BiAlO3-BaTiO3介电陶瓷制备及介电性能研究毕业论文
2020-04-05 10:44:23
摘 要
多层陶瓷电容器(MLCC)在电子行业中占据着非常重要的位置,BaTiO3因为具备较高的介电常数,无污染等优点逐渐成为研究MLCC瓷料的首选基体材料,但由于BaTiO3居里温度为130oC,居里温度附近介电常数衰减均十分剧烈,无法达到对温度稳定型要求较高的MLCC瓷料的要求。
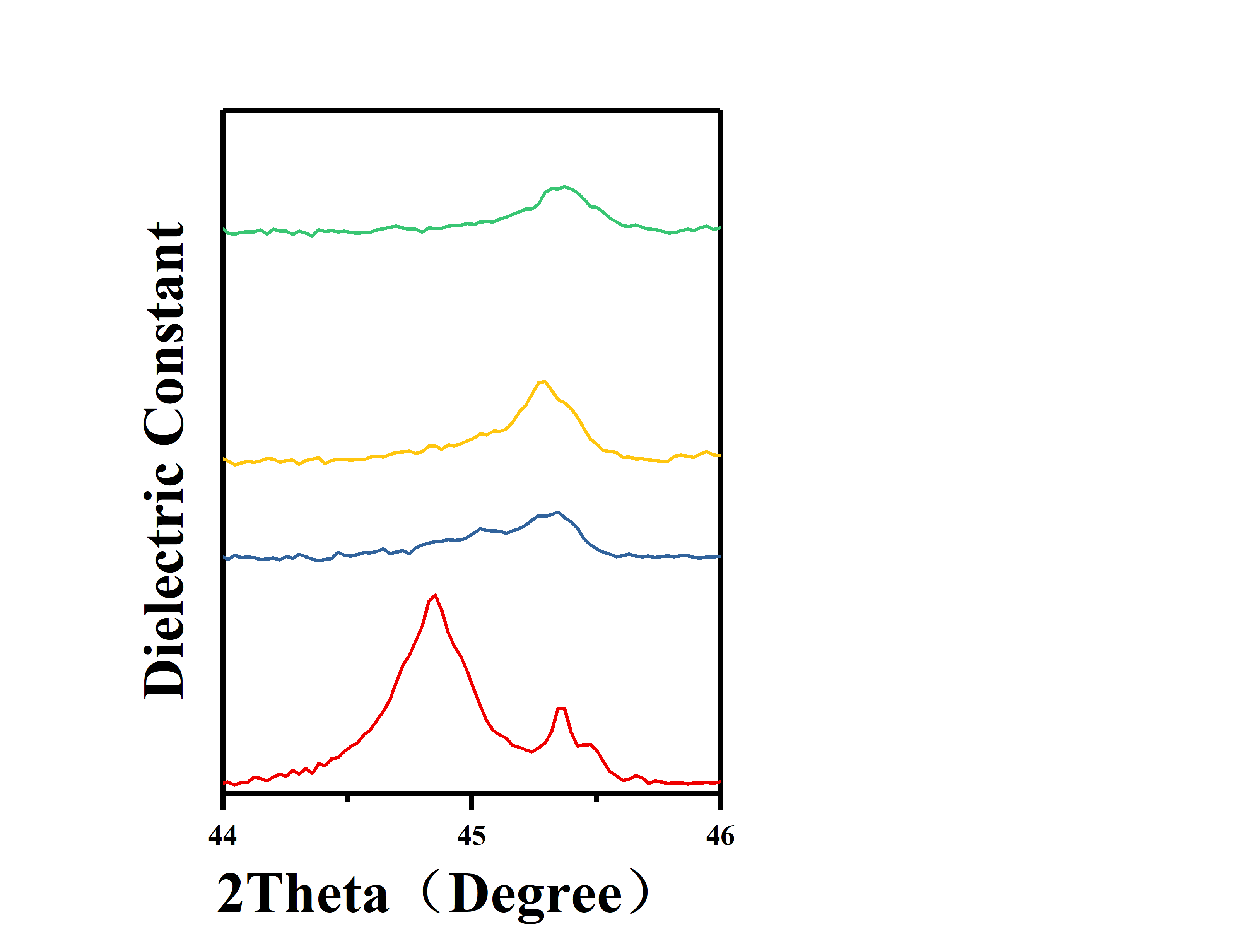
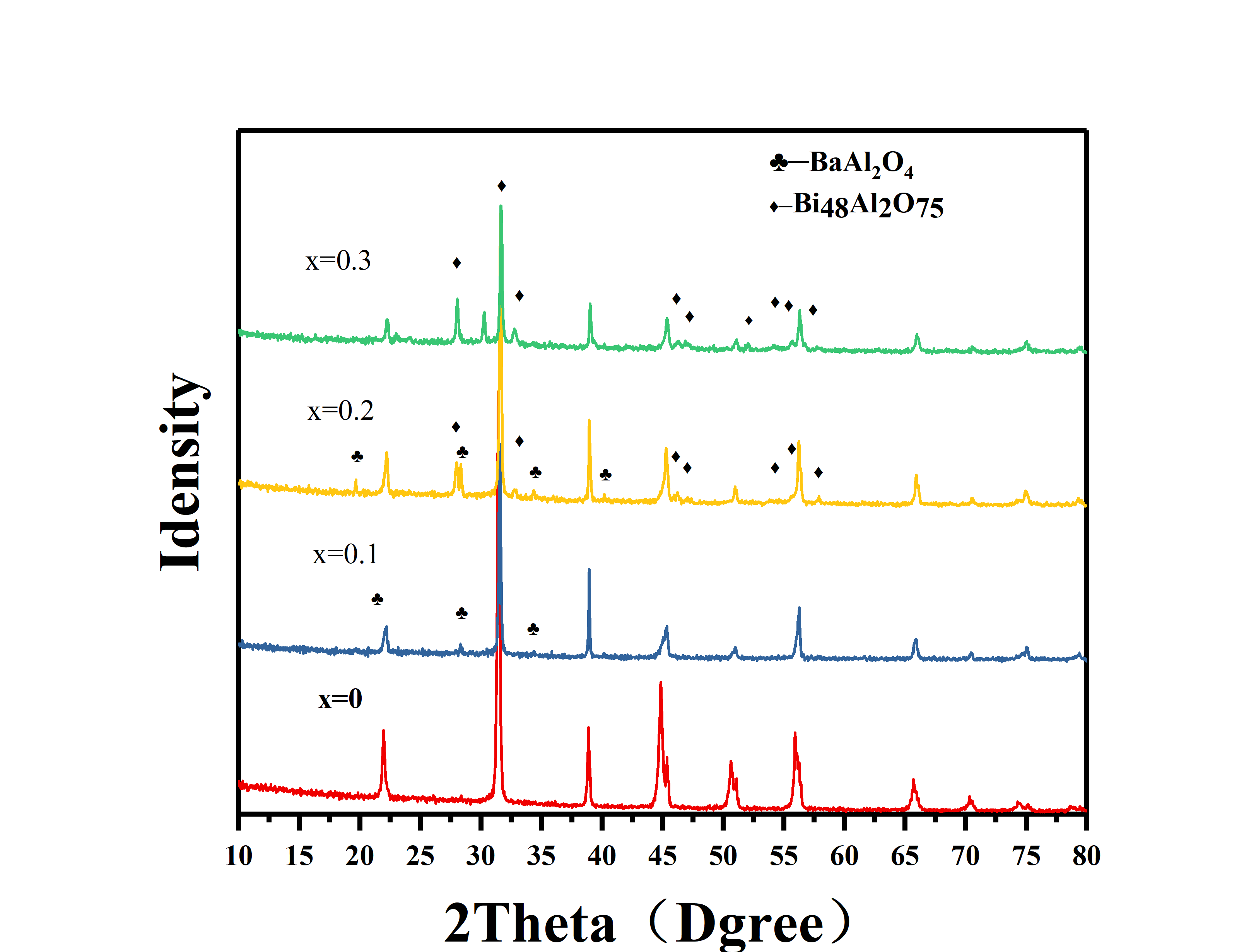
针对该问题,本文选择以xBiAlO3-(1-x)BaTiO3基陶瓷为研究对象,研究了x在0.1-0.3之间的陶瓷的物相结构、显微形貌以及介电性能。发现随着BiAlO3量的增加,有杂相BaAl2O4,Bi48Al2O75出现,并且介电峰逐渐平坦,介电常数降低。综合介电常数与介电性能,选取0.12BiAlO3-0.88BaTiO3组分作为改性基体,符合容温变化率≤的温度范围为-15oC-160oC,室温介电常数为1574。
Sm2O3与La2O3可有效改善低温端的稳定性,掺杂浓度的差异以及烧结温度的差异会对符合容温变化率的温度范围产生影响。本文讨论了Sm和La掺杂体系的显微形貌以及对介电性能产生影响的机理。并且得到了符合X8R型瓷料的1170oC下烧结的2wt%Sm2O3掺杂0.12BiAlO3-0.88BaTiO3陶瓷,容温变化率≤的温度范围为-55oC-150oC,室温介电常数为1681,介电损耗为0.0131;以及1130oC下烧结的3wt%Sm2O3掺杂0.12BiAlO3-0.88BaTiO3陶瓷,室温介电常数为1857,室温下介电损耗为0.00942。La2O3掺杂的组分均满足X7R标准,其中最佳组分为1170oC烧结的1wt%La掺杂0.12BiAlO3-0.88BaTiO3陶瓷,室温下介电常数为1812,介电损耗为0.00396。
为进一步提高介电温度稳定性能,在2wt%Sm掺杂0.12BiAlO3-0.88BaTiO3与1wt%La掺杂0.12BiAlO3-0.88BaTiO3基础上进行Yb2O3的掺杂,对介电性能进行测试,发现居里温度提高,容温变化率≤的温度范围得到拓宽,并且1130oC下烧结的2wt%Sm2O3与等同化学计量Yb2O3共掺杂0.12BiAlO3-0.88BaTiO3陶瓷,容温变化率≤的温度范围为-55oC-170oC,室温下介电常数为1704,介电损耗为0.0123。
关键词:多层陶瓷电容器;介电常数;容温变化率
Abstract
Multilayer ceramic capacitors (MLCC) are very important in the electronics industry. BaTiO3 has gradually become the preferred matrix material for MLCC dielectric powder due to its high dielectric constant and environment-friendly properties. However, since the Curie temperature of BaTiO3 is 130oC, near the Curie temperature dielectric constant decreases sharply. BaTiO3 cannot meet the requirements of dielectric temperature stability at higher temperature.
In order to solve this problem, the microstructure and dielectric properties of xBiAlO3- (1-x) BaTiO3-based ceramics were studied in this paper. It is found that with the BiAlO3 increase, BaAl2O4 and Bi48Al2O75 impurity appear, and the dielectric peak becomes flat and the dielectric constant decreases. Based on the dielectric constant and dielectric properties, 0.12BiAlO3-0.88BaTiO3 was selected as the modified matrix with C/C25oC≤from-15℃ to 160℃.The dielectric constant at room temperature is 1574 .
Sm2O3 and La2O3 can effectively improve the stability of the low-temperature end, the difference of the doping concentration and the difference of the sintering temperature have an impact on the temperature range, and the micro-morphologies and the influence on the dielectric properties of Sm and La doping systems are discussed mechanism. And the 2wt% Sm2O3-doped 0.12BiAlO3-0.88BaTiO3 ceramic sintered at 1170°C conforming to the X8R-type porcelain was obtained with C/C25oC≤from-55℃ to 150℃.Dielectric constant at room temperature for 2wt% Sm2O3-doped 0.12BiAlO3-0.88BaTiO3 ceramic is 1681 ,and dielectric loss is 0.0131. And 3wt% Sm2O3 doped with 0.12BiAlO3-0.88BaTiO3 ceramics sintered at 1130oC, the dielectric at room temperature constant is 1857 and the dielectric loss is 0.00942 at room temperature. The La2O3-doped components all satisfy the X7R standard. The best composition is 1wt% La-doped 0.12BiAlO3-0.88BaTiO3 ceramics sintered at 1170 oC with a dielectric constant of 1812 and a dielectric loss of 0.00396 at room temperature.
In order to further broaden the Curie peak, Yb2O3 doping was performed on the basis of 2wt% Sm-doped 0.12BiAlO3-0.88BaTiO3 and 1wt% La-doped 0.12BiAlO3-0.88BaTiO3. The dielectric properties were tested and found that the Curie temperature increased, Temperature range of C/C25oC≤ ± 15% of the temperature range is broadened And 2wt% Sm2O3 and equivalent stoichiometry Yb2O3 co-doped 0.12BiAlO3-0.88BaTiO3 ceramics sintered at 1130 oC, the temperature range of -55 oC-170 oC, dielectric constant of 1704 at room temperature, the dielectric loss of 0.0123.
Key Words:Multilayer ceramic capacitors; Dielectric constant; Temperature variation of capacitance
目录
第1章 绪论 1
1.1 选题背景及意义 1
1.2 MLCC概述 1
1.2.1 MLCC结构及原理 1
1.2.2 MLCC分类及发展趋势 2
1.3 BaTiO3基体瓷料 3
1.3.1 BaTiO3晶体结构 3
1.3.2 BaTiO3的介电性能 4
1.3.3 BaTiO3的改性 5
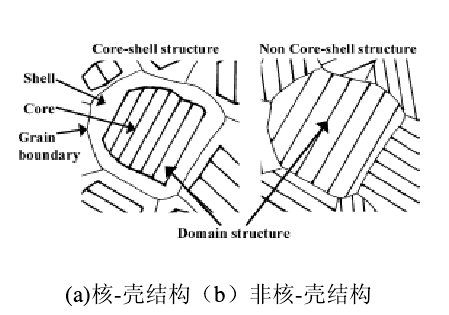
1.3.3.1 核壳结构 6
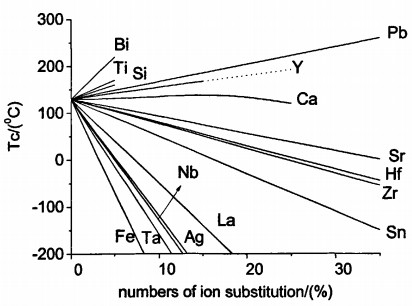
1.3.3.2移峰效应与压峰效应 7
1.3.3.3稀土掺杂 9
1.4 材料体系的选择 9
1.5 本论文研究目的与内容 9
第2章 BA-BT基瓷料的制备、结构及性能表征 11
2.1 实验原料 11
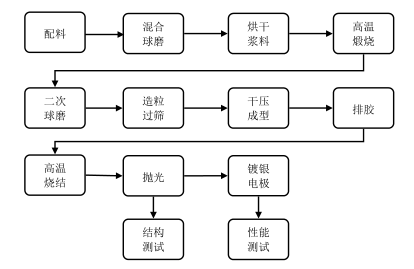
2.2 制备工艺 12
2.2.1 固相法制备BA-BT陶瓷及稀土掺杂陶瓷 12
2.3 结构表征及性能测试 13
2.3.1 体积密度 13
2.3.2 X射线衍射分析(XRD) 14
2.3.3 扫描电子显微镜(SEM) 14
2.3.4 介电性能测试 14
第3章 xBiAlO3-(1-x)BaTiO3陶瓷的制备及性能表征 16
3.1 xBA-(1-x)BT陶瓷的制备 16
3.2 xBA-(1-x)BT烧结温度 17
3.3 xBA-(1-x)BT陶瓷的物相结构 17
3.4 xBA-(1-x)BT陶瓷的显微形貌 18
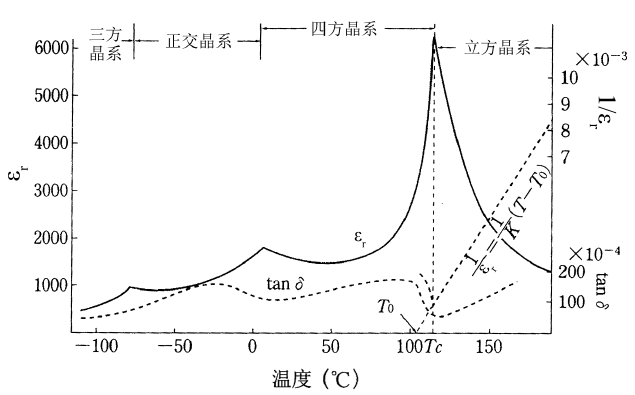
3.5 xBA-(1-x)BT陶瓷的介电性能 19
3.5.1 介温谱 19
3.5.2 容温特性 22
3.6 小结 23
第4章 0.12BiAlO3-0.88BaTiO3的低温介电性能改性 24
4.1稀土Sm掺杂改性的研究 24
4.1.1 稀土Sm掺杂瓷料的制备 24
4.1.2. 稀土Sm掺杂瓷料的体积密度 25
4.1.3 稀土Sm掺杂瓷料的物相结构分析 25
4.1.4 稀土Sm掺杂的显微结构分析 26
4.1.5 稀土Sm掺杂瓷料的介温图谱 27
4.2.1 稀土La掺杂改性研究 32
4.2.2 稀土La掺杂瓷料的制备 32
4.2.3 .稀土La掺杂瓷料的体积密度 33
4.2.4稀土La掺杂瓷料的物相结构分析 34
4.2.5稀土La掺杂显微形貌分析 35
4.2.6稀土La掺杂瓷料的介温性能 36
4.3 小结 39
第5章 BA-BT陶瓷高温介电性能改性 40
5.1高温端改性原理 40
5.2陶瓷粉料制备 40
5.3部分样品介电性能测试 41
5.4小结 44
第6章 总结 45
参考文献 47
致谢 49
第1章 绪论
1.1 选题背景及意义
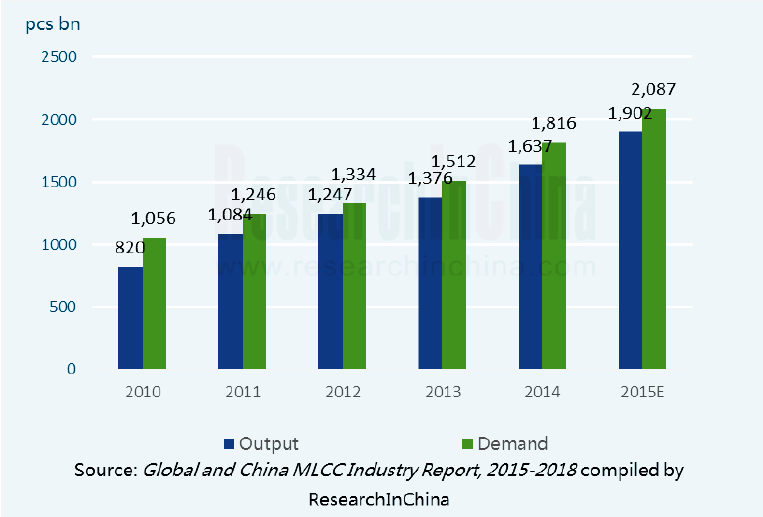
随着电子行业的发展,多层陶瓷片式电容器(Multilayer Ceramic Capacitor,简称MLCC)凭借其体积小、内部电感低、绝缘电阻高及漏电流小、介质损耗低 、价廉等优势占据了巨大的市场空间。近几年来目前MLCC在国内的需求量也在持续提升,如图1.1所示[1]。常见的低频MLCC有X7R、X8R等。根据美国电子工业协会(Electronic Industries Association,EIA)宽温稳定型 MLCC EIA-198-D 标准,“X”表示下限工作温度“-55oC”,“7”、“8”分别对应上限工作温度为“125 oC”和“150 oC”,“R”表示工作温度区间内。目前市场中MLCC主要为X7R型,市场容量约为MLCC总量的40%[2]。但随着电子行业的发展,X7R型瓷料已不能满足行业需要,尤其是在汽车电子、航空航天、军工等领域电子器件的工作温度高于125 oC,拓宽瓷料符合容温变化率的工作温度范围显得尤为重要。
 出于环境友好需求,无铅化是MLCC未来的发展趋势。BaTiO3基陶瓷作为最早商业化MLCC瓷料,被广泛关注。但纯BaTiO3在居里温度附近介电常数发生显著改变,不能满足商用需求。对其进行掺杂,工艺优化,显微结构调控来改善体系介电温度稳定性[3],是近年来研究MLCC瓷料的主要手段。
出于环境友好需求,无铅化是MLCC未来的发展趋势。BaTiO3基陶瓷作为最早商业化MLCC瓷料,被广泛关注。但纯BaTiO3在居里温度附近介电常数发生显著改变,不能满足商用需求。对其进行掺杂,工艺优化,显微结构调控来改善体系介电温度稳定性[3],是近年来研究MLCC瓷料的主要手段。
图1.1 2010-2015中国MLCC产量及需求量
Fig1.1 The Output and Demand Chart for MLCC in China during 2010 to 2015
1.2 MLCC概述
1.2.1 MLCC结构及原理
如图1.2,多层陶瓷片式电容器(MLCC)由陶瓷浆料经流延的陶瓷膜和金属内电极交替堆叠而成,整体上形成“独石”结构。与MLCC端电极相连的金属内电极相互并联,而端电极与外电路连接,实际上就是多层瓷膜并联而成。瓷料的成分对MLCC的温度稳定型起到了决定性作用。
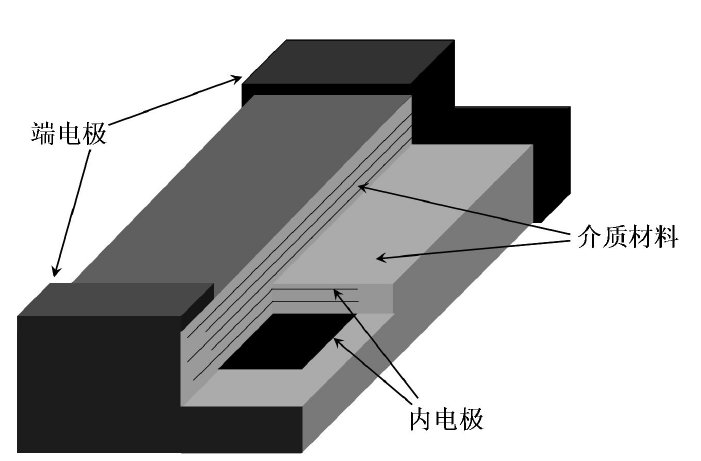
图1.2 MLCC结构示意图
Fig1.2 The schematic diagram of MLCC
1.2.2 MLCC分类及发展趋势
根据温度特性MLCC可被分为两类,分别为I类陶瓷电容器与II类陶瓷电容器。I类为温度补偿型陶瓷电容器,常用于温度稳定性高并且损耗低的高频电路中。II为固定型陶瓷电容器,通常为铁电陶瓷电容器,介电常数较高且不随温度呈线性变化,用于低频电路。美国电子工业协会(Electronic Industries Association,EIA)对II类陶瓷电容器进行了如下分类如表1-1[3]其中三个参数分别为最低工作温度,最高工作温度,工作温区内允许最大误差。对于X9R电容器,EIA并没有给出明确的标准但一般认为温度上限为200oC。而从X5R到X9R,随着上限温度的提升,制备难度也会增加。
表 1.1 电容温度稳定性 EIA 标准
Table1.2 Criteria of EIA for temperature stable capacity
最低温度 | 最高温度(oC) | 最大电容值变化率(%)ΔC/C25oC | ||||
Z= 10 | 4= 65 | 5= 85 | A=±1.0 | B=±1.5 | C=±2.2 | D=±3.3 |
Y=-30 | 6= 105 | 7= 125 | E=±4.7 | F=±7.5 | P=±10 | R=±15 |
X=-55 | 8= 150 | S=±22 | T= 22/-33 | U= 22/-56 | V= 22/-82 | |
随着电子工业的不断发展,MLCC在将来将向大容量化,微型化,环境友好化,内电极贱金属化,宽温化等方向发展。
1.3 BaTiO3基体瓷料
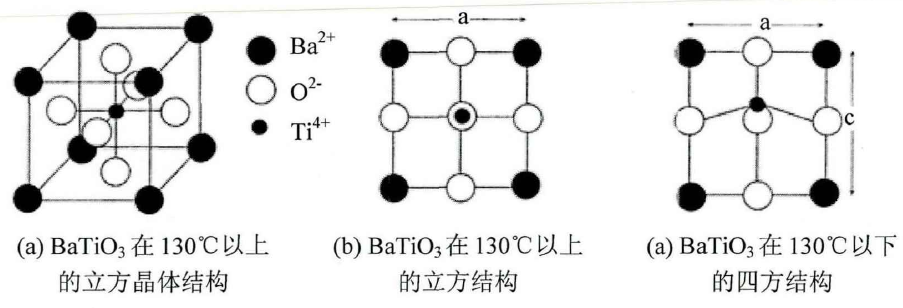
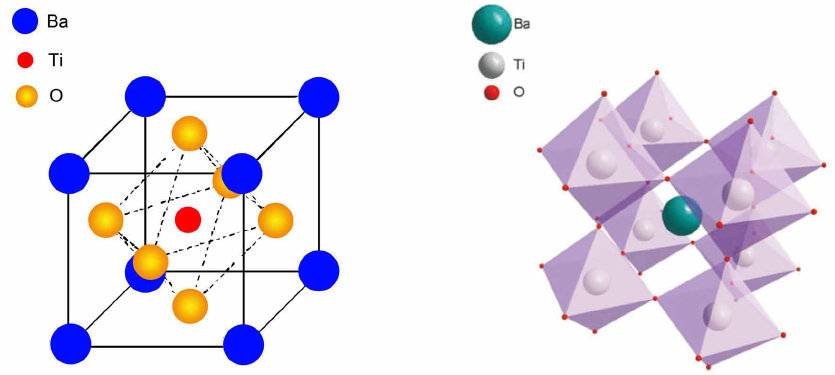 1.3.1 BaTiO3晶体结构
1.3.1 BaTiO3晶体结构
图1.3 BaTiO3晶体结构
Fig1.3 the structure of perovskite
以上是毕业论文大纲或资料介绍,该课题完整毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、程序设计、图纸设计等资料请添加微信获取,微信号:bysjorg。
相关图片展示:
您可能感兴趣的文章
- 改善锂离子电池中硅基负极存储性能的策略研究外文翻译资料
- 通过添加压电材料BaTiO3提高大功率锂离子电池的微米级SiO @ C/CNTs负极的电化学性能外文翻译资料
- Pd和GDC共浸渍的LSCM阴极在固体氧化物电解池高温电解CO2中的应用外文翻译资料
- 利用同步回旋加速器粉末衍射的方法来研究在有其他物相的情况下C4AF的水化作用外文翻译资料
- 外国循环流化床锅炉发展现状外文翻译资料
- 含石蜡基复合材料的多壁碳纳米管的热性能外文翻译资料
- 矸石电厂炉渣机制砂的应用研究外文翻译资料
- 机动车螺旋弹簧的失效分析外文翻译资料
- 从废阴极射线管和锗尾矿制备高强度玻璃泡沫陶瓷外文翻译资料
- 作为导热液体的液态金属在太阳能储热中的应用外文翻译资料




