氯毒素靶向碘-131标记功能材料用于神经胶质瘤SPECTCT双模态成像及放射性治疗毕业论文
2020-04-26 12:49:36
摘 要
目的:根据当前的研究报告和社会现状显示,癌症的增长速度和死亡率仍然居高不下,手术等传统治疗手段仅适用于部分患者,且术后复发率及各种并发症导致死亡的几率高达60%以上,高危险指数以及低治愈率使癌症仍是医药界待攻克的难题之一。我们急需新的手段去治疗癌症。
方法:本论文探究并在常温常压下制备了氯毒素(CTX)靶向功能化聚乙烯亚胺包裹金纳米颗粒[(Au0)200-PEI.NHAc-FI-HPAO-(PEG-CTX)-(mPEG)]NPs,由于CTX的修饰其可与神经胶质瘤细胞特异性结合,基于mPEG-COOH、MAL-PEG-SVA、HPAO、FI的修饰,其可构建稳定的功能化聚乙烯亚胺纳米载体,最后包裹金纳米颗粒形成功能材料作为性质良好的纳米造影剂。之后对其进行了氢核磁共振图谱表征、紫外可见光谱表征、不同温度及pH下的稳定性测试,形貌及粒径表征等。
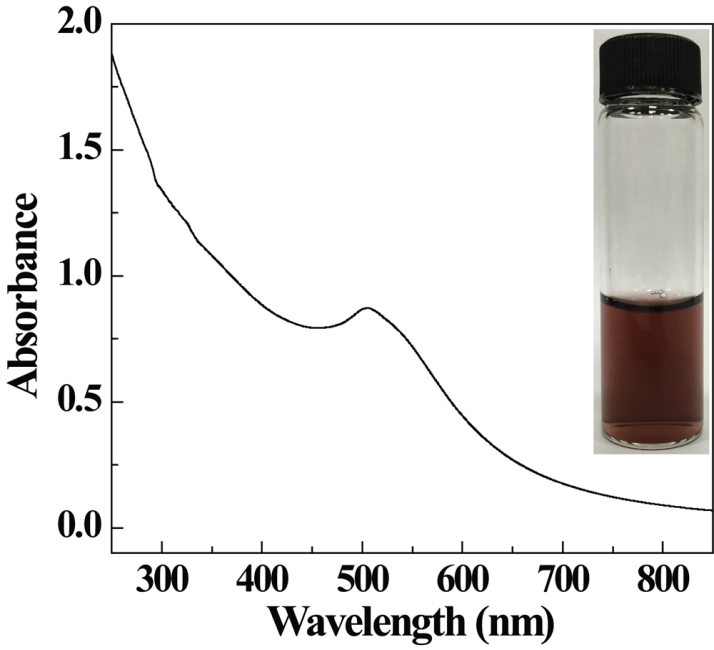
结果:本实验结果证明,所制得的氯毒素靶向的功能化聚乙烯亚胺包裹金纳米颗粒在不同温度及pH条件下具有良好的稳定性。透射电镜测试结果证明形成的金纳米颗粒呈现球型,粒径约为4.4 nm ± 1.3 nm。选定区域电子衍射图谱以及高分辨透射电镜图证明其有良好的二维晶格结构。紫外可见光谱显示其在510 nm处具有金纳米颗粒的表面等离子体共振峰,显示其形成了金纳米颗粒。
结论:制备的CTX靶向功能化聚乙烯亚胺包裹金纳米颗粒可作为标记功能材料后期用于神经胶质瘤SPECT/CT双模态成像以及放射性治疗,对人体无伤害且有较好的稳定性。降低了传统治疗癌症的高风险率,为未来治疗癌症提供了新思路与方法。
关键词:癌症 聚乙烯亚胺 金纳米颗粒 氯毒素 稳定性
Chlorotoxin Targeted Iodine-131 Labeled Functional Materials for SPECT/CT Dual Model Imaging and Radiotherapy of Gliomas
ABSTRACT
Objective: According to the current research report and social situation, the growth rate and mortality rate of cancer are still high, and traditional treatments such as surgery are only suitable for some patients. The recurrence rate and the probability of death caused by various complications are as high as 60%. High risk index and low cure rate make cancer still one of the difficult problems to be solved in the medical field. We are badly need of new means to cure cancer.
Methods: In this paper, Chlorotoxin (CTX) targeted functional polyethyleneimine entrapped gold nanoparticles [(Au0)200-PEI.NHAc-FI-HPAO-(PEG-CTX)-(mPEG)]NPs were prepared at room temperature and pressure. Because the modification of CTX, the formed [(Au0)200-PEI.NHAc-FI-HPAO-(PEG-CTX)-(mPEG)]NPs can specifically bind to glioma cells. Based on the modification of mPEG-COOH, MAL-PEG-SVA, HPAO, FI, it can construct a stable functional polyethyleneimine nanocarrier. Finally, gold nanoparticles were entrapped into the functional polyethyleneimine to form functional materials as nano-contrast agents with good properties. Then using hydrogen nuclear magnetic resonance spectra, UV-vis spectra, stability tests at different temperature and pH conditions, morphology and particle size analysis to characterize the formed nanoparticles.
Results: The experimental results show that the functionalized polyethyleneimine entrapped gold nanoparticles targeted by chlorotoxin have good stability at different temperature and pH conditions. Transmission electron microscope test results turn out the gold nanoparticles are spherical,with a particle size of about 4.4 nm ±1.3 nm. The electron diffraction patterns and high-resolution transmission electron microscope patterns show that the selected region has a good two-dimensional lattice structure. The surface plasmon resonance peaks of gold nanoparticles were observed at 510 nm by UV-Vis spectroscopy, indicating that gold nanoparticles are formed.
Conclusion: The prepared CTX targeted functional polyethyleneimine entrapped gold nanoparticles can be used as labeling functional materials for SPECT/CT dual model imaging and radiotherapy of glioma. It is harmless to human body and has good stability. It reduces the high-risk rate of traditional cancer therapy and offers new thoughts and approachs for cancer therapy in the future.
Key words: cancer; polyethyleneimine; gold nanoparticle; chlorotoxin; stability
目录
第一章 文献综述 6
1. 传统癌症治疗方法 6
1.1手术治疗 6
1.2放疗 6
1.3化疗 6
2. 肿瘤诊断技术与治疗方法 7
2.1 单电子发射计算机断层显像(SPECT)技术 7
2.2 电子计算机断层扫描(CT)技术 7
2.3 SPECT/CT技术 8
2.4 放射性治疗方法 8
3. 功能化修饰 9
3.1氯毒素 9
3.2 靶向碘-131标记功能 9
4. 研究意义 10
第二章 实验方法 11
第三章 结果与讨论 17
3.1核磁共振氢图谱表征 17
3.1.1 PEI.NH2-(mPEG)的核磁共振氢谱 17
3.1.2 PEI.NH2-(PEG-MAL)-(mPEG)的核磁共振氢谱 17
3.1.3 PEI.NH2-(PEG-CTX)-(mPEG)的核磁共振氢图谱 18
3.1.4 PEI.NH2-HPAO-(PEG-CTX)-(mPEG)的核磁共振氢图谱 19
3.1.5 PEI.NH2-FI-HPAO-(PEG-CTX)-(mPEG)的核磁共振氢谱 19
3.2 紫外可见光谱表征 20
3.3 稳定性表征 20
3.3.1 不同温度下稳定性表征 21
3.3.2 不同pH下稳定性表征 21
3.4 纳米粒子结构研究 22
3.4.1金纳米粒子TEM透射电镜图像 22
3.4.2纳米粒子平均粒径 23
3.4.3 高分辨透射电镜 23
3.4.4 选区电子衍射图谱 23
第四章 结论与展望 24
4.1结论 24
4.2 课题研究展望 24
参考文献 25
致谢 29
第一章 文献综述
传统癌症治疗方法
人类目前的癌症治疗仍然是有待攻克的全球性难题。传统癌症治疗包括手术、放疗、化疗、靶向治疗、基因治疗等方法,但这些都不能显著提高癌症患者的生存率。在所有病例中,宿主、肿瘤、治疗之间有着及其微妙的关系。
1.1手术治疗
手术治疗癌症的方法治疗效果干脆,能将最先发生癌变的某个组织或部位彻底去除,有一定几率使患者痊愈。并且手术治疗手段属于一次性治疗,因此费用一般低于放射性治疗。
然而,癌症的手术治疗有其局限性。由于其属于局部治疗手段,多数只适用于早期未扩散的肿瘤。手术还有一定的失败几率,人体越脆弱部位的癌症手术危险系数越高,如神经肿瘤。同时,对人体自身伤害也较大,会降低患者自身免疫力,对疾病的抵抗能力下降等。
1.2放疗
放疗即放射治疗,是利用不同能量的电磁辐射线作用于肿瘤,使生物分子结构改变,达到破坏或抑制癌细胞目的的一种治疗方法[1]。原理是癌细胞对放射线敏感,辐射能使癌细胞自身DNA破坏[2-3]。目前临床上应用的主要是放射性同位素产生的Χ线治疗和γ线治疗两种。
1.3化疗
即化学药物治疗方法,用合成药物通过血液循环到达病灶部位,杀死或抑制肿瘤细胞的生长、繁殖、浸润、转移和促进肿瘤细胞分化的一种治疗方法[4-6]。因其作用效果为全身,故而选择性弱,会将人体正常细胞视作肿瘤细胞一同给予抑制效果,易伤害人体的自我保护系统,具有一定的副作用。
肿瘤诊断技术与治疗方法
准确地监测肿瘤对抗癌症治疗的反应,可以极大地帮助临床医生识别无反应的患者,并将其与更有效、更个性化的治疗方法配合。目前,治疗反应通常通过计算机断层扫描(Computed Tomography,CT)、磁共振成像(Magnetic Resonance Imaging,MR)、单光子发射计算机断层成像(Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography,SPECT)和正电子发射断层成像(Positron Emission Tomography,PET)技术来进行癌症的早期诊断与监测 [6-7]。然而,肿瘤大小的显著减少只发生在初始治疗后的几周到几个月。这使得现有的常规成像技术在早期评价其治疗效果方面存在局限性和不足。
相关图片展示: