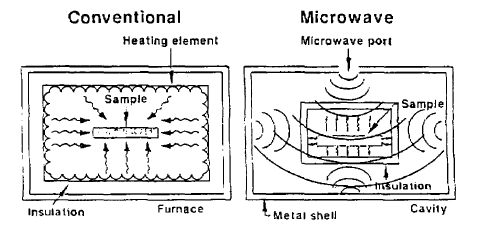
1.3 烧结工艺对陶瓷显微结构的影响 8
1.4 钛酸锶钡(BST)储能介质陶瓷 10
1.4.1 包覆钛酸锶钡(BST)储能介质陶瓷粉体的制备 10
1.5论文的研究思路 11
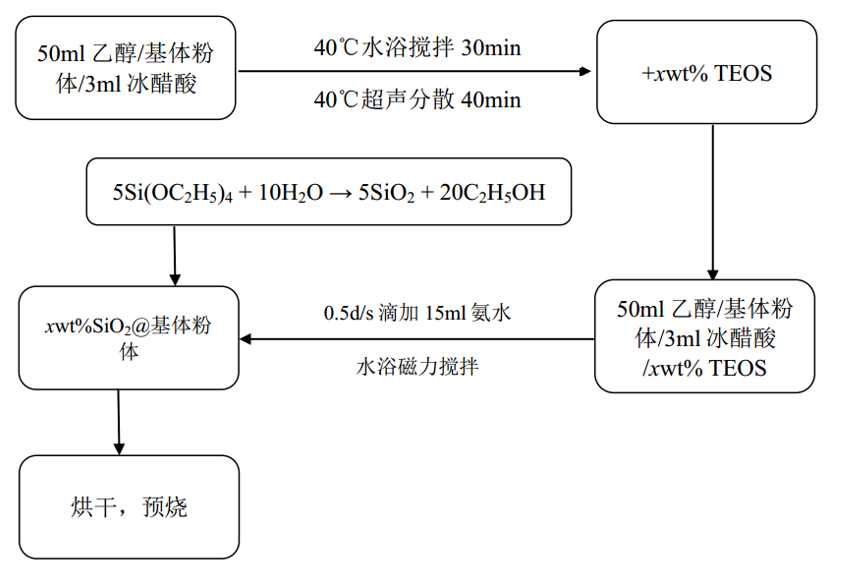
2 SiO2包覆Ba0.4Sr0.6TiO3陶瓷的制备及测试方法 12
2.1实验设计与工艺路线 12
2.2 实验原料及设备 13
2.3 结构与性能表征方法 15
2.3.1 密度测试 15
2.3.2 物相及晶体结构分析 15
2.3.3 显微结构分析及平均晶粒尺寸计算 15
2.3.4 电学性能测试 15
3 SiO2包覆纳米Ba0.4Sr0.6TiO3粉体的制备 17
3.1 Ba0.4Sr0.6TiO3基体粉制备 17
3.1.1 草酸盐共沉淀法制备Ba0.4Sr0.6TiO3的反应机理 17
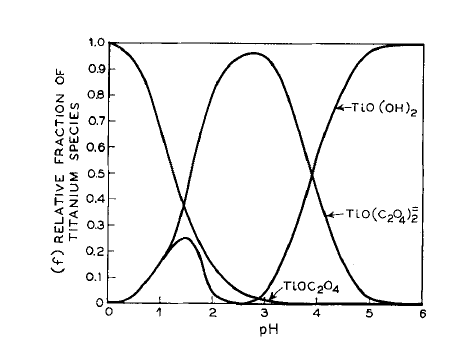
3.1.2 溶液pH值对Ba0.4Sr0.6TiO3相组成的影响 18
3.1.3 Ba0.4Sr0.6TiO3基体粉体的物相结构 19
3.1.4 Ba0.4Sr0.6TiO3基体粉体的显微结构 20
3.2 Ba0.4Sr0.6TiO3基体粉体的SiO2包覆 20
3.2.1 xωt%SiO2包覆Ba0.4Sr0.6TiO3粉体的显微结构分析 21
3.3 xωt%SiO2包覆Ba0.4Sr0.6TiO3陶瓷的微波烧结工艺 22
3.4 xωt%SiO2包覆Ba0.4Sr0.6TiO3陶瓷的物相结构 23
3.5 xωt%SiO2包覆Ba0.4Sr0.6TiO3陶瓷的显微结构分析 24
3.6本章小结 25
4 SiO2包覆Ba0.4Sr0.6TiO3陶瓷的介温与储能性能 27
4.1 SiO2包覆Ba0.4Sr0.6TiO3陶瓷的介温性能 27
4.2 SiO2包覆Ba0.4Sr0.6TiO3陶瓷的储能性能 28
4.3本章小结 30
5. 结论 31
参考文献 32
致 谢 35
1 绪论
1.1 脉冲形成线储能介质材料的现状
脉冲功率技术,全称为高电压大功率脉冲技术,是将大量的能量(可高达几百千至几十兆焦耳)储存于电容、电感等储能元件中,通过快速开关(动作时间可低至毫微秒量级)将这些能量在短时间(可低至毫微秒到微秒)内有效释放至负载,以获得极高的功率(可高达兆瓦量级)。在20世纪中后叶,随着核物理技术、粒子加速器技术、电子束和等离子技术等新兴技术的研究和应用,脉冲功率技术得以迅猛发展。许多国家的高校院所与研究单位,如美国的Sandia国家实验室、海军研究实验室、加州大学、物理国际公司、日本东京大学等,都相继开展了脉冲功率技术的研究[1]。
初始
能源
中间
储能
介质
脉冲
形成
回路
能量供给单元
能量输出单元
图1-1 脉冲功率系统
Figure1-1 The pulse power system
脉冲功率系统的结构模式如图1-1所示,主要由初始能量源、能量储存单元组成的功率供给系统和由脉冲形成回路和负载组成的高功率输出系统两个板块构成[2]。脉冲功率系统中,脉冲的产生过程包括慢脉冲的产生与快脉冲的产生两个阶段。一般情况下,慢脉冲由能量储存单元采用Marx发生器和脉冲变压器产生,快脉冲则由脉冲形成回路采用Blumlein脉冲发生器与叠积式传输线形成。图1-2给出了典型的单极Marx发生器和Blumlein脉冲发生器的设计示意图[3]。
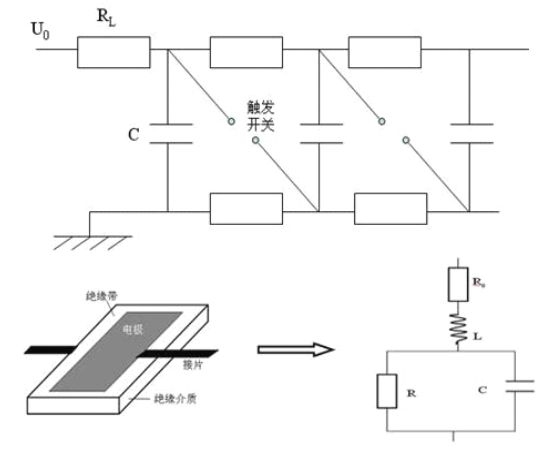

图1-2 单极Marx发生器(左)和简化Blumlein脉冲形成线(右)设计示意图
以上是毕业论文大纲或资料介绍,该课题完整毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、程序设计、图纸设计等资料请添加微信获取,微信号:bysjorg。
相关图片展示:
您可能感兴趣的文章
- 改善锂离子电池中硅基负极存储性能的策略研究外文翻译资料
- 通过添加压电材料BaTiO3提高大功率锂离子电池的微米级SiO @ C/CNTs负极的电化学性能外文翻译资料
- Pd和GDC共浸渍的LSCM阴极在固体氧化物电解池高温电解CO2中的应用外文翻译资料
- 利用同步回旋加速器粉末衍射的方法来研究在有其他物相的情况下C4AF的水化作用外文翻译资料
- 外国循环流化床锅炉发展现状外文翻译资料
- 含石蜡基复合材料的多壁碳纳米管的热性能外文翻译资料
- 矸石电厂炉渣机制砂的应用研究外文翻译资料
- 机动车螺旋弹簧的失效分析外文翻译资料
- 从废阴极射线管和锗尾矿制备高强度玻璃泡沫陶瓷外文翻译资料
- 作为导热液体的液态金属在太阳能储热中的应用外文翻译资料




