壳管式换热器传热与流动耦合特性数值模拟研究毕业论文
2021-03-13 23:01:28
摘 要
随着现代工业的飞速发展,换热器的用途的愈加的广泛。而在换热器中使用最普遍的则是管壳式换热器,壳程多为空气,流动方式十分的复杂,变化不定;管程流体多为水和其他制冷剂。然而传统单弓形折流板管壳式换热器的性能换热效率低,流体流动阻力大,所以研究管壳式换热器的传热与流动的具体过程是十分重要来改善换热器的换热性能的方法。主要提高点在于如何提改善换热效率的同时降低流动的阻力。由于实验研究的方法成本较高,且不易观察,所以使用仿真软件对管壳式换热器的传热与流动进行数值模拟已经成为研究的重要方法之一。
本文圆管管翅式换热器作为研究对象,选取部分管束(四排)作为模拟区域。通过建立三维模型,导入到WORKBENCH中,由mesh模块进行网格划分。后导入FLUENT仿真软件中,进行数值模拟,设定边界调节,确定以进口速度作为变量,通过输入不同的进口速度初始值,计算得到换热器的压力场、流场、温度场等物理特性,再通过对比不同速度下各个场云图,得出结论:随着进口流速的减小,其流体速度梯度变小,流体与换热壁面的接触面减小,换热系数下降,导致换热器的换热量减小,温度梯度减小。
得出结论后,本文以纵向管束间距作为研究对象,通过仿真不同流速下(雷诺数)各个纵向管束间距的流动阻力和换热性能,发现努塞尔数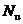 和阻力因子随着管径增大而减小,并逐渐趋于平缓。通过JF因子分析得出:纵向管束间距在阻力允许的范围内,增加可以提高换热器的换热性能的结论。
和阻力因子随着管径增大而减小,并逐渐趋于平缓。通过JF因子分析得出:纵向管束间距在阻力允许的范围内,增加可以提高换热器的换热性能的结论。
关键词:管壳式换热器;传热;流动;数值模拟;纵向管束间距;结构优化
Abstract
With the rapid development of modern industry, the use of heat exchanger more widely. In the heat exchanger is the most common use is shell and tube heat exchanger, shell side for the air, the flow is very complex, variable; pipe fluid and water for many other. However, the performance of traditional single-arched baffle shell-and-tube heat exchangers is low and the fluid flow resistance is high. Therefore, it is very important to study the heat transfer and flow of shell and tube heat exchangers to improve the heat exchanger Heat transfer performance method. The main improvement point is how to improve the good heat transfer efficiency while reducing the flow resistance. As the method of experimental research is costly and difficult to observe, it is one of the important methods to study the heat transfer and flow of shell and tube heat exchangers by using simulation software.
In this paper, the tube tube fin heat exchanger as the research object, select part of the tube bundle (four rows) as a simulation area. Through the establishment of three-dimensional model, into the WORKBENCH, mesh module for the grid. And then enter the FLUENT simulation software, the numerical simulation, set the boundary adjustment, to determine the import speed as a variable, by entering the different import speed of the initial value of the heat exchanger to calculate the pressure field, flow field, temperature field and other physical properties, Then, by comparing the field velocity at different speeds, it is concluded that as the inlet velocity decreases, the fluid velocity gradient becomes smaller and the contact surface between the fluid and the heat transfer wall decreases and the heat transfer coefficient decreases. Heat transfer decreases, the temperature gradient decreases.
After the conclusion, the longitudinal pipe bundle spacing is taken as the object of study. By analyzing the flow resistance and heat transfer performance of each longitudinal tube bundle spacing at different flow rates (Reynolds number), the longitudinal pipe bundle spacing is within a certain range by JF factor analysis Increase the heat exchanger can improve the heat transfer performance of the conclusion.
Key words: shell-and-tube heat exchanger; heat transfer; flow; numerical simulation; longitudinal tube spacing; structural optimization
摘要 I
Abstract II
第一章 绪论 1
1.1 目的及意义 1
1.2 国内外研究现状 2
第二章 基础理论及软件介绍 5
2.1 计算流体力学 5
2.2 强化传热基础 11
2.3 WORKBENCH与FLUENT软件介绍 13
第三章 壳管式换热器的模型建立与数值模拟 14
3.1 建立三维模型 14
3.2 边界条件设置和模型选择 16
3.3 壳管式换热器的数值模拟 17
3.4 壳管式换热器的结构尺寸优化 22
第四章 全文总结和课题展望 26
4.1 全文总结 26
4.2 课题展望 26
参考文献 28
致 谢 30
第一章 绪论
1.1 目的及意义




