载Zr-La双金属复合吸附剂的制备及其除氟性能毕业论文
2020-04-16 16:36:03
摘 要
目前,世界各国普遍存在着水体氟污染的问题。氟虽然作为人体必需微量元素,但不合理的摄入会对人体健康造成危害。摄入量过高时,则很有可能患上氟斑牙、氟骨症等疾病。因此,如何高效除氟一直是环保领域持续关注的热点问题之一。
本论文采用大孔强碱性阴离子交换树脂D201作为载体,将纳米镧、锆氧化物进行负载,制备了新型纳米镧锆氧化物复合吸附剂La-Zr-D201。为探究该复合吸附剂的除氟性能与吸附机理,论文以La-Zr-D201与D201作对比,进行了吸附等温线实验、pH 影响实验、竞争吸附实验、吸附动力学实验及柱吸附实验,并对La-Zr-D201的微观结构进行了表征。通过XRD数据及TEM图像显示,纳米镧、锆氧化物以水合氧化物的形态成功负载于D201上,颗粒粒径分布在30~60nm范围内;等温线实验表明,La-Zr-D201吸附过程为吸热反应,温度的升高有利于其吸附效果,且该吸附过程与Langmuir 吸附方程拟合度更高,在25℃的情况下,Langmuir 拟合最大吸附容量可达36.325mg/g;pH对其除氟效果有着较大影响,酸性情况下,表观吸附量最大,且随碱度增加而减小;在以SO42-、NO3-、Cl-和PO43-作为竞争离子时,四种离子对吸附剂除氟的影响能力大小为:PO43->SO42->NO3->Cl-,但材料依然表现出可观的吸附量与较强的选择性;吸附动力学拟合结果显示,其除氟过程与准二级吸附方程更加吻合,可以在15min内到达吸附平衡,吸附速率较快;柱吸附结果显示,相较于D201处理量有很大提升,可达112.5BV,经过脱附再生之后也依然表现良好,具有一定的可再生性。
关键词:镧氧化物;锆氧化物;树脂;复合吸附剂;除氟;La-Zr-D201
Abstract
At present, there is a widespread problem of fluorine pollution in water bodies all over the world. Although fluorine is a necessary trace element in human body, unreasonable intake will cause harm to human health. When the intake is too low, the incidence of dental caries will increase significantly; when the intake is too high, it is likely to suffer from dental fluorosis, skeletal fluorosis and other diseases. In addition, the presence of high fluorine water can also hinder the growth of plants, or even poison them. The distribution of high-fluorine groundwater in China is very extensive, and the people who drink high-fluorine groundwater all the year round are very large. The discharge of three wastes from steel, building materials, glass, ceramics, semiconductor, aluminum electrolysis, fertilizer and pharmaceutical industries has aggravated the situation of fluorine pollution, which not only pollutes the environment, but also poses a threat to people's life and health. Therefore, how to remove fluoride efficiently has been one of the hot issues in the field of environmental protection. In this paper, macroporous strong basic anion exchange resin D201 was used as carrier, nano-lanthanum oxide and zirconium oxide were loaded, and a new composite adsorbent La-Zr-D201 loaded with nano-lanthanum oxide and zirconium oxide was prepared on the basis of D201. In order to explore the fluoride removal performance and adsorption mechanism of the composite adsorbent, the adsorption isotherm experiment, pH influence experiment, competitive adsorption experiment, adsorption kinetics experiment and column adsorption experiment were carried out by comparing La-Zr-D201 with D201, and the micro-structure of La-Zr-D201 was characterized. The experimental results show that nano-lanthanum and zirconium oxide have been successfully loaded on D201 by XRD data and TEM images, and the particle size distribution is in the range of 30-60 nm. Isothermal experiments show that the adsorption process of La-Zr-D201 is endothermic reaction, and the increase of temperature is beneficial to its adsorption effect, and the adsorption process is in accordance with Langmuir adsorption equation. The fitting degree is higher, the maximum adsorption capacity of Langmuir can reach 36.325 mg/g at 25 ℃. pH has a great influence on the effect of fluoride removal. Under acidic conditions, the apparent adsorption capacity is the largest and decreases with the increase of alkalinity. When SO42-、NO3-、Cl-and PO43-are used as competitive ions, the four ions can remove fluoride from adsorbents. The influencing capacity is PO43->SO42->NO3->Cl-, but the material still shows considerable adsorption capacity and strong selectivity. The adsorption kinetics fitting results show that the fluoride removal process is more consistent with the quasi-second-order adsorption equation, and the adsorption equilibrium can be reached within 15 minutes, and the adsorption rate is faster. The column adsorption results show that the adsorption process is better than that of D201. The treatment capacity has been greatly improved, reaching 112.5BV. After desorption and regeneration, it still performs well and has a certain degree of regeneration.
Key words: lanthanum oxide; zirconium oxide; resin base; composite adsorbent; defluorination;La-Zr-D201
目 录
摘 要 I
Abstract II
第一章 绪 论 1
1.1研究背景 1
1.1.1 氟污染的危害及现状 1
1.1.2水体中氟的来源 2
1.2除氟方法进展 2
1.2.1沉淀法 2
1.2.2 电凝聚法 3
1.2.3 反渗透法 3
1.2.4离子交换法 4
1.2.5 吸附法 4
1.3除氟吸附剂研究进展 5
1.4本课题的提出 6
第二章 实验部分 7
2.1实验试剂及仪器 7
2.2实验方法 8
2.2.1 La-Zr-D201材料制备 8
2.2.2氟溶液的配制 9
2.2.3 TISAB总离子强度缓冲溶液的配制 9
2.2.4 确定镧锆最佳配比实验 9
2.2.5 吸附等温线实验 9
2.2.6 pH值的影响实验 10
2.2.7 竞争吸附实验 10
2.2.8 吸附动力学实验 11
2.2.9 吸附柱实验 12
2.3分析与测定 12
2.3.1吸附剂的表征 12
2.3.2氟离子浓度的测定 12
2.3.3吸附量的计算 13
第三章 结果与讨论 14
3.1镧锆最佳配比的筛选 14
3.2镧锆复合吸附剂(La-Zr-D201)的表征 14
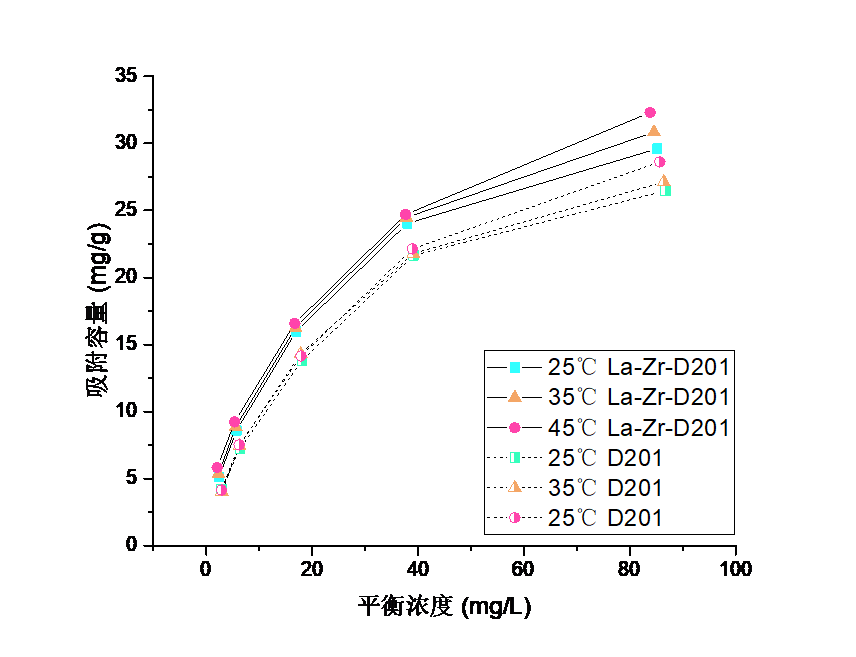
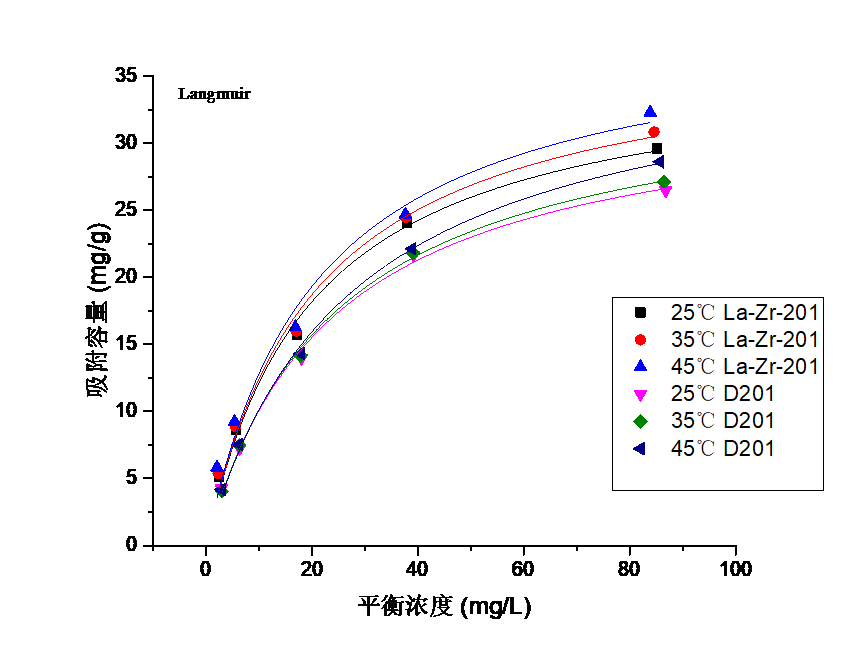
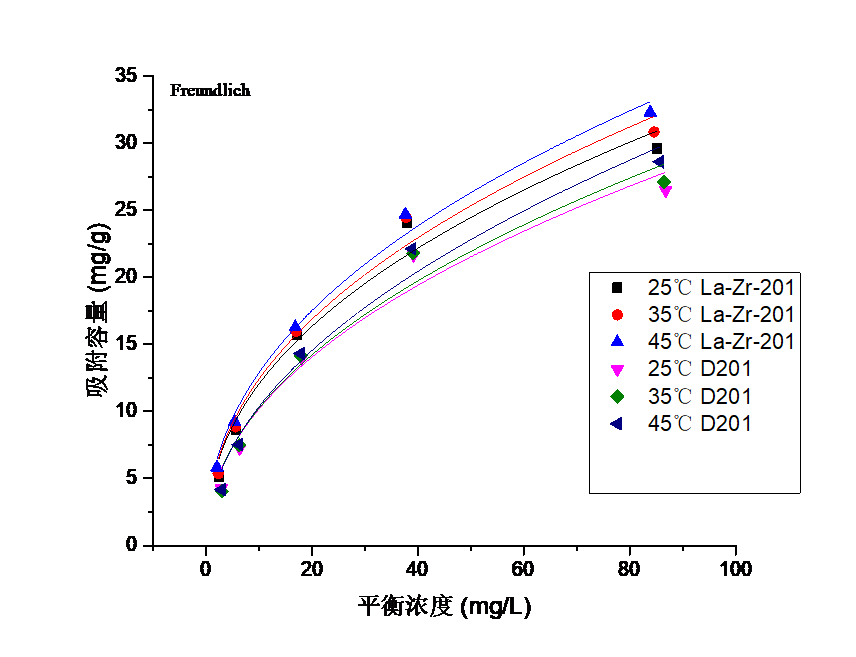
3.3吸附等温线实验结果分析 16
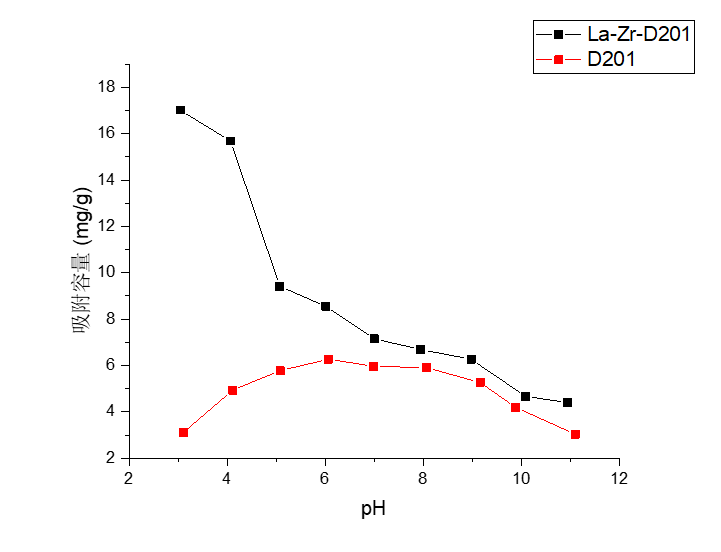
3.4 pH值的影响实验结果分析 18
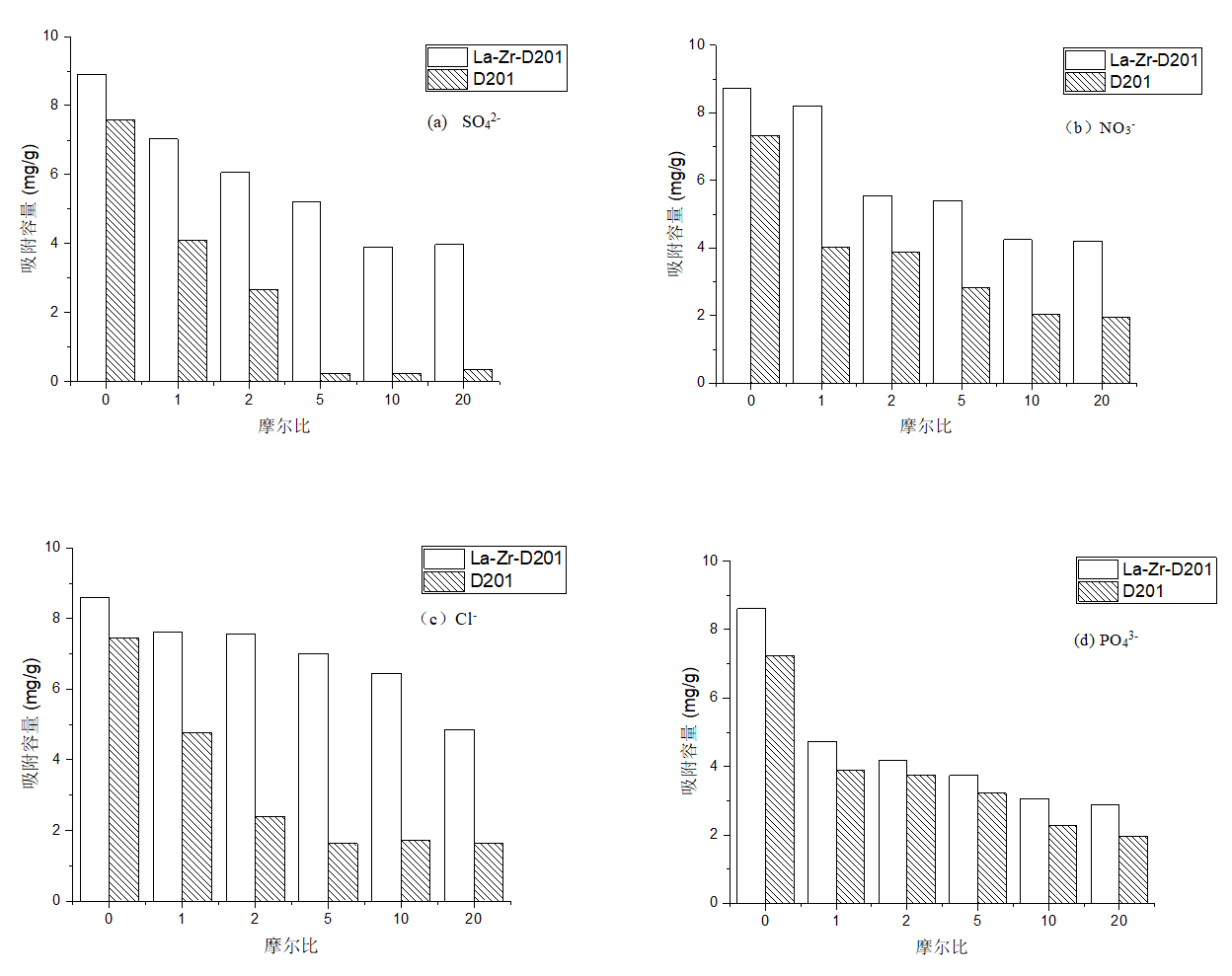
3.5竞争吸附实验结果分析 19
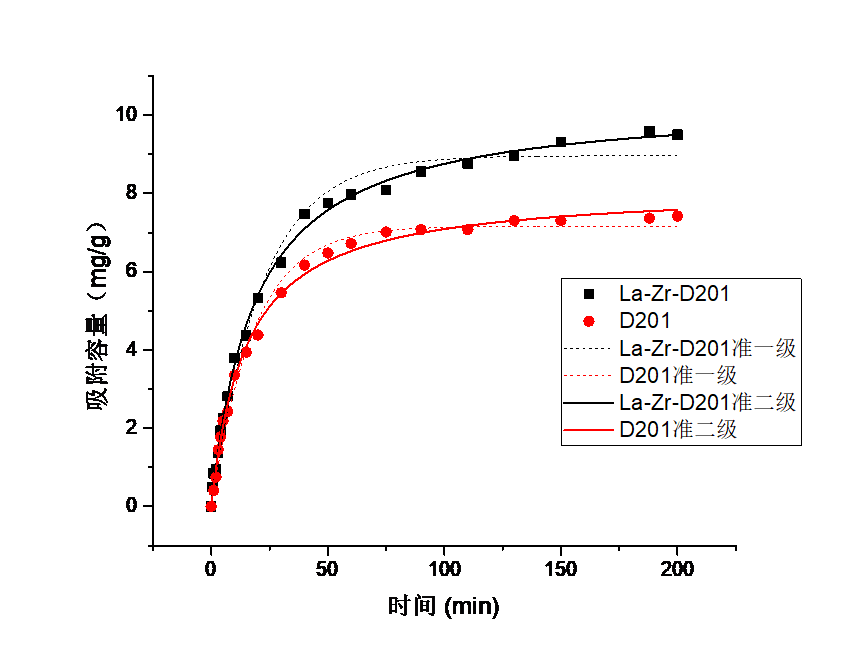
3.6吸附动力学实验结果分析 20
3.7柱吸附实验结果分析 22
第四章 结论与展望 24
4.1结论 24
4.2展望 25
参考文献 26
致 谢 29
绪 论
1.1研究背景
1.1.1 氟污染的危害及现状
氟作为人体所必需的微量元素之一,其摄入量的控制是极其重要的[1],过多或者过少都不利于人体健康。WHO将氟列为“低剂量时人体可能必需但有潜在毒性的微量元素”[2]。适量的氟含量便于体内环境合成氟化钙,从而提高人体牙齿和骨骼的硬度[3],有利于降低龋齿、氟骨症和氟斑牙的患病率。研究表明,长期饮水氟含量为0.5-1.0ppm时与氟相关的疾病的患病率最低。当长期饮水氟含量低于0.5ppm时,儿童患龋齿的概率就会明显升高。但是氟对人体存在着双阈值效应,所以当摄入氟含量过高时也会引发一系列问题。当其含量高于2-4ppm时,会导致氟中毒,甚至还会影响神经系统和内分泌系统,甚至致癌[4,5]。最典型的氟中毒就是氟斑牙和氟骨症,其中又以氟斑牙发病率最高,其症状为牙齿表面没有光泽,牙齿发黄、软化甚至变形[6]。所以我国对饮用水中氟含量的限定是0.5-1.0ppm,《污水综合排放标准》中规定污水排放的一级标准其氟化物质量分数应小于10 mg/L [7-9]。
氟不仅会影响人体机能的运作,对生态环境中的植物也会有不同程度的影响。氟对植物,尤其是对作物的有害影响主要表现为成穗率低、产量降低、光合作用能力下降、呼吸作用与新陈代谢受抑制、叶绿退色变为红褐色等[10]。氟对作物的毒害作用机理主要表现在其对植物细胞结构的破坏。氟含量较高会导致叶绿体和细胞膜系统受损,较高的氟浓度会打破植物细胞内离子平衡,继而使得光合作用、呼吸作用及其他关键酶活性受到抑制, 植物叶片将会出现伤斑,甚至枯黄、坏死[11-13]。
以上是毕业论文大纲或资料介绍,该课题完整毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、程序设计、图纸设计等资料请添加微信获取,微信号:bysjorg。
相关图片展示: