热还原法制备石墨烯及性能表征毕业论文
2020-07-09 20:25:39
摘 要
石墨烯是一种极具吸引力的二维纳米材料,厚度大约为0.335nm,具有独特的性能,如高比表面积,载流子迁移率,导电性,热导率和优良的光吸收能力,在电子器件、复合材料、能源领域拥有无比广阔的发展前景。
本文通过采用改进的Hummers法,以天然鳞片石墨Graphite作为原料,得到了氧化石墨GO,经过离心干燥等后处理后,在管式炉中于氮气保护下分别经400、500、600、700、800℃的热处理,最终得到了热还原氧化石墨烯rGO。采用XRD、FT-IR、TG-DTA与电导率测试等手段,对样品进行了结构及性能表征。
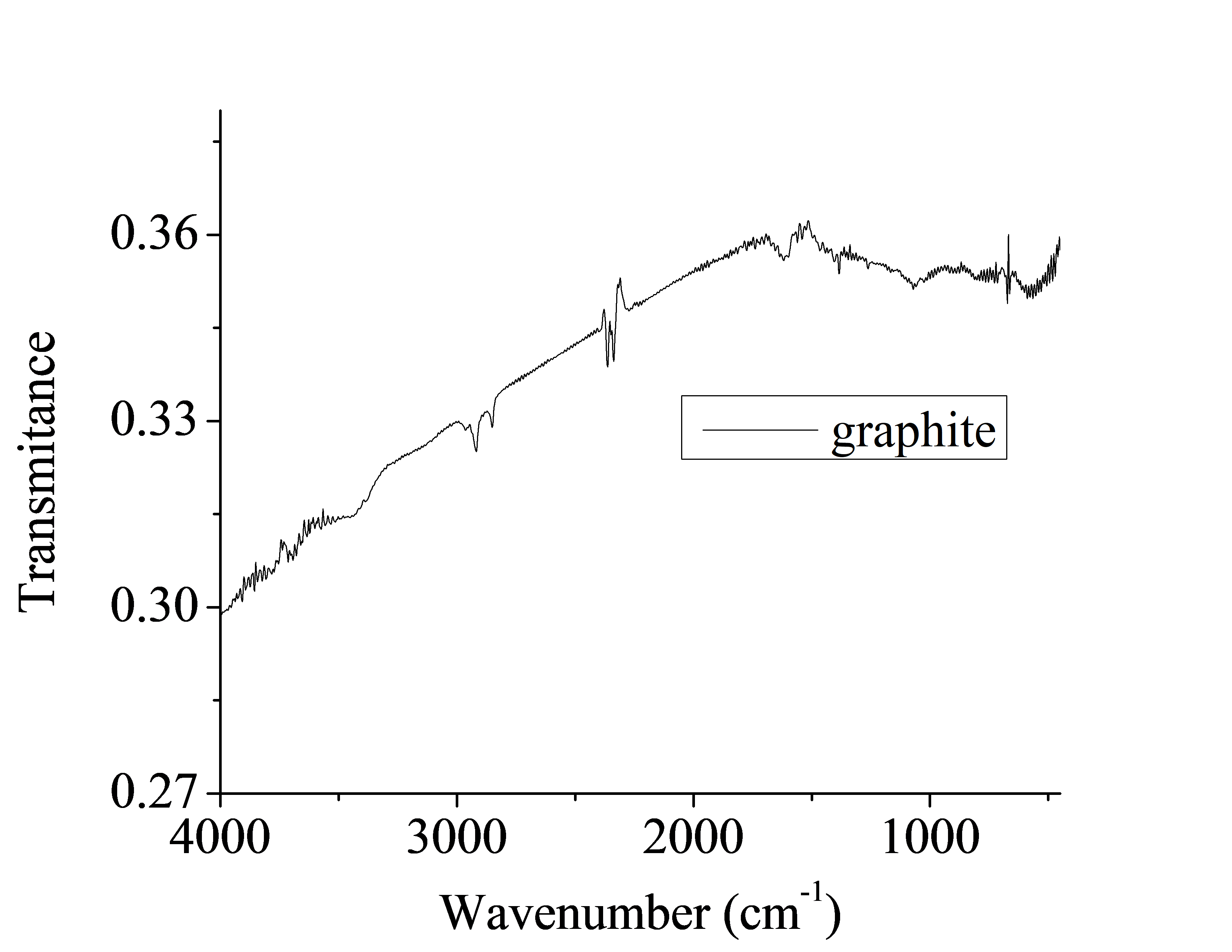
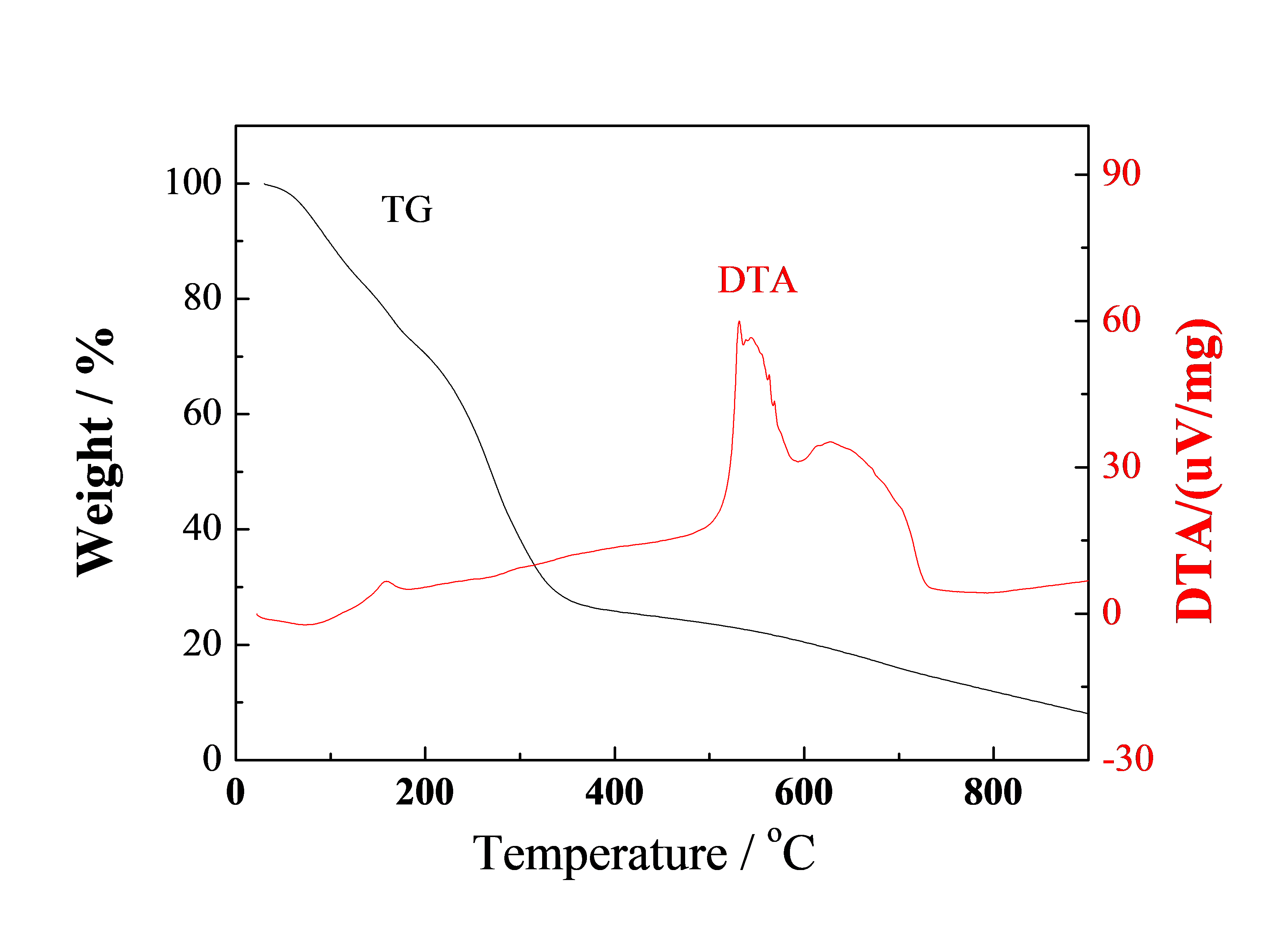
实验结果表明,石墨鳞片原料层间距为0.421nm,经改进的Hummers法氧化后得到的GO的层间距增大为0.496nm,经热处理后,其层间距又减小。这是因为氧化过程中在层间引入了层间水和含氧官能团,而热处理又使得层间水与含氧官能团脱除导致片层间距减小。随着热处理温度的升高,氧化石墨烯GO表面含氧官能团脱除得越多,其顺序为-COOH、C-O-C、C-OH。因此热处理温度越高,层间距越小。
另外,随着热处理温度的升高,还原氧化石墨烯rGO的导电率逐渐增大。这是因为随着热处理温度升高,其表面含氧官能团脱除量增加,使其具有更加完整的sp2网络结构,这大大提高了电子转移能力,从而促进电导率增大。因此,可以通过改变热处理的温度以达到调控石墨烯导电性的目的。
关键词:还原氧化石墨烯 石墨烯 氧化石墨烯 热还原
Preparation and characterization of graphene by thermal reduction
ABSTRACT
Graphene is an attractive two-dimensional nanomaterials with a thickness of about 0.335nm. It has unique properties such as high specific surface area, carrier mobility, conductivity, thermal conductivity and excellent optical absorption. It has a broad application prospect in the field of electronic devices, composite materials and energy.
In this paper, graphene oxide (GO) was prepared by modified Hummers method using graphite as raw material. After centrifugation and vacuum drying, the graphene oxide (rGO) was obtained by heat treatment at 400,500,600,700,800℃ in a tube furnace protected by nitrogen. The structure and properties of the samples were characterized by means of XRD,FT-IR,TG-DTA and conductivity measurement.
The experimental results show that the spacing of graphite scales is 0.421 nm, and that of GO prepared by modified Hummers method increases to 0.496 nm, and decreases after heat treatment.This is due to the introduction of interlaminar water and oxygen functional groups in the oxidation process and the reduction of lamellar spacing due to the removal of interlaminar water and oxygen functional groups by heat treatment.With the increase of heat treatment temperature, the more oxygen functional groups were removed on the surface of graphene oxide, the order was -COOH,C-O-C,C-OH. Therefore, the higher the heat treatment temperature, the smaller the interlayer spacing.
In addition, the conductivity of reduced graphene (rGO) increases with the increase of heat treatment temperature.This is because with the increase of heat treatment temperature, the amount of oxygen functional groups on the surface increases, which makes it have a more complete sp2 network structure, which greatly improves the electron transfer ability and promotes the increase of electrical conductivity.Therefore, the conductivity of graphene can be controlled by changing the temperature of heat treatment.
Key Words: Reduced graphene oxide; Graphene; Graphene oxide; Thermal recovery
目 录
摘要······························································Ⅰ
ABSTRACT·······················································Ⅱ
第一章 文献综述··················································1
1.1前言························································1
1.2石墨烯的概念················································1
1.3石墨烯的制备方法············································2
1.3.1氧化还原法··············································2
1.3.2其他制备方法············································3
1.4石墨烯的国内外研究进展······································4
1.5本课题的主要内容、研究目的及意义····························5
第二章 实验·······················································7
2.1主要药品····················································7
2.2仪器设备····················································7
2.3实验过程····················································7
2.3.1氧化石墨烯的制备········································7
2.3.2氧化石墨烯的热还原······································8
第三章 结果与讨论················································9
3.1石墨鳞片的表征··············································9
3.2氧化石墨烯的表征···········································10
3.3热还原氧化石墨烯的表征·····································12
第四章 结论与展望··········································`····15
4.1结论·······················································15
4.2展望·······················································15
参考文献·························································17
致谢······························································19
第一章 文献综述
1.1 前言
社会的快速发展促使材料领域迅猛发展,各领域对其需求量逐年扩大,要求也不断提高,其中具有特殊的优异性能的新型碳材料受到全世界研究者的关注。其既能成为最硬的金刚石,也能成为最软的石墨;既能成为绝热体,也能成为良导热体;既能成为绝缘体,也能成为半导体,超导体。因此,碳材料具有无比广阔的前景。
碳在地球上的含量多且分布极为广泛,人们已经发现了它的多种同素异形体。自1924年以来,研究者们先后确定了石墨、金刚石、富勒烯、碳纳米管和石墨烯,这极大地鼓励了研究者们在碳材料领域的深入探索。直至今日,石墨烯仍然是各相关领域的研究热点。
相关图片展示:



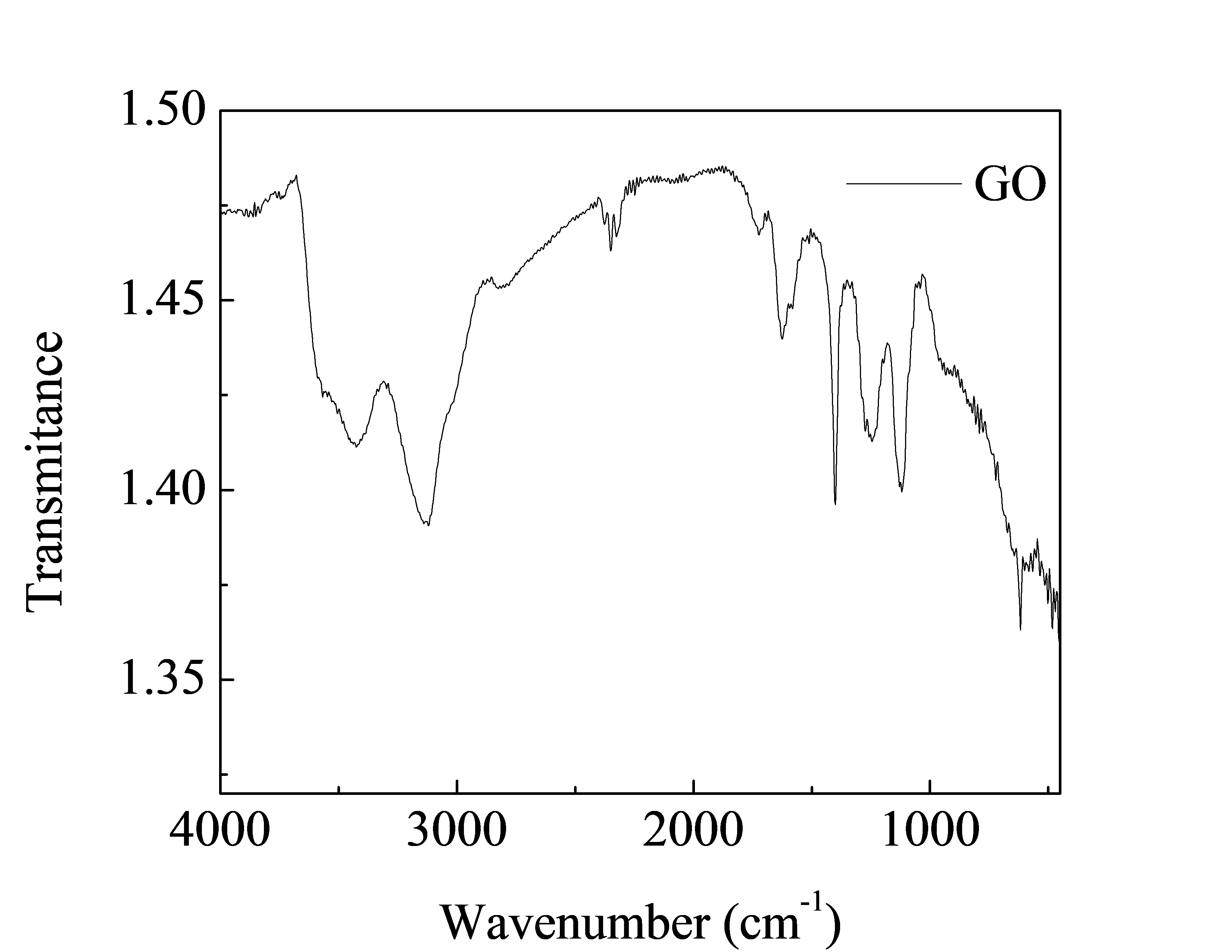
您可能感兴趣的文章
- BN嵌入型四苯并五苯:一种工具高稳定性的并五苯衍生物外文翻译资料
- MoS2和石墨烯作为助催化剂在增强的可见光光催化H2生产活性的多臂CdS纳米棒的作用外文翻译资料
- 通过在BiVO4的不同晶面上进行双助剂的合理组装制备高效率的光催化剂外文翻译资料
- 非编码RNA的固相合成研究外文翻译资料
- 氢化驱动的导电Na2Ti3O7纳米阵列作为钠离子电池阳极外文翻译资料
- 高能量及功率密度的可充电锌-二氧化锰电池外文翻译资料
- 利用导电聚合物纳米线阵列来增强电化学性能外文翻译资料
- 自支撑Na2Ti3O7纳米阵列/石墨烯泡沫和石墨烯泡沫准固态钠离子电容器电极外文翻译资料
- 基于碳纳米管金纳米粒子辣根过氧化物酶构建的过氧化氢生物传感器毕业论文
- 新型联二吡啶Pt(II)炔配合物的设计、合成及光物理性质研究毕业论文




