基于CDC减振器的空气主动悬架系统设计毕业论文
2020-04-10 14:40:15

本科生毕业设计(论文)
学生姓名:何文丰
导师姓名、职称:冯智勇(副教授)
所属学院:国际教育学院
专业班级:车辆gj1401
设计(论文)题目:基于CDC减振器的汽车主动空气悬架的设计
2018年 5 月 30 日
学位论文原创性声明
本人郑重声明:所呈交的论文是本人在导师的指导下独立进行研究所取得的研究成果。除了文中特别加以标注引用的内容外,本论文不包括任何其他个人或集体已经发表或撰写的成果作品。本人完全意识到本声明的法律后果由本人承担。
作者签名: 何文丰
2018年 6 月 9 日
学位论文版权使用授权书
本学位论文作者完全了解学校有关保障、使用学位论文的规定,同意学校保留并向有关学位论文管理部门或机构送交论文的复印件和电子版,允许论文被查阅和借阅。本人授权省级优秀学士论文评选机构将本学位论文的全部或部分内容编入有关数据进行检索,可以采用影印、缩印或扫描等复制手段保存和汇编本学位论文。
本学位论文属于1、保密囗,在 年解密后适用本授权书
√
2、不保密囗 。
(请在以上相应方框内打“√”)
作者签名:何文丰 2018 年 6月 9 日
导师签名:冯智勇 2018年 6月 9 日
Abstract
With the improvement of people's requirements for riding comfort and the development of suspension technology, the application of air suspension on vehicles Increasingly broad, and with the promotion of electronic technology applications and the development of vehicle control technology, electronic control will gradually replace With the mechanical control of the system, it can be foreseen that the application of electronically controlled air suspension systems in automobiles will become increasingly common, and In this paper, we have conducted a deeper study on the design of automotive active suspension and the integrated design of pneumatic system. Systematic research work.
First, the theoretical basis of automotive vibration, the characteristics of air springs, and the main parameters of air spring height, effective area, and volume are introduced. The mathematical model of the air spring was deduced using the relevant thermodynamics knowledge, and the damping force of the shock absorber and its speed characteristic curve were given. Integrated suspension the design requirements determine the height of the normal driving conditions of the vehicle body and the height of special driving conditions, and advances the height control strategy.
Modular design. .
Second, the main features of the body height adjustment system are introduced. Analysis of pneumatic circuit system deflation at the same time, the system was parameterized and the system was calibrated sensor.
Key Words : suspension air spring shock absorber height adjustment
Contents
ChapterⅠ: Overview 5
1.1 Air Suspension Overview 6
1.2 Design Target Vehicles and Parameters 7
ChapterⅡ: Air Suspension Vibration Analysis and Parameter Design 8
2.1 The choice of the main parameters of the suspension 8
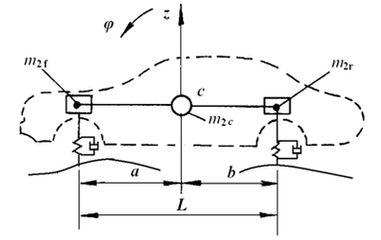
2.2 Spatial geometric parameters of the suspension: 8
2.3 Analysis of Basic Principles of Automobile Vibration 9
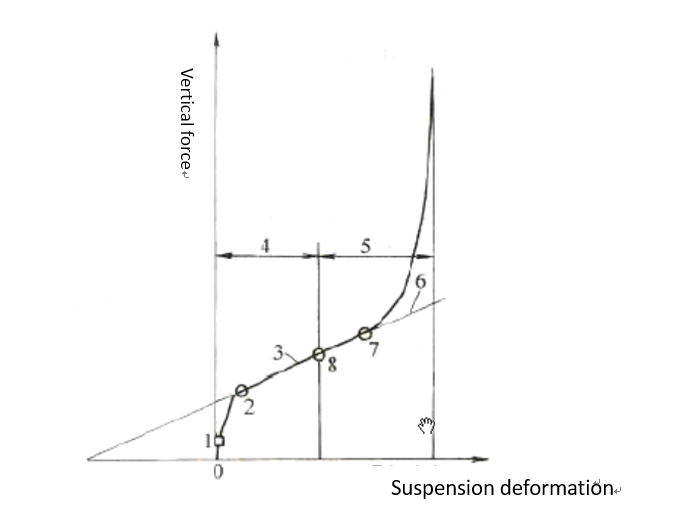
2.4 Suspension elastic characteristics and working stroke: 11
2.4.2 Selection of Suspension Frequency: 12
2.4.3 Working Schedule of Suspension: 12
2.4.4 Suspension Elasticity Selection 13
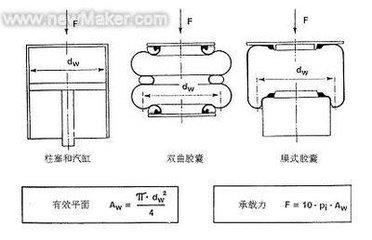
2.4.5 Design of Suspension Air Springs 14
2.5 Design of main performance parameters of shock absorbers 21
2.5.1 Effect of relative damping coefficient ψ 22
2.5.2 Determination of shock absorber damping coefficient δ 22
2.5.3 Determination of the maximum unloading force 23
2.5.4 Selection of Main Size of Shock Absorber 23
2.6 Calculation of wall thickness, cylinder head, piston rod and lowest guide mechanism of hydraulic cylinder 25
2.6.1 Calculation of Wall Thickness of Hydraulic Cylinder 25
2.6.2 Determination of shock absorber piston stroke 26
2.6.3 Calculation of Stability of Hydraulic Cylinder 26
2.6.4 Calculation of cylinder head thickness 27
2.6.5 Calculation of Piston Rod 28
2.6.6 Check the strength of the piston rod 28
2.6.7 Determination of the minimum guide length 29
2.6.8 Structural Design of Hydraulic Cylinder 29
2.6.8 Piston and Valve System Dimension Calculation 30
ChapterⅢ: Structural Design of Air Suspension System 32
3.1 Analysis and design of vehicle height adjustment system 32
3.1.1 Body height 32
3.1.2 Determination of standard height of air spring 32
3.2 Air suspension control strategy based on CDC shock absorber 32
3.2.1 CDC Control Strategy 32
3.2.2 Air Spring Control 33
3.2.3 Air suspension pneumatic system 34
3.2.4 Electronic Control System with Correction Unit 35
3.2.5 Electronically Controlled Air Suspension System 37
3.2.6 Electronic Control Unit (ECU): 38
3.6.7 Solenoid valve 39
3.6.8 height sensor 40
3.6.9 gas system 40
3.7. Study on the Method of Body Height Adjustment 41
ChapterⅤ: Summary and Expection 42
Summary : 42
Expection: 43
References 44
ChapterⅠ: Overview
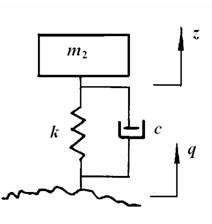
Suspension is located between the axle and the body. It is the general name of all the force transmission devices. The typical automobile suspension is composed of elastic elements, shock absorbers and guide mechanism. The individual devices are also provided with buffer blocks and stabilizer bars, and elastic elements. The elastic elements can be divided into leaf springs, coil springs, torque springs and air springs and other forms spring , modern automobile use spiral springs and torque springs, shock absorbers are the main components of the damping, its role is to consume the energy of vibration, improve the car ride comfort ,The working process is that during the vibration of the car, the piston of the shock absorber reciprocates, the oil in the shock absorber passes through the throttle hole, the liquid friction consumes energy, and the kinetic energy is attenuated, thereby improving ride comfort. The CDC-based air active suspension can adjust the damping and stiffness of the vibration system. In the actual process, the CDC system judges the running status of the vehicle based on the data of the vehicle's body acceleration sensors, wheel acceleration sensors, and lateral acceleration sensors. The central control unit ECU performs calculations, and then the ECU issues corresponding commands to the CDC control valve on the shock absorber and controls the opening of the valve to provide damping to adapt to the current state. The air suspension can adjust the suspension stiffness according to the driving conditions of the vehicle, and improve the comfort while ensuring the pass ability.
Nowadays, in foreign countries, the air suspension system is used up to 80% on heavy goods vehicles. Some cars are also equipped with an air suspension system. When the road conditions change, the active suspension adjusts its own parameters when the wheels leave the ground. At the same time, adjust the stiffness and damping of the suspension so that it is in the best damping state to ensure pass ability and comfort, so that the car is in the best working condition.
Development history of active suspension at homeland and abroad: In 1954, GM company Erspiel-labrosse first proposed the idea of active suspension in suspension design.
In 1973, D.A. Crosby and D.C.karpopp first proposed the idea of semi-active suspension.
Ford's Thunderbird TURBO sedan is equipped with a so-called ride comfort program-controlled suspension system, abbreviated PRC
Nissan Motor Co., Ltd. developed a so-called sonar suspension device that was first installed on the 1988 Maxima sedan.
The magneto-rheological damper (Magneride) produced by Delphi has been used in semi-active suspension systems for Chevrolet Corvette, Cadillac Seville wagons and Audi Tr sports cars.Volvo s60r,Volvo v70r,
The latest Audi a6l and Audi All-road models are equipped with adjustable damping CES semi-active suspensions from Tenneco
以上是毕业论文大纲或资料介绍,该课题完整毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、程序设计、图纸设计等资料请添加微信获取,微信号:bysjorg。
相关图片展示: