基于Carsim的四驱电动汽车ACC控制算法仿真研究毕业论文
2020-04-10 16:57:26
摘 要
在汽车逐渐成为大众化交通工具的今天,汽车保有量的增大带来了一系列社会问题,例如环境污染、能源危机、交通拥堵、交通事故频发等等。为此,各国政府和汽车企业纷纷将目光转向了汽车的电动化、智能化、网联化。汽车的电动化能够有效解决环境污染和能源危机问题,而纯电动汽车凭借着价格优势、零排放等特点逐渐从众多新能源汽车中脱颖而出,成为更多消费者的首选。汽车自适应巡航控制系统(ACC)作为先进驾驶员辅助系统的初级阶段,在提高驾驶员舒适性和安全性的同时,能够有效地提高道路运输能力,缓解交通拥堵、减少交通事故的发生。因此,为了响应国家发展新能源车、智能网联汽车号召,提出了基于Carsim的四驱电动汽车ACC控制算法仿真研究这一课题。
首先,对自适应巡航控制系统的历史发展进程、框架结构、国内外研究现状进行了总结,并提出了ACC控制系统存在的一些问题。
其次,利用Carsim2016软件对四驱电动汽车进行了建模。选取了一辆传统D级轿车作为参考车型,在Carsim中修改了其传动系统和相关尺寸参数。分析了电动汽车不同的驱动方案,选择了轮毂电机的驱动形式并总结了轮毂电机驱动的优点。采用面向性能的建模方法,根据驱动电机的外特性在Simulink中对电机进行了建模,并通过Carsim与Simulink的联合仿真,完成了四驱电动汽车整车模型的搭建,并对整车模型进行了仿真验证。
接着,制定了ACC控制系统的结构方案和控制策略。确定了三层式ACC控制器结构:上层负责控制模式的切换;中层根据传感器雷达得到的前车信息、自车信息、环境信息决策出当前工况下的期望加速度;下层根据期望加速度值,分时控制驱动/制动系统,实现车辆的纵向行驶。制定了三种控制策略:驱动与制动切换策略、驾驶员主动干预策略、控制模式切换策略。提出了一种基于固定跟车时距的安全车距模型,并对模型的稳定性进了验证,同时为了满足不同驾驶员的驾驶特性,提供了5个不同的档位以供调节。
然后,基于上述结构方案和控制策略对三层控制器进行了设计建模。基于控制模式切换策略完成了对上层控制器的开发,分为6种工况:紧急避撞、定速巡航、稳态跟车、接近前车、急减速、急加速,并对6种工况进行编号,在Simulink中完成了建模。基于PID控制理论完成对了中层控制器和下层控制器的开发。根据每一种控制模式的特点和驾驶员驾驶特性设计了6种中层控制器,与6种控制模式一一对应,提出了线性跟车模型和匀减速跟车模型并在Simulink中完成了搭建。在下层控制器的设计中,以车辆逆动力学模型为基础,建立了驱动模型和制动模型,依据驱动与制动切换策略对驱动系统、制动系统分时作用,实现了车辆的纵向行驶。
最后,设定了若干仿真工况对该ACC控制系统进行了仿真验证。仿真工况包含了两大类:单工况和复杂切换工况,前者分别对该ACC控制系统在定速巡航、稳态跟车、紧急避撞三种模式下的控制效果进行了仿真。后者主要对在复杂工况下的切换效果和控制效果进行了仿真,切换的工况包括定速巡航、稳态跟车、接近前车、急加速、急减速。仿真结果表明,该ACC控制器能够准确识别当前车辆所处工况并调用合适的控制器进行车辆控制,能够实现较好的车速跟随、车距保持和期望加速度跟随,在保证行车安全的同时减轻了驾驶员的操作负担,提高了道路的运输能力。
关键词:自适应巡航控制;四驱电动汽车;控制算法;Carsim
ABSTRACT
Today, as automobiles have gradually become a popular means of transport, the increase in car ownership has brought about a series of social problems such as environmental pollution, energy crisis, traffic congestion, frequent traffic accidents and so on. For this reason, governments and automobile companies in various countries have turned their attention to the electrification, intelligence, and networking of automobiles. Electric vehicles can effectively solve the problem of environmental pollution and energy crisis. Pure electric vehicles, based on price advantages and zero emissions, gradually emerge from many new energy vehicles and become the first choice for more consumers. The adaptive cruise control system (ACC), as the initial stage of the advanced driver assistance system, can improve the driver's comfort and safety while effectively improving the road transportation capacity, alleviating traffic congestion and reducing traffic accidents. Therefore, in order to respond to the country's call about development of new energy vehicles, intelligent networking car, put forward the simulation research based on Carsim's four-wheel drive electric vehicle ACC control algorithm.
First of all, it summarizes the history of adaptive cruise control system, the framework structure and the research status at home and abroad, and puts forward some problems in the ACC control system.
Second, the four-wheel drive electric vehicle was modeled using Carsim 2016 software. A traditional D-Class sedan was selected as a reference model. In Carsim, its transmission system and related dimensional parameters were modified. The different driving schemes of the electric vehicle were analyzed, the driving mode of the hub motor was selected and the advantages of the hub motor drive were summarized. Using the performance-oriented modeling method, the motor was modeled in Simulink based on the external characteristics of the drive motor, and the complete vehicle model of the four-wheel-drive electric vehicle was completed through the joint simulation of Carsim and Simulink and the vehicle model was verified by simulation.
Next, the structure and control strategy of the ACC control system were formulated. A three-level ACC controller structure is determined: the upper layer is responsible for the switching of the control mode; the middle layer determines the expected acceleration under the current working conditions based on the preceding vehicle information, the own vehicle information, and the environmental information by the sensor radar; The lower layer controls the drive/braking system in a time-sharing manner based on the desired acceleration value to achieve longitudinal travel of the vehicle. Three control strategies were formulated: drive and brake switching strategies, driver intervention strategies, and control mode switching strategies. A safe vehicle distance model based on the Constant time headway is proposed, and the stability of the model is verified. At the same time, in order to meet the driving characteristics of different drivers, 5 different gears are provided for adjustment.
Then, a three-layer controller was designed based on the above structure scheme and control strategy. Based on the control mode switching strategy completed the development of the upper controller, divided into 6 kinds of working conditions: emergency collision avoidance, cruise control, steady-state follow-up car, approaching the front car, rapid deceleration, rapid acceleration, and numbering of 6 kinds of working conditions, and modeling in Simulink. Based on PID control theory, the development of the middle controller and lower controller was completed. According to the characteristics of each control mode and the driving characteristics of the driver, six types of middle-level controllers are designed, which correspond to six types of control modes. A linear follow-up model and a uniform deceleration follow-up model were proposed and completed in Simulink. In the design of the lower controller, based on the inverse dynamic model of the vehicle, a drive model and a brake model were established. According to the driving and braking switching strategy, the driving system and the braking system are time-sharing, and the longitudinal driving of the vehicle is realized.
Finally, some simulation conditions were set to verify the ACC control system. The simulation conditions include two categories: single condition and complex switching conditions. The former simulates the control effects of the ACC control system in three modes: cruise control, steady-state follow-up, and emergency avoidance. The latter mainly simulates the switching effect and control effect under complex conditions. The switching conditions include cruise control, steady-state follow-up, approaching vehicle, rapid acceleration and rapid deceleration. Simulation results show that the ACC controller can accurately identify the current vehicle operating conditions and call the appropriate controller for vehicle control, and can achieve better vehicle speed following, vehicle distance keeping and expected acceleration following. While ensuring traffic safety, the burden on the driver's operation is reduced, and the road's transportation capacity is improved.
Key Words:adaptive cruise control; four-wheel drive electric car; control algorithm; Carsim
目 录
第1章 绪论 1
1.1 研究背景及意义 1
1.2 自适应巡航系统简介 4
1.2.1 自适应巡航系统历史发展进程 4
1.2.2 自适应巡航系统框架结构 6
1.3 自适应巡航控制研究现状 8
1.3.1 国内外研究现状 8
1.3.2 研究现状分析与存在的问题 14
1.4 本文的主要研究内容 14
第2章 四驱电动汽车仿真模型的建立 16
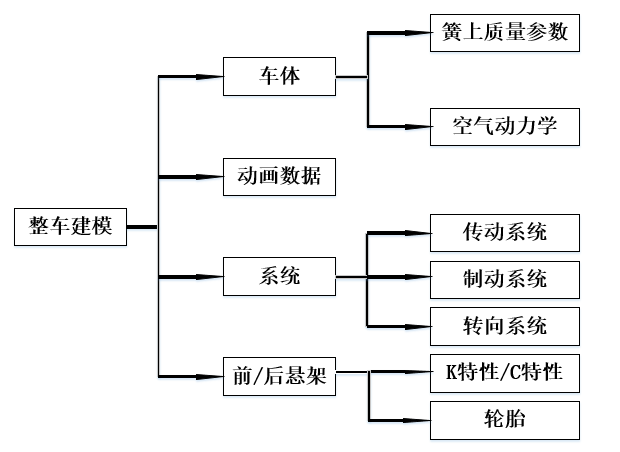
2.1 整车动力学模型 16
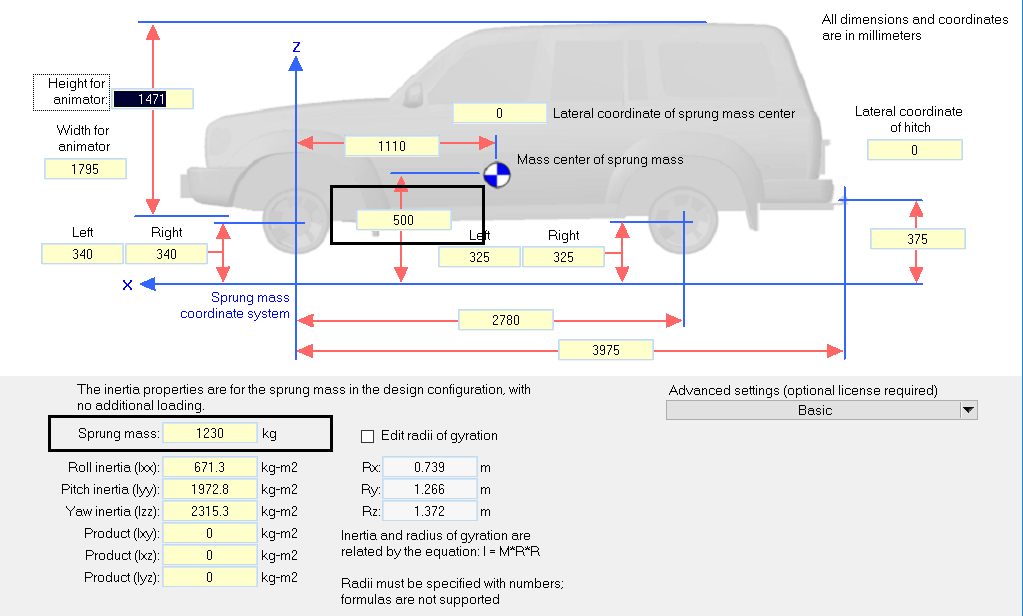
2.1.1 车体模型 16
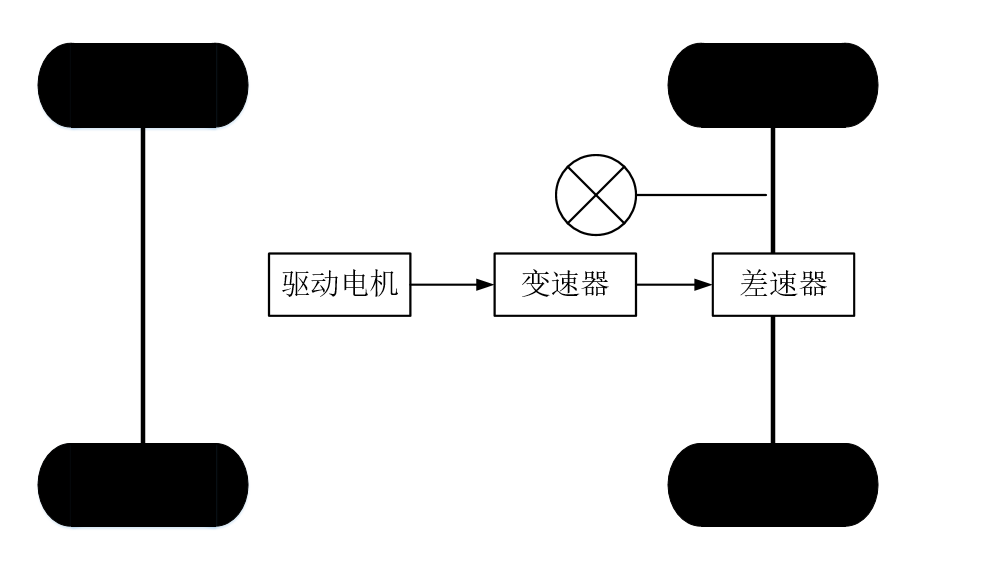
2.1.2 系统模型 18
2.1.3 悬架模型 20
2.2 电机的选择与建模 22
2.2.1 电动汽车驱动方案的选择 22
2.2.2 电机类型的选择 23
2.2.3 电机性能参数的选择 25
2.2.4 轮毂电机的建模 26
2.3 四驱电动汽车仿真模型验证 28
2.4 本章小结 31
第3章 ACC控制系统算法的设计与实现 32
3.1 ACC控制系统的结构设计 32
3.2 ACC系统控制策略 34
3.2.1 驱动与制动切换策略 34
3.2.2 驾驶员主动干预策略 37
3.2.3 控制模式切换策略 38
3.3 期望安全车距模型 40
3.4 上层控制器设计 43
3.4.1 避撞模式优先 43
3.4.2 定速巡航与跟车模式切换 43
3.4.3 跟车模式切换 43
3.4.3 上层控制器搭建 44
3.5 中层控制器设计 47
3.5.1 PID控制原理 47
3.5.2 定速巡航控制器 48
3.5.3 稳态跟车控制器 49
3.5.4 接近前车控制器 50
3.5.5 急减速控制器 51
3.5.6 急加速控制器 52
3.5.7 紧急避撞控制器 53
3.6 下层控制器设计 53
3.6.1 车辆逆动力学模型 53
3.6.2 基于PID控制的下层控制器搭建 57
3.7 本章小结 57
第4章 基于MATLAB、CARSIM的ACC控制策略、算法仿真与分析 58
4.1 仿真软件介绍 58
4.2 联合仿真平台介绍 61
4.3 设定工况仿真方法与结果分析 61
4.3.1 定速巡航工况仿真 61
4.3.1 稳态跟随工况仿真 63
4.3.2 紧急避撞工况 65
4.3.3 工况切换仿真 67
4.4 本章小结 73
以上是毕业论文大纲或资料介绍,该课题完整毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、程序设计、图纸设计等资料请添加微信获取,微信号:bysjorg。
相关图片展示: