微反应器辅助合成纳米磷酸锰锂正极材料及其电化学性能研究毕业论文
2020-05-22 21:10:42
摘 要
相比于已经成功商业化的LiFePO4。LiMnPO4有着比LiFePO4更加高的氧化还原反应电位(4.1 V vs. Li /Li)。因此其具有更高的能量密度(701 Whkg-1)。从而引起研究人员的广泛关注。但也由于LiMnPO4本征的电子电导率和离子电导率均比较低,导致电化学活性很低。为了克服上述缺点,研究者对此展开了大量研究,目前为止主要改性方法有颗粒的纳米化、表面碳包覆处理以及离子掺杂等技术。本文利用微通道反应器设备合成出纳米前驱体颗粒,再与碳源或者锂源或者碳源共同球磨混合,经高温煅烧可得到具备高电化学活性的纳米LiMnPO4/C正极材料。本文分别对共沉淀和单沉淀两种不同的制备方法分别进行了深入的探讨,通过热重分析(TG-DSC)、电感耦合等离子光谱分析法(ICP)、X射线衍射(XRD)、扫描电子显微镜(FESEM)、元素分析仪、透射电子显微镜(TEM)对前驱体及LiMnPO4的微观结构、成分、形貌及物相进行分析与表征,通过循环伏安法(CV)、恒流充放电、交流阻抗(EIS)等测试手段对LiMnPO4/C正极材料进行了电化学性能分析,探究了LiMnPO4/C正极材料的微观结构与其电化学性能之间的内在联系。
本文利用微反应器共沉淀法制备出纳米前驱体颗粒Li3PO4和Mn3(PO4)2,并与葡萄糖球磨混合制备得纳米级LiMnPO4/C正极材料。本文主要讨论水浴温度对前驱体以及最终产物LiMnPO4物相的影响。研究碳源加入量对LiMnPO4/C及其电化学性能的影响。经过研究发现,碳源能够在一定程度上抑制晶粒生长,然过量的碳会造成锂离子脱嵌困难。当碳源加入量为20 wt%时,其材料的电化学活性最高,
在0.05 C倍率下的首次放电的容量为119 mAh g-1。此外,还探究了微反应器过程中反应物的流速对LiMnPO4/C及其电化学性能的影响。结果显示,在150 ml/min流速下制备出的LiMnPO4/C复合材料电化学性能最好,并且在0.05 C倍率下的首次放电容量为127 mAh g-1。
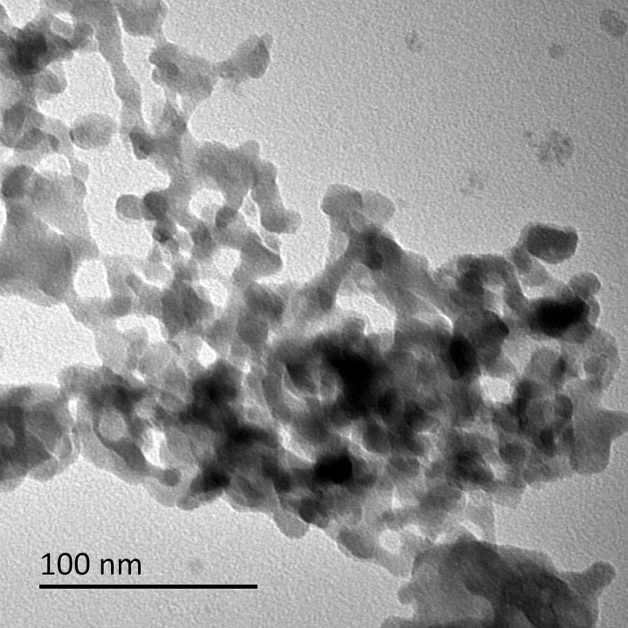
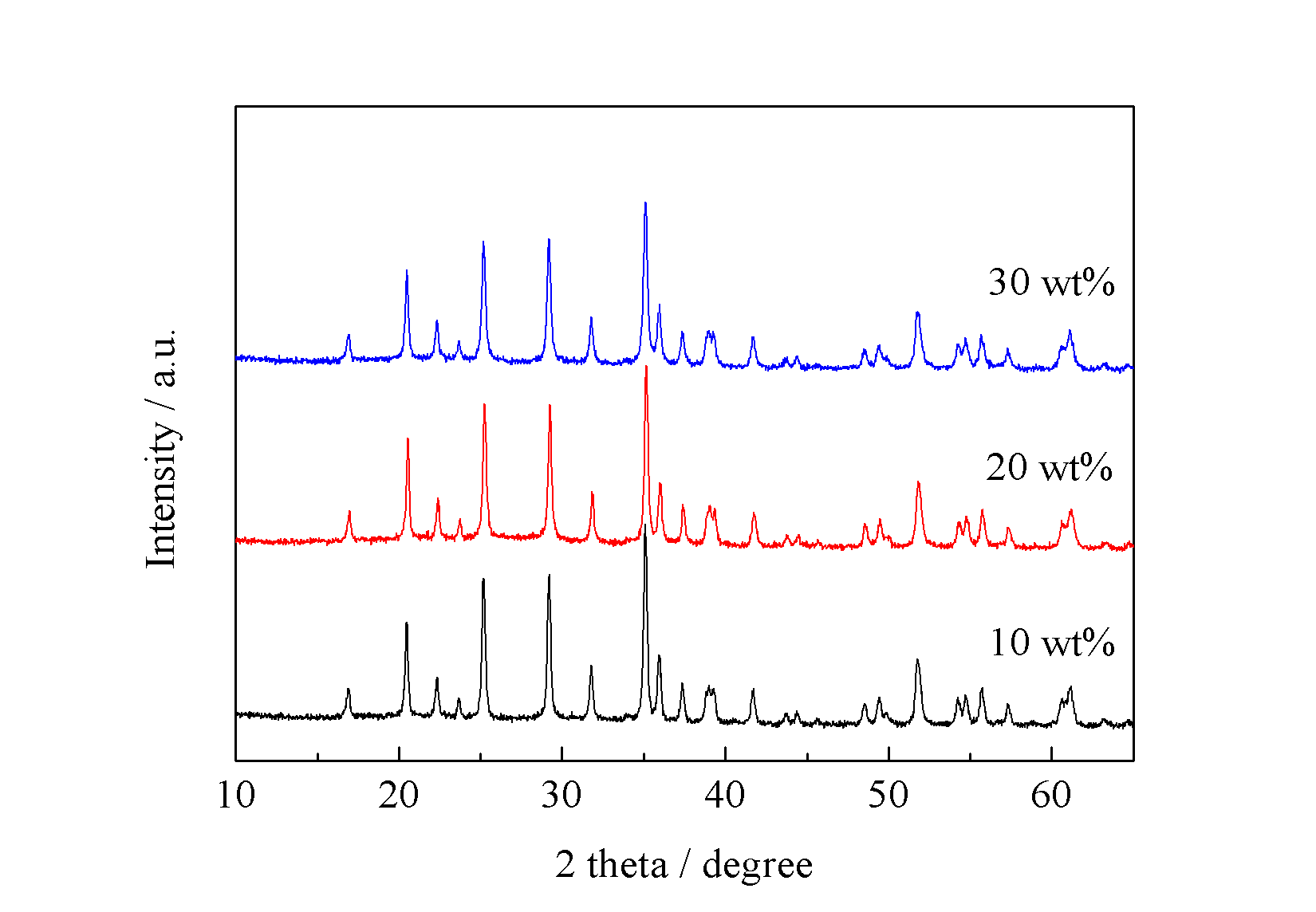
由于在共沉淀过程中Li3PO4和Mn3(PO4)2两相同时共沉淀,比较难以控制最终产物的纯度,虽然水浴能够消除杂质,但耗时比较长,再加上Li: Mn: P的原料比为3:1:1,导致了锂源在一定程度的浪费,这都会加大工业化生产的难度。因此本文也尝试了利用微反应器较先合成磷酸锰前驱体,再通过与锂源、碳源的球磨混合,经过高温煅烧后制备出LiMnPO4/C的正极材料。醋酸锰和磷酸氢二钠反应后生成磷酸锰是一个快速的沉淀反应,微反应器由于其有良好的微观混合效果,使得所制备磷酸锰颗粒分散性能良好,将不会出现传统沉淀法的团聚现象。通过理论计算可得到最佳的Mn与P的原料配比为1.2:1,这时溶液中的Mn2 与PO43-离子的摩尔比为3:2,与Mn3(PO4)2·3H2O中的Mn与P的摩尔比相一致,这使得所有的离子在碰撞过程瞬间能够全部反应而且不会导致颗粒长大。研究不同原料配比(1.2:1、1.3:1和1.4:1)对前驱体产物的颗粒尺寸的影响。研究结果表明,随着原料配比的增加,颗粒的尺寸逐渐变大。当Mn与P的原料配比为1.2:1时,所得到前驱体颗粒的尺寸最小。这主要是因为当Mn的浓度提高了以后,未完全反应的Mn2 将会与后续电离出的PO43-反应,导致颗粒长大。
关键词:锂离子电池 磷酸锰 磷酸锰锂 微反应器 共沉降 电化学性能
ABSTRACT
Compared to the successfully commercialization LiFePO4, LiMnPO4 has a higher redox potential (4.1 V vs. Li /Li) than LiFePO4, which indicates a higher energy density (701 Whkg-1). However, the electrochemical activity of LiMnPO4 is very low on account of the knockdown electronic conductivity and ion diffusion rate. Furthermore, the John-Teller distortion effect during charging-discharging process, large volume change during the procedure of LiMnPO4/ MnPO4 phase transformation, side reaction during Li ion prolapse process and the instability of MnPO4 phase, which will also restrict the large-scale application of LiMnPO4. In order to overcome the above drawbacks, considerable research have been carried out by researchers. As so far, the major modification methods including particle size nanocrystallization, carbon coated and ion doping. In this study, a novel preparation method has been presented. Carbon coated and particle size nanocrystallization will be adopted to enhance the electrochemical activity. Nano-sized precursor particles can be synthesized by microreactor, which will be mixed with lithium source and carbon source. After that, the mixture will be calcined under high temperature to obtain the LiMnPO4/C cathode material. Deeply discussion about two different preparation methods will be conducted. The microstructure, ingredient, morphology and physical phase of precursor and LiMnPO4 samples will be analyzed by TG-DSC, XRD, ICP, FESEM, TEM and elemental analyzer. Electrochemical performance of LiMnPO4/C cathode materials will be measured by charge/discharge test, cyclic voltammetry(CV) and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy(EIS).
Microreactor will be employed to prepare precursor samples by co-precipitation method. Then, precursor particles will be mixed with glucose to obtain LiMnPO4/C cathode materials. The influence of various bath temperatures and carbon on precursor and LiMnPO4/C has been study. The results show that carbon addition can inhibit the growth of grains to some extent. However excess carbon will hinder the prolapse of lithium ion. When the carbon addition is 20 wt%, the LiMnPO4/C achieved the best electrochemical performance, of which the initial discharge capacity is 119 mAh g-1 at 0.05 C.
Due to the precipitation of two phases happened at the same time during the co-precipitation process, which is difficult to control the purity of products. Although bath can eliminate impurity, the bath is very time-consuming. Hence, the manganese phosphate was attempted to synthesized by microreactor. Manganese phosphate prepared by manganese acetate and disodium hydrogen phosphate is a fast precipitation process. The precursor manganese phosphate prepared by microreactor has a good dispersibility due to its better micro-mixing. The best raw material ratio can be obtained by relevant theoretical calculation and study the influence of raw material ratio on the size of precursor particles. The results indicate that with the improvement of raw material ratio, the particle size will also increase. When the ratio of Mn and P is 1.2:1, the particle size is the smallest.
KEYWORD: Li-ion battery;Manganese phosphate;Lithium manganese phosphate;Microreactor;Co-precipitation;Electrochemical performance
目 录
摘 要 I
ABSTRACT i
目 录 1
第一章 文献综述 1
1.1 引言 1
1.2 锂离子电池简介 1
1.2.1 锂离子电池的特点 1
1.4 橄榄石型正极材料LiMnPO4的研究现状 2
1.4.1 LiMnPO4的晶体结构 2
1.4.2 LiMnPO4的电化学性能 2
1.5 本论文的研究背景和研究内容 3
第二章 实验研究方法 5
2.1 前言 5
2.2 实验原料和实验设备 5
2.2.1 实验原料 5
2.2.2 实验设备 6
2.3 材料的制备 7
2.3.1 共沉淀法 7
2.3.2 固相法(微反辅助) 7
2.4 材料的电化学性能分析 7
2.4.1 电极的制备及扣式电池的组装 7
2.4.2 电化学性能测试 8
第三章 微反应器共沉淀法制备纳米LiMnPO4/C正极材料 10
3.1 引言 10
3.2 LiMnPO4的制备过程 10
3.4 水浴温度对产物的影响 11
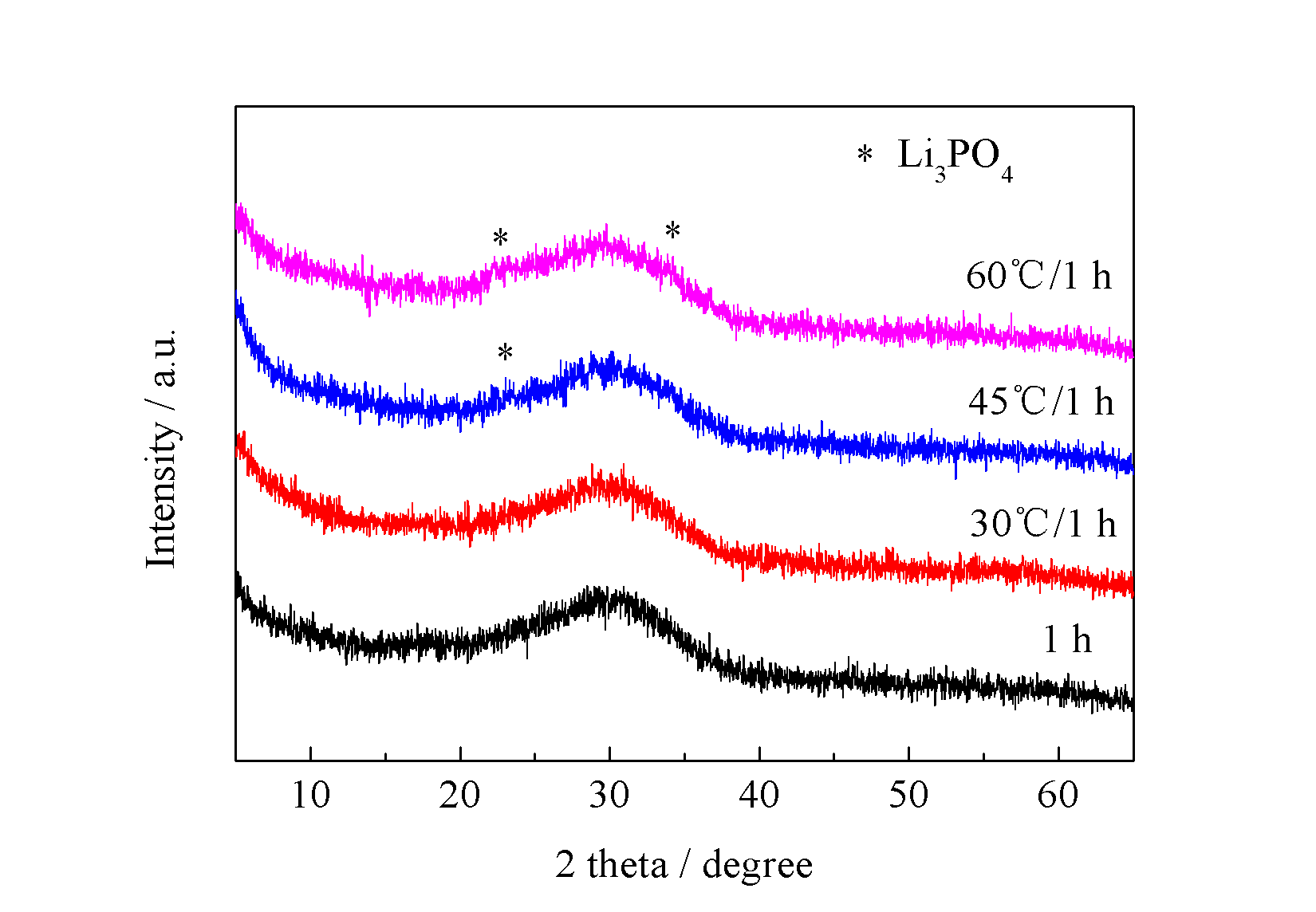
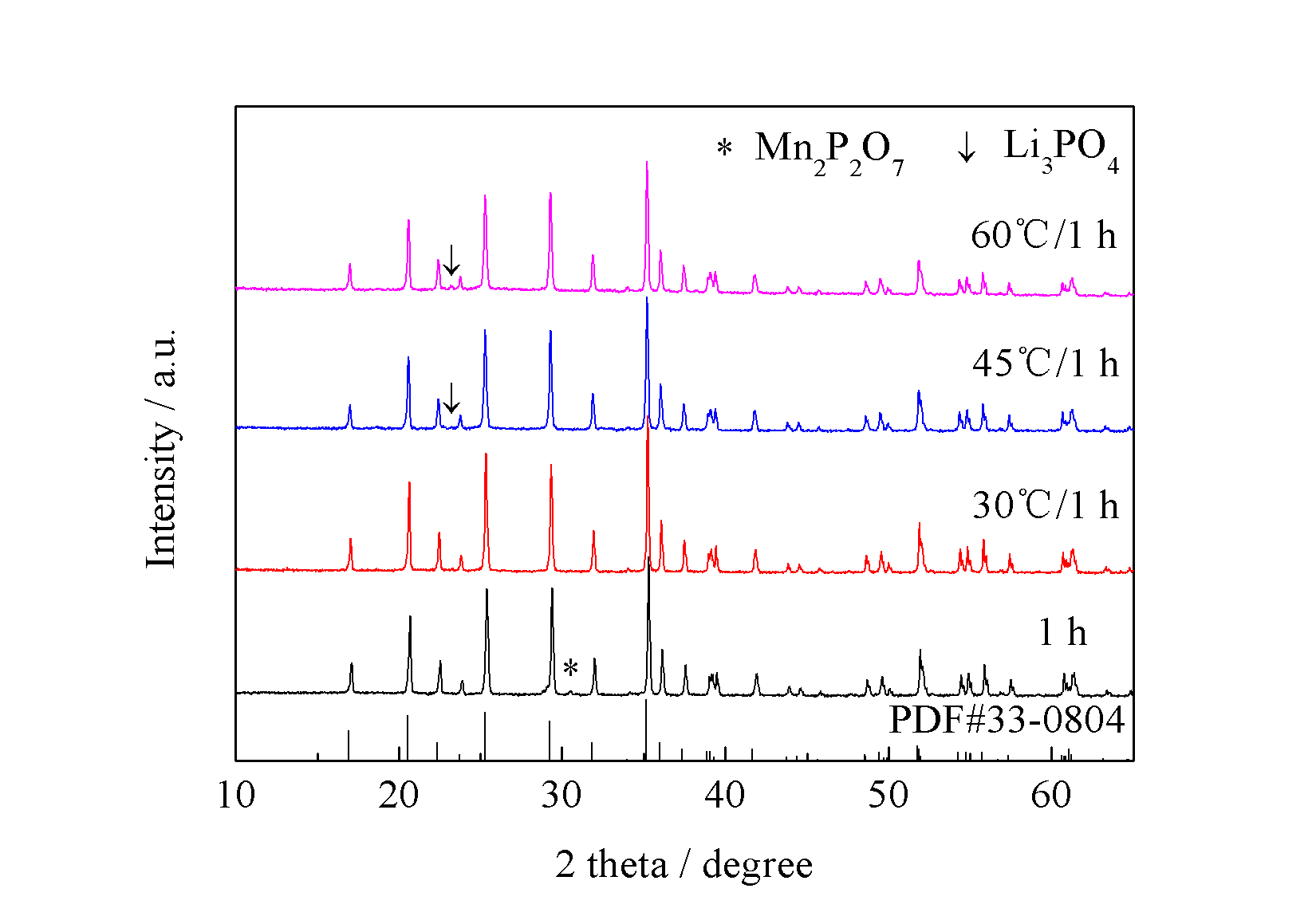
3.4.1 不同水浴温度对前驱体的影响 11
相关图片展示:

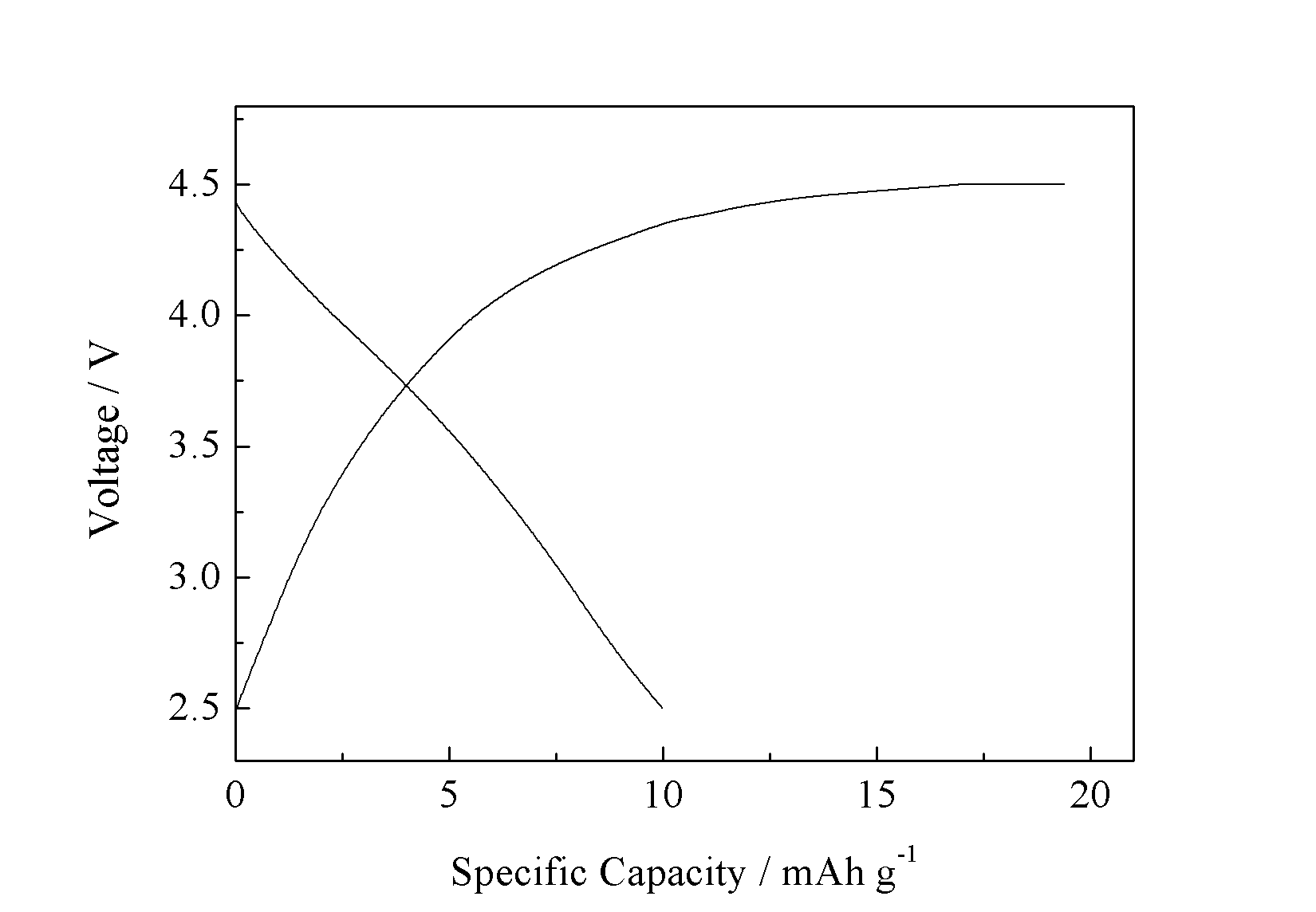
您可能感兴趣的文章
- 改善锂离子电池中硅基负极存储性能的策略研究外文翻译资料
- 通过添加压电材料BaTiO3提高大功率锂离子电池的微米级SiO @ C/CNTs负极的电化学性能外文翻译资料
- Pd和GDC共浸渍的LSCM阴极在固体氧化物电解池高温电解CO2中的应用外文翻译资料
- 利用同步回旋加速器粉末衍射的方法来研究在有其他物相的情况下C4AF的水化作用外文翻译资料
- 外国循环流化床锅炉发展现状外文翻译资料
- 含石蜡基复合材料的多壁碳纳米管的热性能外文翻译资料
- 矸石电厂炉渣机制砂的应用研究外文翻译资料
- 机动车螺旋弹簧的失效分析外文翻译资料
- 从废阴极射线管和锗尾矿制备高强度玻璃泡沫陶瓷外文翻译资料
- 作为导热液体的液态金属在太阳能储热中的应用外文翻译资料




