肿瘤坏死因子α在大肠杆菌中的高效可溶性表达研究毕业论文
2020-04-15 20:39:10
摘 要
目的:肿瘤坏死因子α(tumor necrosis factor α)是一种涉及全身炎症及免疫反应的最重要的多功能细胞因子之一,可以选择性杀伤多种肿瘤细胞,因此被广泛应用于自身免疫疾病和肿瘤治疗的研究中。由于TNFα的来源受到限制,其生物功能的研究不能广泛开展。本研究目的是用新型融合标签Ffu209实现TNFα在大肠杆菌中的高效可溶性表达。
方法:本课题组前期研究中发现的来源于阿氏节杆菌NJEM01的β-呋喃果糖苷酶可以在大肠杆菌中实现高效分泌表达,并基于其强的分泌能力和稳定性等特性将其开发成新型融合标签Ffu。本研究选择分子量较小、可溶性高的标签Ffu209,将其与TNFα融合后克隆至pET-28a中制备成重组质粒pET/Ffu209-TNFα,导入BL21(DE3),得到阳性重组菌。优化表达条件,使重组蛋白Ffu209-TNFα得到高效可溶性表达。利用渗透休克法定向释放周质蛋白进行重组蛋白的定位验证。通过阴离子交换色谱纯化重组蛋白。MTT检测重组蛋白对L929细胞的细胞毒活性。
结果:实验表明,对重组蛋白的表达条件进行优化,灰度扫描得重组蛋白可溶性表达量约占总表达量的63%。渗透休克法证实融合标签Ffu209实现重组TNFα在大肠杆菌周质空间中的分泌表达。纯化后的重组蛋产量为12 mg/L。MTT检测结果显示我们的表达系统可以产生分泌至周质空间中的可溶性TNFα,生物活性为3.47×105 U/ mg。结论:本研究将新型融合标签Ffu209与TNFα融合构建重组Ffu209-TNFα蛋白,通过诱导条件优化得到重组蛋白Ffu209-TNFα在大肠杆菌中的高效可溶性表达,且重组蛋白具有一定的生物活性。新型融合标签Ffu为实现异源蛋白,特别是一些含有二硫键的真核生物蛋白,在大肠杆菌中的可溶性表达提供了一个新的工具。
关键词:融合标签 肿瘤坏死因子α 大肠杆菌 周质空间
Efficient soluble expression of tumor necrosis factor α in E. coli
ABSTRACT
Objective:Tumor necrosis factor alpha is one of the most important multifunctional cytokines involved in systemic inflammation and immune response. TNFα has the characteristic of killing various tumor cells selectively, which makes it have widespread use in the research of autoimmune diseases and tumors treatment. Since the source of TNFα is limited, the study of its biological function cannot be widely carried out. The study used the novel fusion tag Ffu209 in order to achieve efficient soluble expression of TNFα in E. coli.
Methods: The β-fructofuranosidase derived from Arthrobacter argenatus NJEM01 discovered by our laboratory in the previous study can achieve high-efficiency secretion and expression in E. coli, and it can be developed into a novel fusion tag Ffu based on its strong secretion ability and stability. The label Ffu209 with a smaller molecular weight and high solubility was selected. The fusion tag Ffu209 was fused with TNFα and cloned into pET-28a to prepare a recombinant plasmid pET/Ffu209-TNFα, which was introduced into BL21 (DE3) to obtain a positive recombinant strain. The expression of recombinant protein Ffu209-TNFα in E. coli was highly soluble with optimized expression conditions. The osmotic-shock method was used to directly release of the periplasmic protein for localization verification of the recombinant protein. We use anion exchange chromatography to purify recombinant protein. MTT assay was used to measure the cytotoxic activity of recombinant protein on L929 cells.
Results: Experiments have shown that the soluble expression of recombinant protein in grayscale scanning was about 63% of the total expression after optimization of the expression conditions. The osmotic-shock method confirmed that the fusion tag Ffu209 achieved secretary expression in the periplasmic space of recombinant TNFα in E. coli. The expression yield of the purified recombinant protein is 12 mg/L. MTT assay showed that our expression system can produce soluble TNFα secreted into the periplasmic space with a biological activity of 3.47×105 U/mg.
Conclusions: In this study, the novel fusion tag Ffu209 was fused with TNFα to construct recombinant protein Ffu209-TNFα. The recombinant protein Ffu209-TNFα was highly soluble in E. coli by optimization of induction conditions, and the recombinant protein had certain biological activity. The fusion tag Ffu provides a new tool for realizing the soluble expression of heterologous protein in E. coli, especially for the eukaryotic proteins containing disulfide bonds.
KEYWORDS: Fusion tag; Tumor necrosis factor α; E. coli; Periplasm space
目 录
摘 要 I
ABSTRACT III
第一章 文献综述 1
1.1 大肠杆菌异源蛋白表达 1
1.1.1 大肠杆菌原核表达系统 1
1.1.2 大肠杆菌周质空间 2
1.2 融合标签概述 2
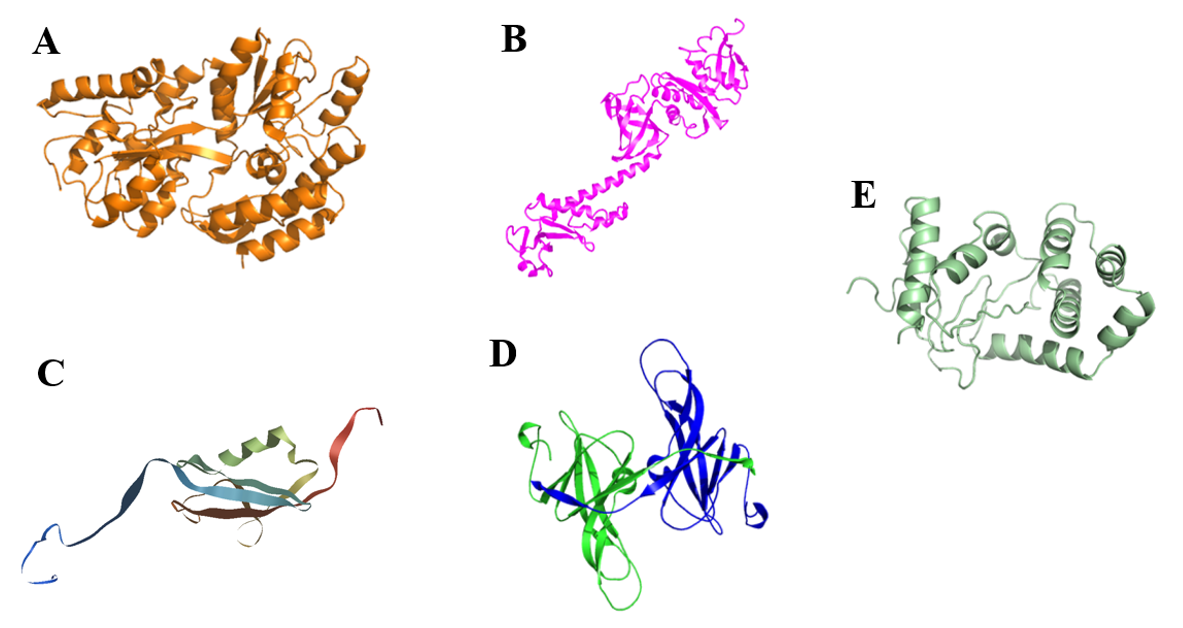
1.3 肿瘤坏死因子α 5
1.3.1 肿瘤坏死因子α的发现 5
1.3.2 TNFα的基因与分子结构 6
1.3.3 TNFα的生物学功能 6
1.3.4 TNFα研究现状 6
1.4 本论文的研究目的及主要内容 7
第二章 实验材料与方法 9
2.1 材料与仪器 9
2.1.1 菌株与质粒 9
2.1.2 实验试剂 9
2.1.3 主要仪器设备 10
2.1.4 培养基及缓冲 11
2.2 融合标签Ffu209介导人TNFα可溶性表达 12
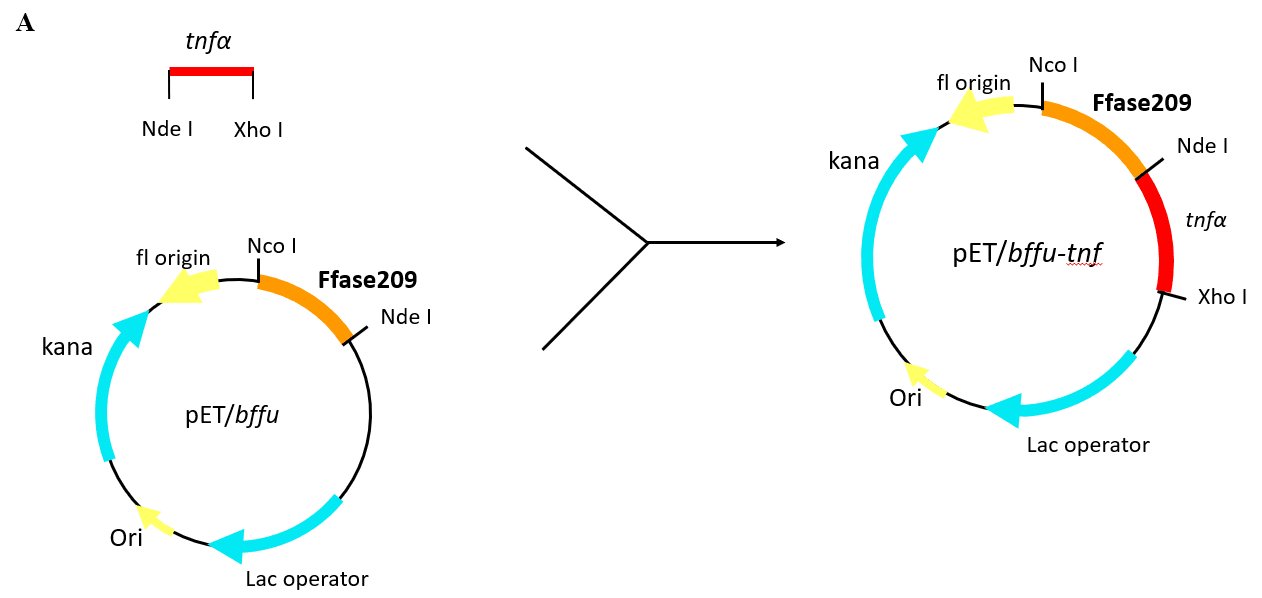
2.2.1 重组表达载体的构建 12
2.2.2 大肠杆菌感受态细胞的制备 13
2.2.3 重组质粒的转化 13
2.2.4 阳性重组子菌落的筛选 13
2.2.5 重组菌的诱导表达及细胞分级分离 14
2.2.6 重组目的蛋白诱导表达条件的优化 14
2.2.7 SDS-PAGE电泳分析 14
2.3 重组Ffu209-TNFα的细胞定位及活性研究 15
2.3.1 渗透压休克法[57]提取周质蛋白 15
2.3.2 重组蛋白的纯化 15
2.3.3 透析脱盐处理 16
2.3.4 BCA法测定蛋白浓度 16
2.3.5 MTT法检测重组蛋白的细胞毒活性 16
第三章 结果与讨论 17
3.1 重组表达载体的构建 17
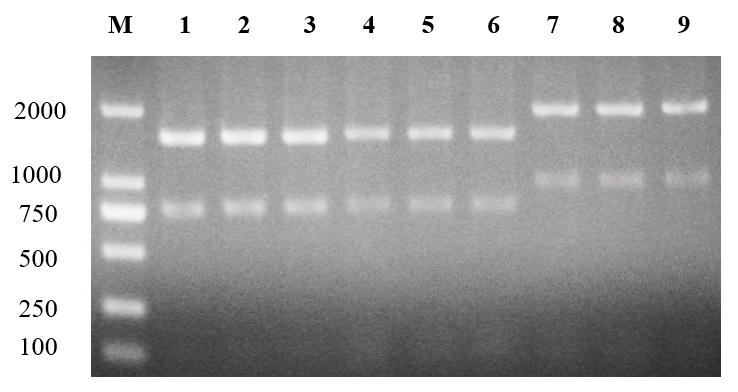
3.2 重组菌落的PCR验证和阳性菌落的测序 17
3.3 重组质粒导入E. coli BL21(DE3)表达宿主 18
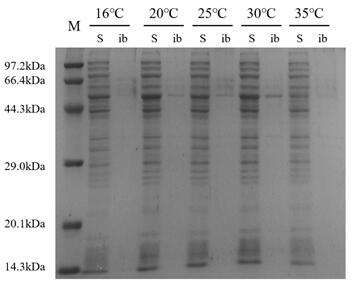
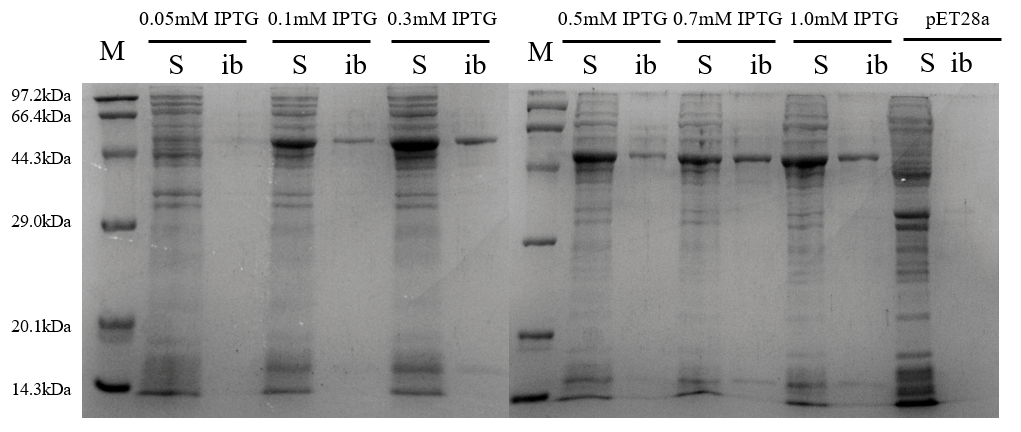
3.4 重组蛋白Ffu209-TNFα的表达及条件优化 18
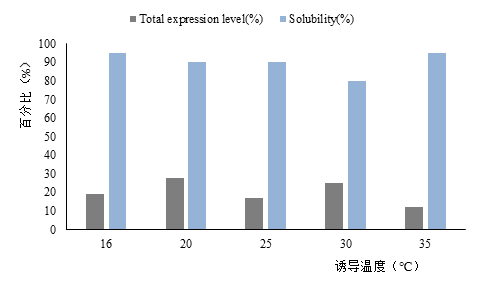
3.4.1 诱导温度 18
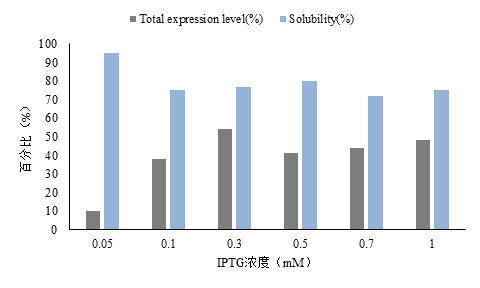
3.4.2 诱导剂浓度 19
3.4.3 诱导时间 20
3.5 Ffu融合蛋白周质空间提取 22
3.6 重组蛋白Ffu209-TNFα的纯化 23
3.7 BCA法测蛋白浓度 24
3.8 MTT检测重组蛋白的细胞毒活性 25
3.9 小结 26
第四章 结论与展望 28
4.1 结论 28
4.2 展望 28
参考文献 29
致谢 34
第一章 文献综述
1.1 大肠杆菌异源蛋白表达
1.1.1 大肠杆菌原核表达系统
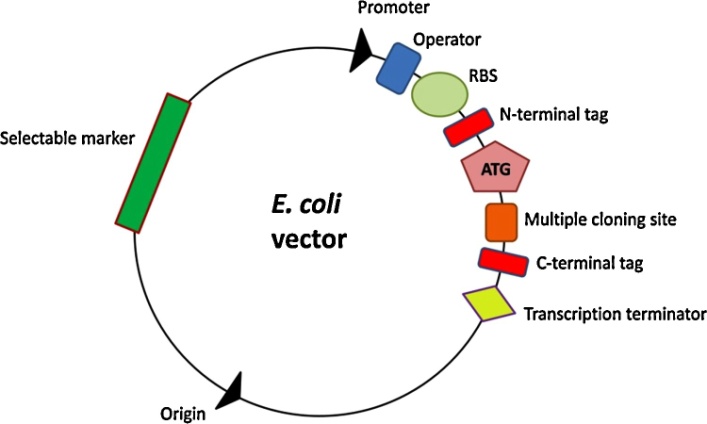
大肠杆菌的生长周期短,易于使用,培养成本低,表达系统成熟稳定等特点使之成为重组蛋白生产的主要宿主[1],表达载体的基本组成如图1-1所示。它是实验室研究和初始开发的优选系统,也作为各种表达平台之间比较的基准。
以上是毕业论文大纲或资料介绍,该课题完整毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、程序设计、图纸设计等资料请添加微信获取,微信号:bysjorg。
相关图片展示: