光交联透明质酸水凝胶的制备及性能毕业论文
2021-12-09 17:28:18
论文总字数:30410字
摘 要
周围神经损伤后神经瘢痕增生,严重抑制了神经再生,目前尚无有效的根治的方法。近年来,水凝胶材料在生物医学领域的应用可为瘢痕治疗提供新途径和新方法并受到人们的广泛关注。其中光交联甲基丙烯酸化透明质酸(MA-HA)具有良好的降解性和生物相容性,其成型和性能可控,但是用于神经瘢痕的形成MA-HA水凝胶材料少见报道。基于此,本文论述了MA-HA水凝胶材料制备方法、交联方式,并重点论述了MA-HA水凝胶材料的常见的性能表征及检测手段。
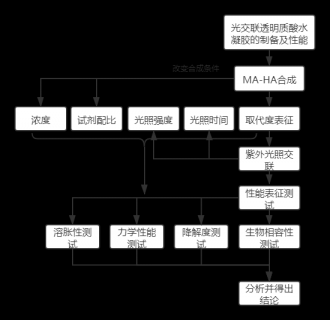
首先,探讨了MA-HA水凝胶材料常见的制备方法。对合成光交联透明质酸水凝胶不同的四种合成方法进行了对比分析。通过在原料选择、所需设备和合成流程方面的差异进行论述。重点对比分析了甲基丙烯酸酐(MA)和甲基丙烯酸缩水甘油酯(GM)合成MA-HA和GMHA两种方法的优缺点,分析结果表明这两种方法主要在合成流程和产物性能方面存在差异,GMHA的合成流程更加简便,耗时更短,且可以多组实验同时进行,而合成的MA-HA在相同甲基丙烯酸基团与HA单体比例下,具有更高的取代度,这表明MA-HA具有更大的力学性能与降解性能可调节范围。可根据实际需求选择水凝胶材料力学性能可控性更好或合成时间更短的制备方法。在交联阶段,由于MA-HA的光交联特性,主要介绍了紫外光交联法的实验流程,在成胶前,还可以加入其他小分子、药物、细胞等物质,使交联形成的水凝胶具有特殊性质,以满足不同的应用要求,扩展了应用范围。
其次,对常见的水凝胶材料性能进行表征,包括取代度,溶胀属性,力学性能,生物降解性和生物相容性。核磁共振氢谱分析材料的合成结果可见,在MA-HA合成中,增加甲基丙烯酸基团与透明质酸(HA)单体的比例,可显著提高MA-HA取代度,在比例为40:1时,MA-HA 可达86%的最高取代度,随取代度的升高,材料的压痕模量也伴随增强,当MA-HA取代度达50%时,模量达最大(5.83 ± 0.20 kPa)。水凝胶的浓度也影响着材料的力学性能和降解性能,取代度一定时,水凝胶浓度越大,材料的模量越高,形成的水凝胶材料的降解时间也越长,最长可达35天以上。
本论文针对MA-HA水凝胶材料合成和性能进行了调控、分析,可为神经损伤后瘢痕抑制与修复提供具体的实验设计和良好的理论依据。
关键词:神经瘢痕;透明质酸水凝胶;MA-HA;光交联; 水凝胶性能分析
Abstract
Nerve scar hyperplasia after peripheral nerve injury severely inhibits nerve regeneration, however there is no effective cure. In recent years, the application of hydrogel materials in the field of biomedicine can provide new ways and new methods for scar treatment and has attracted widespread attention. Among them, photo-crosslinked methacrylic hyaluronic acid (MA-HA) has good degradability and biocompatibility, and its molding and performance can be controlled, but MA-HA hydrogel materials used for the formation of nerve scar are rarely reported . Based on this, this article discussed the preparation methods and cross-linking methods of MA-HA hydrogel materials, and focused on the common performance characterization and detection methods of MA-HA hydrogel materials.
First, the common preparation methods of MA-HA hydrogel materials were discussed. Four synthetic methods for synthesizing photocrosslinked hyaluronic acid hydrogel were compared and analyzed. Differences in raw material selection, required equipment and synthesis process were discussed. The advantages and disadvantages of the two methods of methacrylic anhydride (MA) and glycidyl methacrylate (GM) synthesis MA-HA and GMHA were analyzed and compared. Two methods were mainly in the synthesis process and product performance were described. The synthesized MA-HA has a higher degree of substitution under the same ratio of methacrylic groups and HA monomers, which indicated that MA-HA had a larger adjustable range of mechanical properties and degradation performance. The preparation method of hydrogel material with better controllability of mechanical properties or shorter synthesis time could be selected according to actual needs. In the cross-linking stage, due to the photo-cross-linking characteristics of MA-HA, the experimental process of the UV cross-linking method were mainly introduced. Before forming the gel, other small molecules, drugs, cells and other substances could be embedded to make the cross-linking Hydrogels have special properties to meet different requirements and expand the scope of applications.
Second, characterize the properties of common hydrogel materials, including degree of substitution, swelling properties, mechanical properties, biodegradability, and biocompatibility were described. The synthesis results of NMR hydrogen spectroscopy analysis materials showed that in the synthesis of MA-HA, increasing the ratio of methacrylic acid groups to hyaluronic acid (HA) monomer significantly improved the degree of MA-HA substitution, at a ratio of 40: 1, after 1 hour, the highest degree of MA-HA substitution reached to 86%. As the degree of substitution increased, the indentation modulus of the material also increased. When the degree of MA-HA substitution reached 50%, the modulus reached the maximum (5.83 ± 0.20 kPa). The concentration of the hydrogel also affected the mechanical properties and degradation performance of the material. The hydrogel concentration also affects the mechanical properties and degradation properties of the material. When the degree of substitution is constant, the greater the concentration of hydrogel, the higher the modulus of the material, and the longer the degradation time of the hydrogel material. The longest time can be up to 35 days.
This paper regulated and analyzed the synthesis and performance of MA-HA hydrogel materials, which could provide specific experimental design and good theoretical basis for scar inhibition and repair after nerve injury.
Key Words:Nerve scar; hyaluronic acid hydrogel; MA-HA; photo-crosslinking; hydrogel performance analysis
目 录
第1章 绪论 1
1.1研究背景、目的及意义 1
1.1.1研究背景 1
1.1.2研究目的 1
1.1.3研究意义 2
1.2研究现状 3
1.2.1神经瘢痕 3
1.2.2水凝胶材料研究进展 4
1.2.3生物医用水凝胶研究进展 5
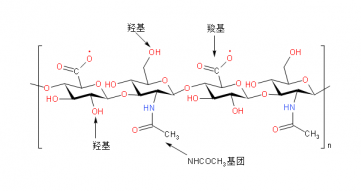
1.2.4透明质酸水凝胶研究进展 6
1.3研究内容和技术路线 8
1.3.1研究内容 8
1.3.2技术路线 9
1.4选题对社会、健康、安全、成本以及环境的影响 9
第2章 MA-HA水凝胶材料制备与交联方法 11
2.1MA-HA制备方法 11
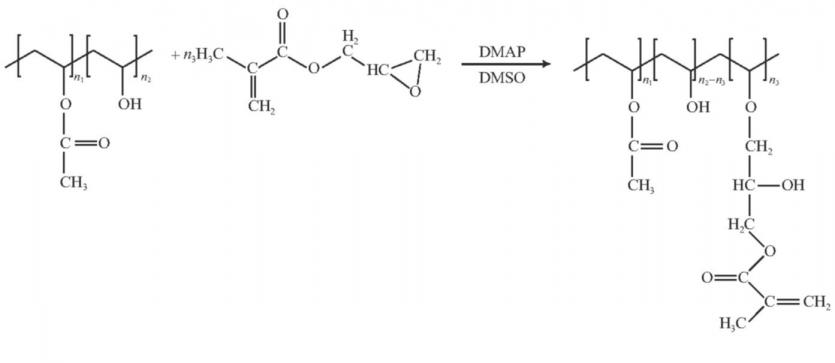
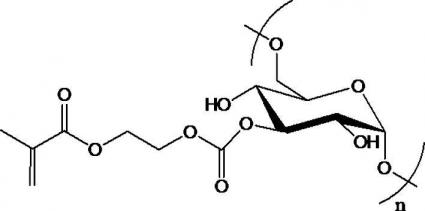
2.1.1制备方法一(MA接枝法) 11
2.1.2制备方法二(GM接枝法) 12
2.1.3制备方法三(两步法) 12
2.1.4制备方法四(DMSO法) 13
2.2MA-HA水凝胶交联方法 13
2.3小结 14
第3章 材料测试与分析技术 16
3.1 MA-HA的取代度测定 16
3.2溶胀测试 17
3.3力学测试 18
3.4生物降解测试 19
3.5生物相容性测试 21
3.6小结 21
第4章 结论 23
4.1 MA-HA水凝胶制备方法 23
4.2 材料测试及分析技术 23
4.3 应用前景 24
参考文献 25
致 谢 28
第1章 绪论
1.1研究背景、目的及意义
1.1.1研究背景
随着我国近年来各类工业和交通行业的迅猛发展,我国神经损伤病例也迅猛增长。据文献报道,我国每年新增约90万神经损伤病人[1]。在受损神经生长恢复的过程中,神经瘢痕增生现象普遍发生。神经瘢痕的形成严重地抑制了神经再生的速度和质量,其中还有10%以上的病人会产生难以缓解的疼痛感,不仅给病人带来巨大的身心痛苦,还增重了病人的经济负担。临床上已形成手术切除,放射治疗,药物治疗 ,基因治疗和表皮干细胞(ESC)治疗等多种治疗手段,但普遍存在无法根治,容易反复,副作用较大和费用昂贵等缺点,所以目前针对抑制神经瘢痕生长,还没有较好的治疗和解决手段。
水凝胶材料由于其优良的生物相容性,灵活多变的合成制备方法以及其理想的物理特性,在生物医用领域广泛受到关注。特别是在再生医学中,水凝胶材料可以作为支架,为组织再生预构一个完整的结构,利用其溶胀属性还可以控制向再生组织定量释放递送药物和蛋白质,并且充当屏障,将再生组织与周围环境隔离开来,为组织正常再生提供适宜的再生条件,还可以通过官能团的结合,使水凝胶材料与其他改性材料结合,从而引入特定所需的物理和化学性质,达到对天然水凝胶材料的改性,使其适用于特定用途,这大大拓展了水凝胶材料的应用领域。
请支付后下载全文,论文总字数:30410字
相关图片展示: