基于核酸双层三脚架纳米结构电化学检测脱脂牛奶中的肠毒素毕业论文
2020-07-05 17:20:13
摘 要
金黄色葡萄球菌是一种存在于我们居住环境所有角落中的极为可怕的致病菌,因其产肠毒素菌株污染食品所引发的急性中毒事件不计其数,而受到广泛的关注。而且被污染的食物经一般加热处理后,其所包含的肠毒素仍具有活性。因此,建立一种快速、简便、灵敏的检测方法是十分必要的。一些用于检测金黄色葡萄球菌肠毒素的传统检测方法,一般要经历几个步骤:样品-gt;增菌-gt;分离-gt;提纯-gt;革兰染色镜检/耐热核酸酶试验/血浆凝固酶试验/生物反应试验/肠毒素检查。这种传统的检测方法存在很多问题:步骤异常繁琐,试验周期长,而且在试验过程中容易造成污染,试验成本高,对试验环境要求高等,一系列的问题推动了对于金黄色葡萄球菌肠毒素的快速检测方法的出现。
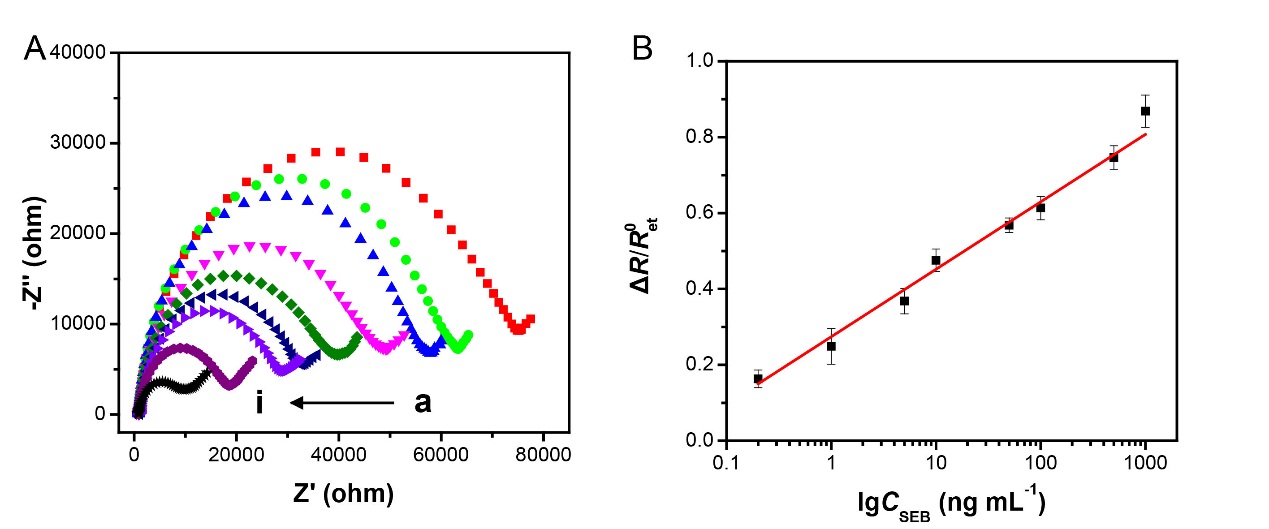
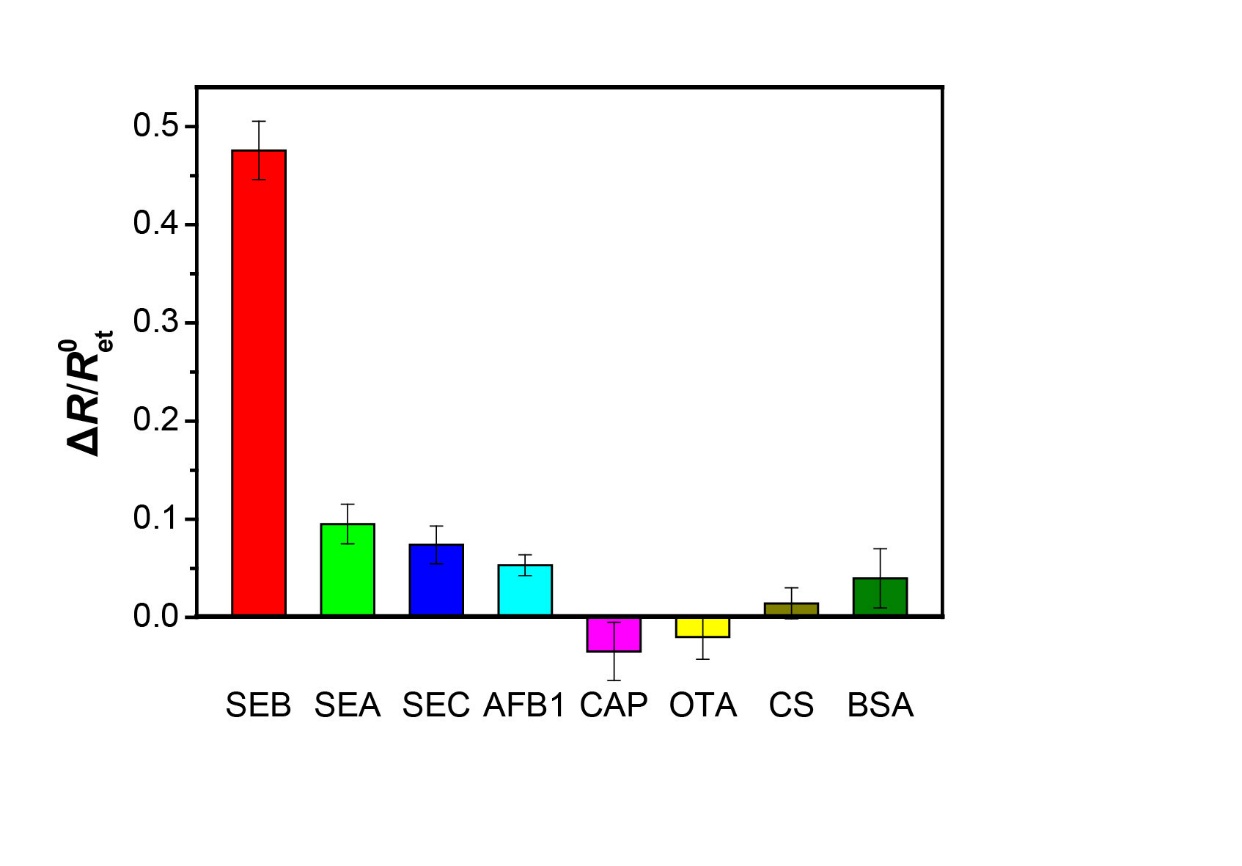
本文主要介绍一种基于核酸双层三脚架纳米结构电化学传感器,可以快速检测金黄色葡萄球菌B型肠毒素(SEB)。把SEB装配在金电极表面,运用循环伏安法(CV)和交流阻抗法(EIS)对修饰过程进行表征。再由修饰电极与10 ng mL-1的SEB反应前后交流阻抗值的变化,优化适配体浓度以及孵育时间。在最优条件下,基于阻抗方法的电化学生物传感器检测SEB的线性范围为0.2 ng mL-1 ~ 1000 ng mL-1,检出限为0.13 ng mL-1 (S/N = 3)。通过对两种SEB同源性毒素以及其它5种化合物的测定来评估所构建的检测方法的选择性。以脱脂牛奶作为样品,与市售商品化ELISA试剂盒作对比,两种方法结果的相对偏差在-6.59% ~ 9.33%之间,进一步证明了所建立的方法有较高的准确度。
关键词:肠毒素 核酸纳米结构 电化学生物传感器
Electrochemical Detection of Staphylococcal Enterotoxin B in Skim Milk Based on Nucleic Acid Double-layer Tripod Nanostructure
Abstract
Staphylococcus aureus is a foodborne pathogen that exists in all corners of our living environment. Due to countless acute poisoning incidents caused by the contaminated foods produced by enterotoxigenic strains, it has received extensive attention. In addition, the contaminated foods are generally heated and the enterotoxins they contain remain active. Therefore, it is very necessary to establish a rapid, simple, and sensitive detection method. Some traditional methods for the detection of staphylococcus aureus enterotoxins generally go through several steps: sample -gt; enrichment -gt; separation -gt; purification -gt; Gram stain microscopy/ thermonuclease/plasma coagulase Test/bioreaction test/test for enterotoxins. There are many problems with this traditional detection method: the procedure is extremely cumbersome, the test cycle is long, and it is easy to cause pollution in the test process, the test cost is high, the test environment is highly demanded, and a series of problems drive the enterotoxin to Staphylococcus aureus The emergence of rapid detection methods.
This article mainly introduces a nucleic acid double-layer tripod nanostructured electrochemical sensor, which can rapidly detect S. aureus type B enterotoxin (SEB). The SEB was modified on the gold electrode surface, and the modification process was characterized by cyclic voltammetry (CV) and alternating current impedance (EIS). The aptamer concentration and incubation time were optimized based on changes in the AC impedance values before and after reaction of the modified electrode with 10 ng mL-1 of SEB. Under the optimal conditions, the linear range of SEB detected by electrochemical biosensor based on impedance method was 0.2 ng mL-1 ~ 1000 ng mL-1, and the detection limit was 0.13 ng mL-1 (S/N = 3). The selectivity of the assays constructed was evaluated by the determination of two SEB homologous toxins and five other compounds. The skimmed milk was used as a sample and compared with commercially available ELISA kits. The relative deviations of the two methods were between -6.59% and 9.33%, which further proved that the established method has higher accuracy.
Keywords: enterotoxin; nucleic acid nanostructure; electrochemical biosensor
目 录
摘 要 I
Abstract II
第一章 文献综述 1
1.1引言 1
1.2肠毒素简介 1
1.3检测方法 2
1.3.1分子生物学检测方法 2
1.3.2免疫学检测方法 3
1.3.3胶体金试纸条检测方法 4
1.3.4基于质谱分析的检测方法 4
1.3.5基于超抗原性的检测方法 4
1.3.6基于适配体传感技术检测方法 5
1.4本课题研究意义 5
第二章 实验材料和方法 8
2.1实验仪器和试剂 8
2.1.1仪器与设备 8
2.1.2试剂与材料 8
2.2实验方法 9
2.2.1适配体传感器的制备 9
2.2.2电化学实验参数 10
2.2.3实验最优条件的确定 10
2.2.4 SEB的电化学检测 10
2.2.5选择性 10
2.2.6 样品中SEB检测的可行性 11
第三章 结果与讨论 12
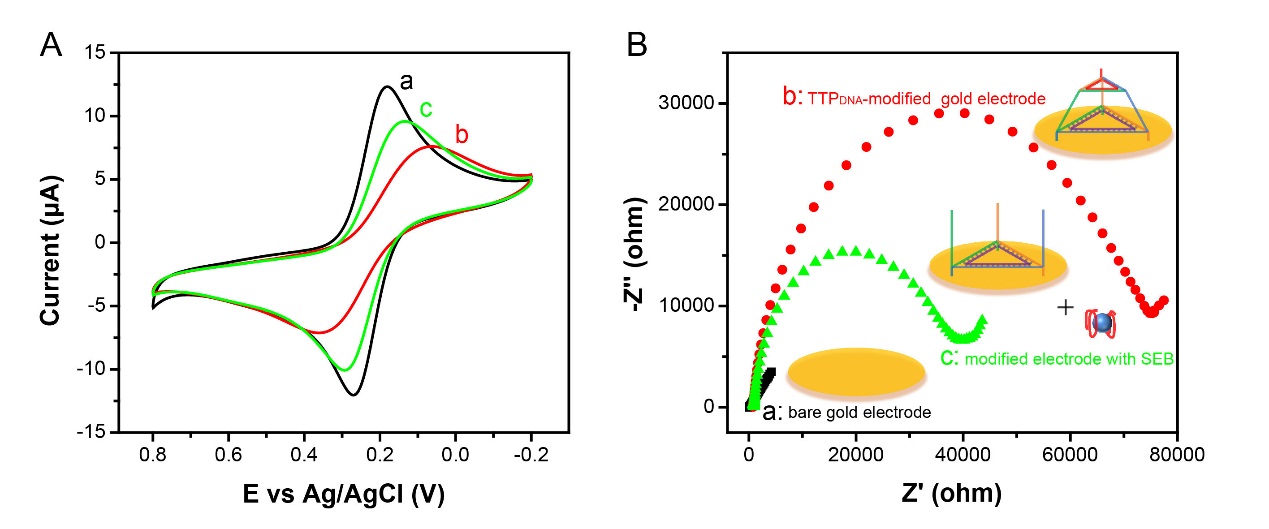
3.1 电化学表征 12
3.2 实验条件的优化 12
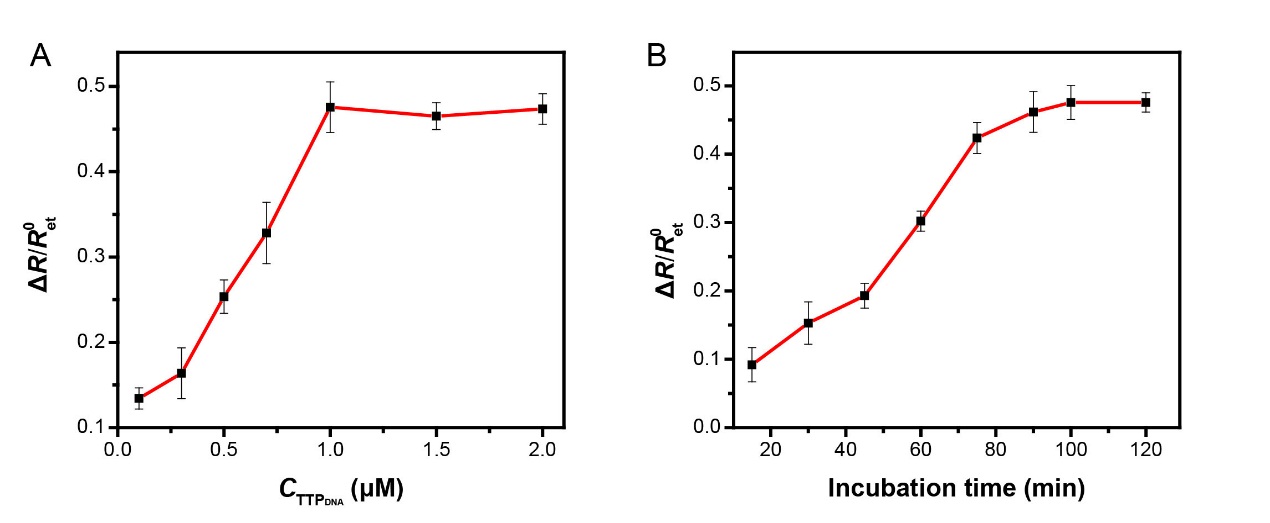
3.2.1 适配体浓度的确定 13
3.2.2适配体与SEB孵育时间的确定 13
3.3 标准曲线 14
3.4 选择性 14
3.5 实际样品检测 15
第四章 结论与展望 17
4.1 结论 17
4.2 展望 17
参考文献 19
致谢 21
第一章 文献综述
1.1引言
金黄色葡萄球菌是一种极度危险的食源性致病菌,在我们生活的周遭环境中大量存在着,因其产肠毒素菌株污染食品所引发的急性食物中毒事件不计其数,并且在由细菌所引起的食物中毒事件中,相当一部分都是由该细菌所引起的,从而受到广泛的关注。据相关报道可知,每年在美国发生的多起食品中毒事件中,单就是由金黄色葡萄球菌所引起的事件,就占据所有事件的近三成,加拿大为45%。所以,这不只是存在于我国的食品安全隐患,更是世界性的公共卫生难题[1]。
正因如此,构建一种灵敏度高,稳定性好,成本低廉的检测方法,是目前最为迫切的需要。现如今,电化学生物传感器用它独有的长处及未来存在无限可能的潜力,在添加剂与污染物的检测和成分的分析领域中独占鳌头。与此同时,核酸适体的出现恰巧给生物分析方法和传感器的研究与构建,带来了新的思考方式。
相关图片展示: