表面活性剂热制备超四面体簇化合物毕业论文
2020-07-07 21:55:20
摘 要
晶态金属硫属化物具有复杂多样的结构和优异的光学、电学、半导体、催化等性质,在石油化工、生态治理、光电器件等领域中具有广阔的应用前景。由于这些丰富的物理化学特性,晶态金属硫属化物在无机化学合成领域受到广泛的亲睐。随着合成该类化合物方法的不断革新,传统的合成方法由早期的高温固相法发展到熔融盐法和溶剂热法。近年来,离子热法和表面活性剂热法也被用于这类材料的合成。本课题主要探索利用表面活性剂热制备超四面体簇化合物。表面活性剂相对于传统的分子溶剂,具有低的蒸气压力、良好的热稳定性。同时,表面活性剂种类繁多,价格低廉,利用表面活性剂来合成不同的晶态硫属化物很快得到了研究者的青睐。本课题在In-Sn-Se体系合成出一种全新的纯相超四面体T2簇晶态硫属化物,其具有四方晶系,属于Pnmc空间群。该化合物是分子式为[In2.5Sn1.5Se6S2][C4H11N][C4H12N]2.5,其结构特征为无限延伸的阴离子二维层结构,结构包含由四个角共享MQ4四面体形成的金刚烷型M4Q10单元,这些单元排列在ab平面中以给出[M2Q4]层,单元格包含两个[M2Q4]层,以ABA的排列方式沿c轴延伸。
关键词:晶态金属硫属化物 表面活性剂热法 超四面体簇 Tn簇Surfactant-thermal Synthesis of Supertetrahedron Cluster Compound
Abstract
Crystalline metal chalcogenides have complex and diverse structures and excellent optical, electrical, semiconductor, catalytic properties, and have promising application prospects in the petrochemical, ecological governance, emerging product synthesis and other fields. Crystalline chalcogenides have considerable and specific properties because of their flexible composition and varied structure. Due to these various properties, crystalline metal chalcogenides are widely favored in the field of inorganic chemical synthesis. With the continuous innovation of the method for synthesizing this type of compound, the traditional synthesis methods range from the original high-temperature solid-phase method to the molten salt method, the solvothermal method to the ionothermal method, and the surfactant thermal method in recent years. This topic mainly explores the use of surfactants for the preparation of hypertetrahedral clusters of chalcogenides. Surfactants have low vapor pressure and good thermal stability compared to traditional molecular solvents. At the same time, there are many kinds of surfactants and they are inexpensive. The use of surfactants to synthesize different crystalline chalcogenides has quickly gained the attention of researchers. In this project, a novel pure phase tetrahedral T2 cluster crystalline chalcogenide was synthesized in the In-Sn-Se system. It has a tetragonal system and belongs to the Pnmc group. The compound has the formula [In2.5Sn1.5Se6S2][C4H11N][C4H12N]2.5 two-dimensional layer structure containing adamantane type M4Q10 units formed by four corner sharing MQ4 tetrahedra, these units are arranged in the ab plane to give [M2Q4] layer, the cell contains Two [M2Q4] layers extend in the c-axis direction in an ABA arrangement.
Key words: Mental chalcogenides; Surfactant heating; Supertetrahedral clusters; Tn clusters
目 录
摘 要 I
Abstract II
第一章 绪论 1
1.1 晶态金属硫属化物概述 1
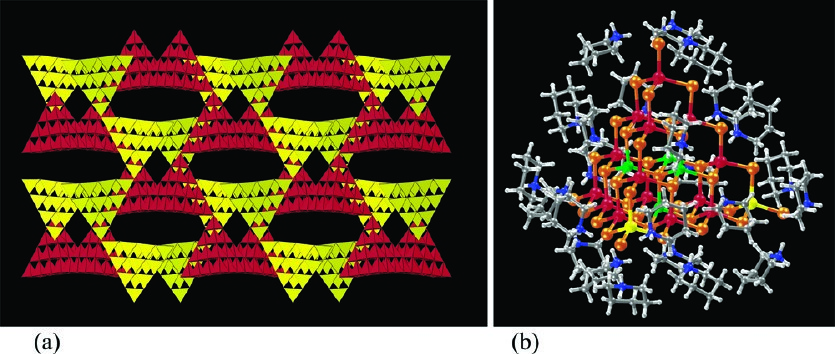
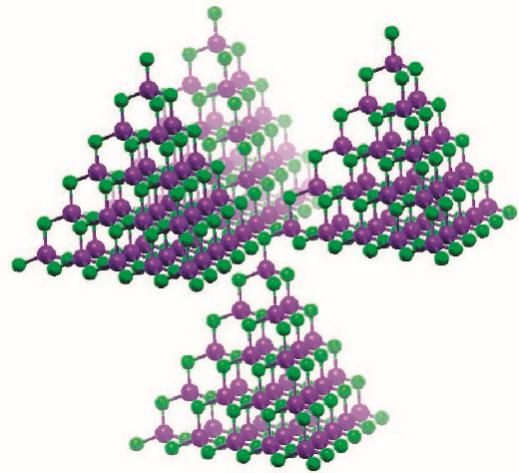
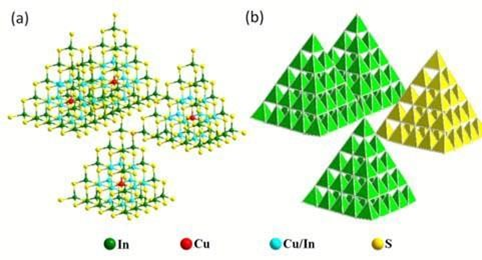
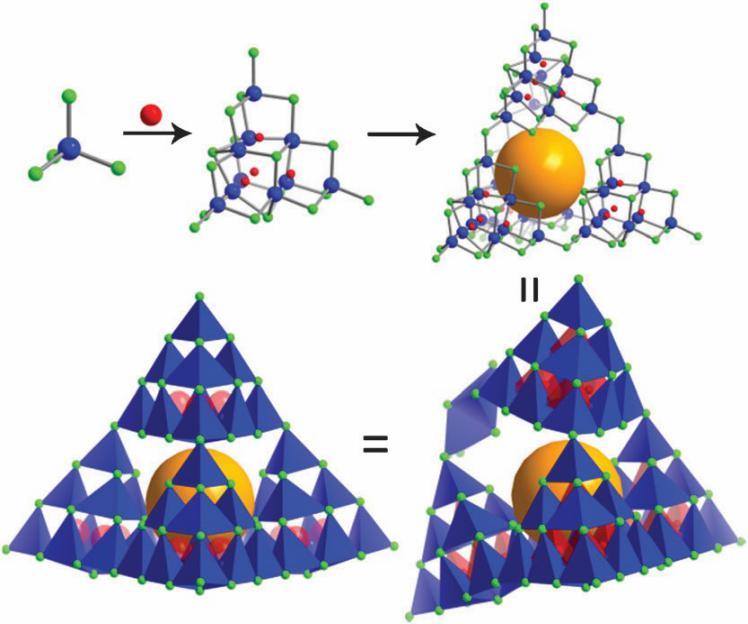
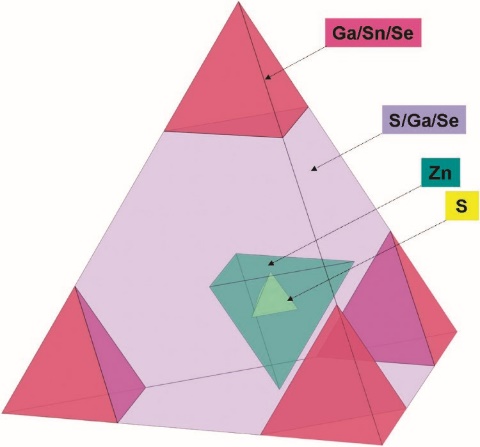
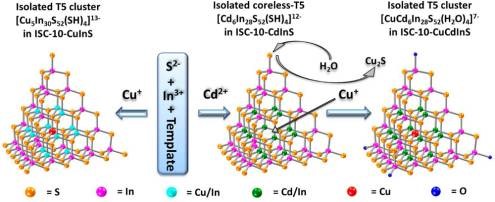
1.2 超四面体簇硫属化物概述与研究进展 1
1.2.1 由沸石到超四面体微孔化物 1
1.2.2 超四面体簇硫属化物进展 2
1.2.3 超四面体簇的量子点特性 8
1.2.4 超四面体簇硫属化物的掺杂特性 8
1.3 晶态金属硫属化物的合成方法 10
第二章 实验部分与测试方法 12
2.1 实验设计方案 12
2.2 实验药品和仪器 12
2.2.1 实验药品 12
2.2.2 实验设备 13
2.3 合成与测试方法 14
2.3.1 [In2.5Sn1.5Se6S2][C4H11N][C4H12N]2.5的合成路径 14
2.3.2 性能测试 14
2.3.3 晶体结构测试 14
第三章 实验结果与分析 14
3.1 [In2.5Sn1.5Se6S2][C4H11N][C4H12N]2.5的EDS表征 14
3.2 [In2.5Sn1.5Se6S2][C4H11N][C4H12N]2.5的元素分析 15
3.3 [In2.5Sn1.5Se6S2][C4H11N][C4H12N]2.5结构描述 15
3.4 [In2.5Sn1.5Se6S2][C4H11N][C4H12N]2.5的PXRD表征 16
第四章 总结与展望 19
4.1 总结 19
4.2 展望 19
参考文献 20
致谢 22
- 绪论
- 晶态金属硫属化物概述
金属硫属化物是指硫属元素(S,Se,Te)与不同金属元素共价连接形成的一类化合物,其结构复杂多样,具有独特的理化性质,包括离子交换特性、可见光的催化特性、非线性光学、快离子传导等。
晶态硫属化物属于新型的微孔材料,传统的微孔多孔材料包括天然沸石、人造沸石磷铝酸盐等。晶态多孔硫属化物相对于以前的微孔材料,其骨架阴离子半径更大,价态更低,如Se2-、Te2-、S2-。这种离子可以与重金属离子更好的亲和,从而更容易与它们发生离子交换,达到去除的目的。Huang小组等人层报告了一种具有三维结构的手性硫属化物[(Me)2NH2]2[Sb2GeS6],其具有高的离子交换容量以及高的选择性,可以有效交换环境中的Cs 离子,交换率可达九成以上[1]。
相关图片展示:
您可能感兴趣的文章
- 改善锂离子电池中硅基负极存储性能的策略研究外文翻译资料
- 通过添加压电材料BaTiO3提高大功率锂离子电池的微米级SiO @ C/CNTs负极的电化学性能外文翻译资料
- Pd和GDC共浸渍的LSCM阴极在固体氧化物电解池高温电解CO2中的应用外文翻译资料
- 利用同步回旋加速器粉末衍射的方法来研究在有其他物相的情况下C4AF的水化作用外文翻译资料
- 外国循环流化床锅炉发展现状外文翻译资料
- 含石蜡基复合材料的多壁碳纳米管的热性能外文翻译资料
- 矸石电厂炉渣机制砂的应用研究外文翻译资料
- 机动车螺旋弹簧的失效分析外文翻译资料
- 从废阴极射线管和锗尾矿制备高强度玻璃泡沫陶瓷外文翻译资料
- 作为导热液体的液态金属在太阳能储热中的应用外文翻译资料




