磷脂酶D的固定化及其在磷脂酰丝氨酸合成中的应用毕业论文
2020-07-02 22:52:46
摘 要
磷脂酶D能够催化带有羟基的极性化合物通过转酰基反应连接到磷脂酸上,从而形成新的磷脂,对稀有磷脂的制备具有重要的意义。但由于PLD多用于两相催化体系,大大降低了酶的催化效率,同时由于磷脂酶D难以大量获得,两相催化体系对游离磷脂酶D的利用效率较低,因此本研究中使用来源于链霉菌pmf的磷脂酶D,建立和优化磷脂酶D固定化工艺,解决两相催化的低效率的问题,提高磷脂酶D的利用效率,为磷脂酶D的生产和应用奠定了一定基础。
本课题通过筛选固定化材料,制得了脱氧胆酸钠、钙离子与PLD共沉淀合成的固定化PLD,以结合多种表征手段测定了固定化PLD的物理结构与化学成分组成,同时研究得出固定化PLD的最适反应温度为30°C左右,最适pH为5.5左右,相对于游离PLD,固定化PLD酶活性提高20%以上,并对温度和pH有更好的耐受性。且固定化PLD能够进行重复利用,重复利用5次以后,仍具有50%以上的催化活性。
关键词:磷脂酶D 磷酯酰丝氨酸酶的固定化 酶的表征
Immobilization of Phospholipase D and Its Application in Synthesis of Phosphatidylserine
Abstract
Phospholipase D catalyzes the attachment of polar compounds with hydroxyl groups to the phosphatidic acid via a transacylation reaction to form new phospholipids, which is of great significance for the preparation of rare phospholipids. Since PLD are mostly used in two-phase catalytic systems, the catalytic efficiency of enzymes is greatly reduced, so in this study, in order to overcome the limitation phospholipase D was heterologously expressed and produced. At the same time, PLD was used to catalyze the synthesis of phosphatidylserine by lecithin and serine, and the enzymatic properties of phospholipase D were studied. And optimization of phospholipase D immobilization process, breaking through the two-phase catalytic low efficiency bottleneck, laid a certain foundation for the production and application of phospholipase D.
In this project, by immobilizing immobilized materials, immobilized PLD coprecipitated by sodium deoxycholate, calcium ion and PLD was prepared. The physical structure and chemical composition of the immobilized PLD were determined by combining various characterization methods. At the same time, it was found that the optimum reaction temperature of the immobilized PLD was 30° C. and the optimum pH was 5.5. Compared to the free PLD, the immobilized PLD enzyme activity was increased by more than 20%, and the temperature and pH were better tolerated. The immobilized PLD can be reused, and after 5 times of repeated use, it still has more than 50% catalytic activity.
KeyWords:PhospholipaseD; Phosphatidylserine; Recombinant E. coli; Enzyme Immobilization
目 录
摘要 I
ABSTRACT II
第一章 文献综述 1
1.1 引言 1
1.2 磷脂酶D 1
1.3 固定化酶 2
1.3.1 固定化酶的概述 2
1.3.2 纳米材料固定化酶 3
1.3.3 固定化酶的性质 3
1.4 研究目的 5
第二章 实验部分 6
2.1 前言 6
2.2 实验材料 6
2.2.1 主要实验材料 6
2.2.2 主要实验仪器 7
2.3实验方法 8
2.3.1固定化材料的选择 8
2.3.2 固定化PLD的表征 9
2.3.3 温度对固定化PLD催化活力的影响 9
2.3.4 pH对固定化PLD催化活力的影响 9
2.3.5 固定化PLD的重复利用率 10
2.3.6 固定化PLD在生产磷脂酰丝氨酸中的应用 10
第三章 实验分析 12
3.1 固定化材料的选择 12
3.1.1表面活性剂的选择 12
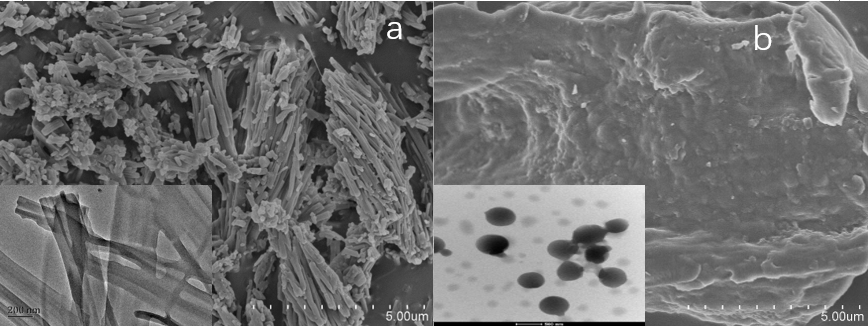
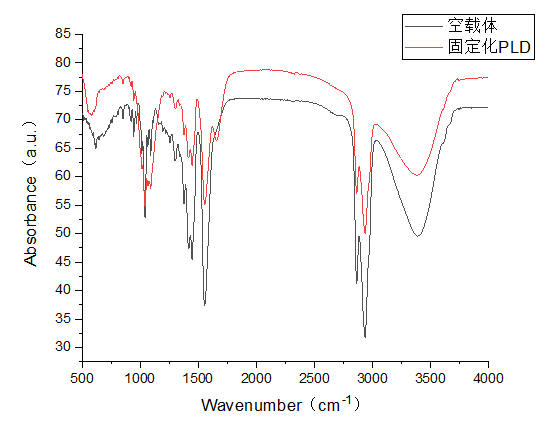
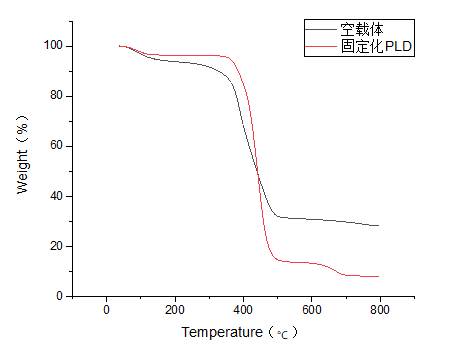
3.2 固定化PLD的表征 13
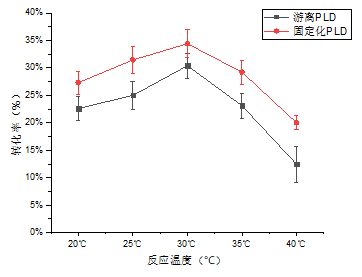
3.3 温度对固定化PLD催化活力的影响 15
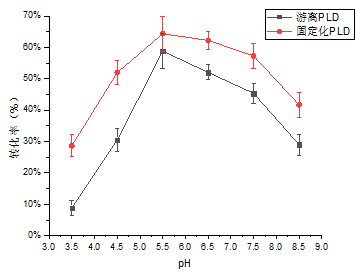
3.4 pH对固定化PLD催化活力的影响 16
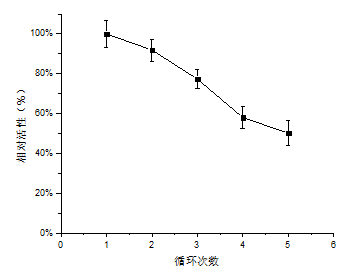
3.5 固定化PLD的重复利用率 17
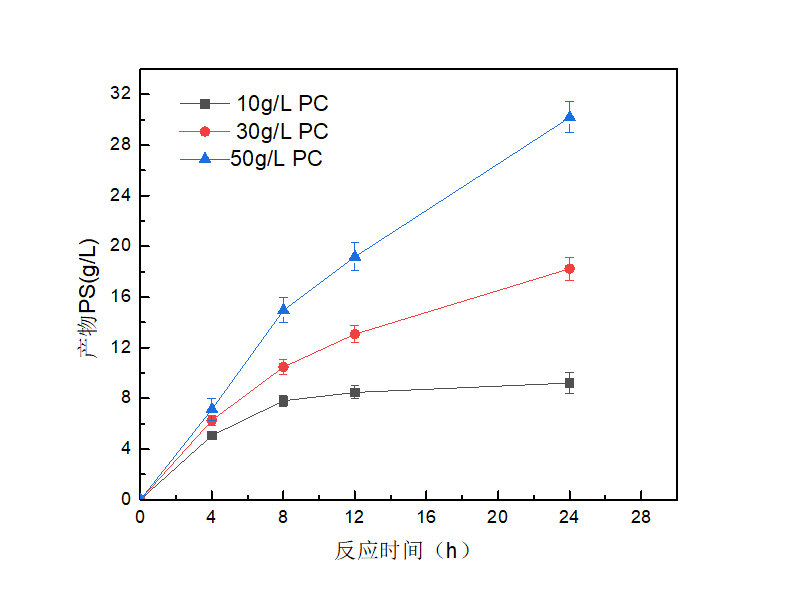
3.6 固定化PLD在生产磷脂酰丝氨酸中的应用 17
第四章 结果与展望 19
4.1结论 19
4.2 展望 20
参考文献 21
致谢 24
第一章 文献综述
1.1 引言
磷脂酶D(PLD)是一类可以水解羟基化合物和磷脂生产磷脂酸的酶,它使用磷脂磷酸二酯键[1]作为催化位点。 除了水解活性之外,PLD还可以通过磷酰基转移来催化磷脂的极性头部基团的转移。 PLD的磷酸转移非常重要。 它可以催化大量磷脂酰胆碱(PC)合成为天然稀有磷脂,如磷脂酰乙醇胺和磷脂酰丝氨酸、磷脂酰甘油[2-6]。 合成磷脂在食品,化妆品和药品中发挥重要作用。 传统的磷脂酶D提取自体植物,后来研究人员从微生物中发现并提取磷脂酶D. 近年来,磷脂酶D的克隆和表达已成为研究热点。
1.2 磷脂酶D
相关图片展示: