气流在泡沫金属内部传热性能研究毕业论文
2020-04-15 18:08:10
摘 要
多孔材料内部骨架的温度分布对研究多孔材料的对流换热具有重要的意义,耦合了多孔材料的太阳能热化学反应器是未来太阳能应用领域的一个重要研究方向。
为了研究气流在泡沫金属内部的传热特性,本文采用局部热非平衡模型(LTNE)建立了太阳能吸热器聚光吸热的物理模型,以SiC为多孔介质材料,结合FLUENT软件模拟计算得到太阳能吸热器内部温度场、速度场及压力场的分布,具体考察气流速度、辐射面温度、多孔材料的孔隙率等参数对太阳能吸热器多孔骨架温度分布的影响,从而为气流在泡沫金属内部的传热确定基础物性和操作参数,提供理论参考。本文主要研究内容和结果如下:
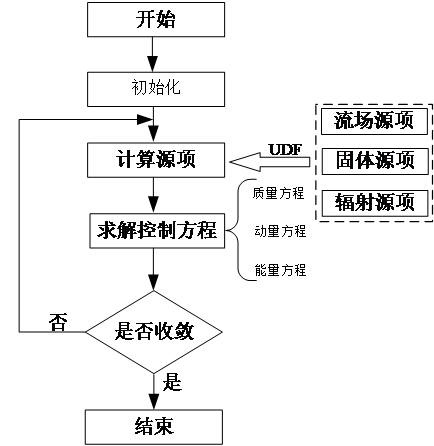
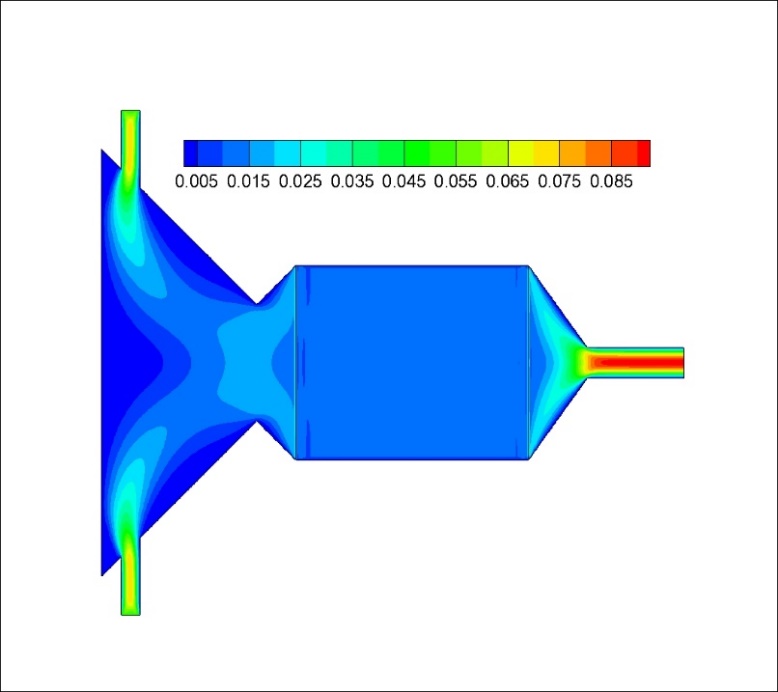
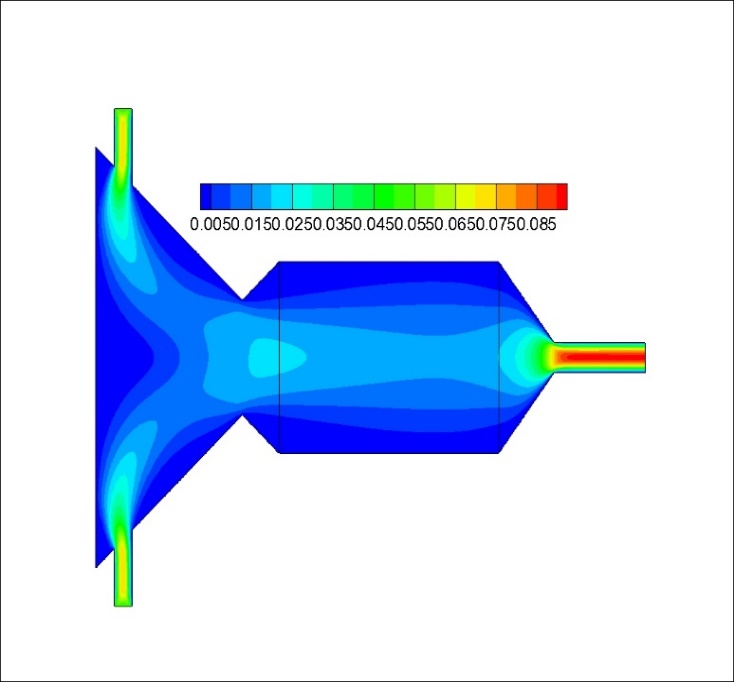
(1)建立了太阳能吸热器物理模型并设置选定模型参数,使用LTNE模型并结合UDF对传热过程进行模拟,并对比了加入和未加入多孔介质时吸热器内部的流场分布。模拟结果显示,加入多孔介质后,吸热腔内温度与气流速度分布更为均衡,多孔介质内部压力呈线性变化,表明加入多孔材料可以均衡气流在吸热器内的温度场与速度场,防止局部过热等情况发生。
(2)分析了气体流速、多孔介质孔隙率与辐射面温度等参数对传热过程的影响,结果显示:气体流速从0.03m/s增加到0.07m/s时,多孔介质整体温差从200K降至50K;孔隙率从0.5增加到0.9时,多孔介质整体温差从103K降至85K;辐射面温度从1200K上升至1600K时,吸热器内部总体温度上升,但多孔介质前后温差也随之上升。研究结果表明,在一定范围内,进气流速越大、多孔介质孔隙率越高,均衡效果越强;增大辐射面温度能提高气相反应温度,但会增加多孔介质前后温差,增大烧穿烧结的风险。可以得出,选取合适的泡沫金属材料与吸热器物性参数,能够有效保证热化学反应的稳定进行。
关键词: 太阳能热化学;泡沫金属;多孔介质;传热模型
ABSTRACT
The temperature distribution of the internal skeleton of porous materials is of great significance to the study of convection heat transfer of porous materials, and the solar thermal chemical reactor coupled with porous materials is an important research direction in the field of solar energy application in the future.
In order to study the heat transfer characteristics of airflow in the foam metal, a local thermal non-equilibrium model (LTNE) is used to establish a physical model of the concentrated heat absorption of the solar heat absorber, with SiC as the porous medium material, and the distribution of the temperature field, velocity field and pressure field inside the solar heat absorber is calculated by simulating the FLUENT software. In this study, the influence of airflow velocity, radiant surface temperature and porosity of porous materials on the temperature distribution of porous skeleton of solar heat absorber is investigated, so as to determine the basic physical property and operating parameters for the heat transfer of air flow in foam metal, and provide theoretical reference. The main research contents and results of this paper are as follows:
(1) The physical model of the solar heat absorber is established and the selected model parameters are set, the heat transfer process is simulated by using the LTNE model and the UDF, and the flow field distribution inside the heat absorber is compared when the porous medium is added and not added. The simulation results show that the distribution of temperature and airflow velocity in the heat-absorbing cavity is more balanced after adding porous media, and the internal pressure of porous media changes linearly, which indicates that adding porous materials can balance the temperature field and velocity field of airflow in the heat absorber, and prevent local overheating and so on.
(2) The effects of gas flow rate, porosity of porous medium and temperature of radiant surface on the heat transfer process are analyzed, and the results show that the overall temperature difference of porous media decreased from 200K to 50K when the gas velocity increased from 0.03m/s to 0.07m/s. , When the porosity increased from 0.5 to 0.9, the overall temperature difference of porous media decreased from 103K to 85K, and when the radiation surface temperature rose from 1200K to 1600K, the internal overall temperature of the heat absorber increased, but the temperature difference before and after the porous medium also increased. The results show that, in a certain range, the larger the air inlet flow rate, the higher the porosity of porous media, the stronger the equilibrium effect, the higher the temperature of the radiation surface can improve the temperature of the gas opposite, but will increase the difference between the porous media before and after, increase the risk of burning through sintering. It can be concluded that the selection of suitable foam metal materials and heat-absorbing objects can effectively ensure the stability of thermal chemical reactions.
Keywords: Solar thermochemical; Foam metal; Porous media; Heat transfer model
目录
摘要 I
ABSTRACT II
第一章 绪论 1
1.1 太阳能热化学 1
1.2 太阳能吸热器相关研究进展 1
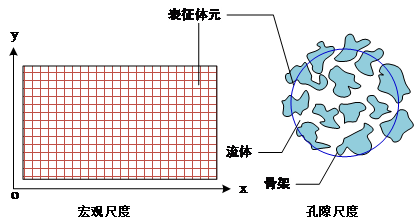
1.3 多孔材料 3
第二章 多孔介质传热模型 6
2.1 模型建立 6
2.1.1 物理模型 6
2.1.2 网格划分 7
2.2 控制方程 8
2.2.1 质量守恒方程 8
2.2.2 动量守恒方程 8
2.2.3 能量方程 9
2.3 边界条件与模型求解设置 11
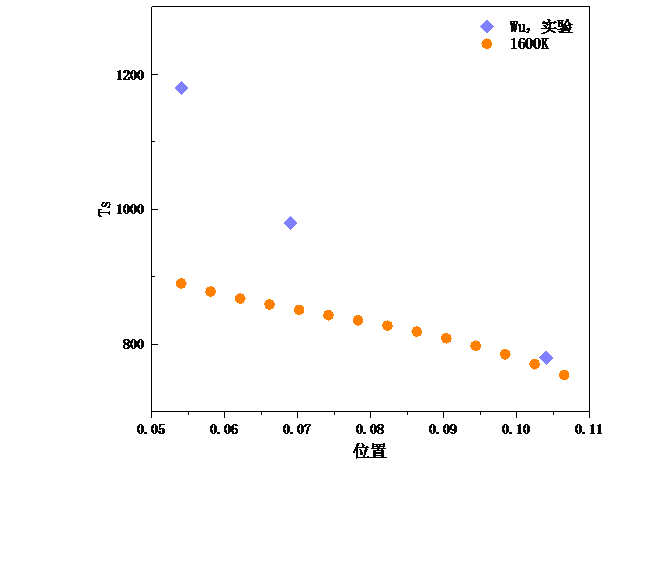
2.4 网格独立性检验与模型验证 12
第三章 结果与讨论 14
3.1 太阳能吸热器内部基础流场分析 14
3.2 流速对吸热器内部气固两相温度的影响 18
3.3 多孔材料孔隙率对太阳能吸热器内部温度场与压力场的影响 19
3.4 辐射面温度对太阳能吸热器内部温度场的影响 20
第四章 反应器成本估算 21
第五章 结论 22
参考文献 23
致谢 25
第一章 绪论
1.1 太阳能热化学
作为最具潜力的清洁能源之一,太阳能储量无尽,且采集过程低碳环保,因此,针对当今环境污染、温室效应以及能量资源不足等问题,发展太阳能利用成为一种有效的解决方案。其中,太阳能热化学是太阳能热利用的技术手段之一。通过典型的热化学反应过程,该技术将聚焦光线所得的热量固定成为碳氢燃料的中的化学能。与传统能源结合使用的太阳能热化学系统在中国西部等太阳能较为充沛的地方可以得到合适应用,通过热化学过程在当地进行动力循环,或将太阳能储存到二次燃料中并输送至外地继续完成循环,可有效完成太阳能的存储,同时解决了太阳能单独热发电系统诸多不利于并网的问题,如发电量不稳定、不持续等,从而提高能量利用率。上述太阳能利用方案解决了当今该领域两个技术困难:太阳能密度较低与发电量不持续。为了提高聚光温度并储蓄能量,通常的太阳能热电循环成本高昂,因此,海内外大量学者将目光投向太阳能热化学的相关研究,尤其瑞士、德国的学者设计了将太阳能结合天然气重整的新型系统,为太阳能热化学的发展提供了新的思路[1]。
近几年,相对于国外不断深入、完备的太阳能热化学燃料转化研究,我国仍较为落后。大体而言,国内大部分学者在金属载体、太阳能吸热反应器的研发与太阳能热化学动力学三个方面进行研究,对太阳能热化学燃料转化能源系统却少有问津,亟待探究。作为新型、卓越的太阳能利用手段,太阳能热化学燃料在与能源系统进行结合时极具优越性,尤其是控制与二氧化碳进行有机结合时,既可高效率转化太阳能,又可以非常低的能量消耗捕获并收集二氧化碳。因其研究内容针对不同功能与过程相结合的系统集成,围绕太阳能热化学利用进行设计的能源系统具备重要的理论价值,并具备极大的应用潜力,因此成为日后国内外太阳能热利用研究的主要目标之一。
1.2 太阳能吸热器相关研究进展
通过聚焦光线,太阳能吸热器捕获太阳辐射并传递给内部介质,最高可将其加热至800~1500℃,因此作为太阳能塔式发电站的主要组成部分[2]。太阳能吸热器可依照不同方法分为许多种,例如,以结构划分可分为容积式、腔式以外部受热式太阳能吸热器。其中外部受热式太阳能吸热器通过吸热管收集太阳辐射,并通过管壁将热能传递给工质,由于热管可通过安装于不同方位的反射镜收集太阳能,因此便于规划定日镜场以及大范围利用太阳能。然而,由于热管大量暴露在外,热能耗散严重,致使热效率偏低,并且,吸热器的安全与稳定会因外界环境转变导致的内部工作介质温度突变而受到威胁[3]。
以上是毕业论文大纲或资料介绍,该课题完整毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、程序设计、图纸设计等资料请添加微信获取,微信号:bysjorg。
相关图片展示: