基于总体最小二乘的建筑物多边形化简方法毕业论文
2020-04-15 21:29:15
摘 要
针对地图综合以及多尺度表达中的建筑物化简引起的数据质量问题,本文提出了一种基于总体最小二乘拟合模型化简建筑物多边形的方法,在该模型中系数矩阵也存在结构化分布的随机误差,因此构建了基于结构化总体最小二乘(STLSC)的解算模型,弥补了传统最小二乘方法在拟合过程中不考虑系数矩阵误差的劣势,同时为了保持建筑物多边形的形状特征、面积属性等,构建了直角、面积、端点约束,保留了建筑物化简之后的主要形状特征,并提高了面积精度。
本文所提出的方法应用在了实际的街区建筑物综合化简中,结果表明:(1)通过在子折线的关键点和中间点上引入基于总体最小二乘的拟合模型,相比较传统的最小二乘方法,能够有效地减少化简前后的几何位置差异,并且原始点和简化点之间的位置差近似为正态分布;(2)通过引入端点约束,有效避免了相邻拟合线段相交产生的几何变形;(3)在所提出的线性拟合模型中引入直角约束、面积约束,使得化简之后的多边形保留原始多边形的主要几何特征及面积属性。
关键词:总体最小二乘模型;线性拟合;直角约束;面积约束;端点约束
Building polygon simplification method based on total least squares
Abstract
Aiming at the data quality problem caused by map simplification in map synthesis and multi-scale expression, this paper proposes a method based on total least squares fitting model to simplify building polygons. In this model, the coefficient matrix also has a structured distribution. Random error, so a solution model based on structured total least squares (STLSC) is constructed, which makes up for the disadvantages of traditional least squares method without considering the coefficient matrix error in the fitting process, and in order to maintain the shape characteristics of the building polygon. , area attributes, etc., built a right angle, area, endpoint constraints, retaining the main shape features after the simplification of the building, and improve the area accuracy.
The method proposed in this paper is applied to the comprehensive buildings simplification of real blocks. The results show that: (1) By introducing a fitting model based on the overall least squares at the key points and intermediate points of the sub-line, the geometric position difference before and after simplification can be effectively reduced which is compared with the traditional least squares method, and the position difference between the original points and the simplified points is approximately a normal distribution; (2) By introducing the endpoint constraint, we can avoid the geometric distortion caused by the intersection of adjacent fitted line segments effectively; (3) Introducing the right angle constraint and the area constraint in the proposed linear fitting model, so that the polygon after simplification retains the main geometric features and area attributes of the original polygon.
Key words: total least squares model; linear fitting; right angle constraint; area constraint; endpoint constraint
目录
摘要 I
Abstract II
目录 III
第一章 绪论 1
1.1 研究背景与意义 1
1.1.1研究背景 1
1.1.2研究意义 1
1.2 研究现状 2
1.3 主要研究内容 3
第二章 基于总体最小二乘的建筑物多边形化简 4
2.1 建筑物多边形子折线的划分 4
2.2 基于STLSC方法简化多边形边界 7
2.2.1利用STLSC方法建立直线拟合的主要模型 8
2.2.2建立端点约束 8
2.2.3建立直角约束 9
2.2.4建立面积约束 10
2.2.5附有约束的总体最小二乘结构化平差(STLSC)拟合模型的解法 11
第三章 建筑物多边形化简实例分析及结果比较 15
3.1 MATLAB简介 15
3.2 基于STLSC、LS方法的比较 15
3.2.1建筑物多边形各点的位移量的比较 16
3.2.2多个建筑物点平均位移量比较分析 18
3.2.3化简前后建筑物多边形周长的比较 19
3.2.4化简前后建筑物多边形面积的比较 21
3.2.5化简前后建筑物多边形轮廓对比图 22
第四章 结论与展望 25
4.1结论 25
4.2展望 26
参考文献 27
致谢 29
附录 30
附录一:建筑物子折线分边算法 30
附录二:建筑物基于经典最小二乘(LS)化简算法 32
附录三:建筑物基于STLSC(添加端点约束)化简算法 34
附录四:建筑物基于STLSC(添加直角、端点约束)化简算法 38
附录五:建筑物基于STLSC(添加面积、直角、端点约束)化简算法 44
第一章 绪论
- 研究背景与意义
1.1.1研究背景
建筑物多边形作为地图中常见的纹理形状,其分布的普遍性、形状的复杂性、简化的重要性使得建筑物多边形的化简一直都是地图制图综合领域的学者所关注的热门问题之一。经过国内外学者的研究下,目前该领域的研究重点可以概括为,在不同比例尺的地图环境下,将建筑物多边形拆分为简单的几何图形即点、线、面,对这些简单的几何要素进行处理分析以及对处理所得到的数据进行评价 [1-2]。经过国内外学者的努力,在线条拟合平差意义上对建筑物多边形化简处理的方法,已经有了重大突破。
Su 等提出了一种通过数学形态学滤波对栅格数据进行处理来获得建筑物多边形的移位的方法[3]; Tong等提出一种利用具有约束条件的总体最小二乘结构调整进行多边形边界简化的区域保留方法, 首先建立基于子多段线上的关键点和中间点的直线段拟合模型,然后引入面积约束和端点约束, 以减少因线路简化而产生的几何扭曲[4];Sester等将数据泛化和抽象化的优化方法,提出了基于优化技术的三种泛化问题的解决方案[5]; Amiri-Simkooei等研究了观测方程正态矩阵的直接反演是否能精确逼近估计参数的协方差矩阵[6]; Guillaume等提出了几种约束条件, 以保持不同类型的形状和特征之间的关系, 同时将数据混合在一起[7];郭庆胜等提出了建筑物图形渐进式综合计算的算法 [8];刘鹏程等首先对简单的点进行分组,将点分组的结果在LS模型下进行处理,同时通过各点的关键程度不同对各点进行定权,然后对部分角度添加直角约束加以控制,进一步完成建筑物多边形的化简[9]。
以上是毕业论文大纲或资料介绍,该课题完整毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、程序设计、图纸设计等资料请添加微信获取,微信号:bysjorg。
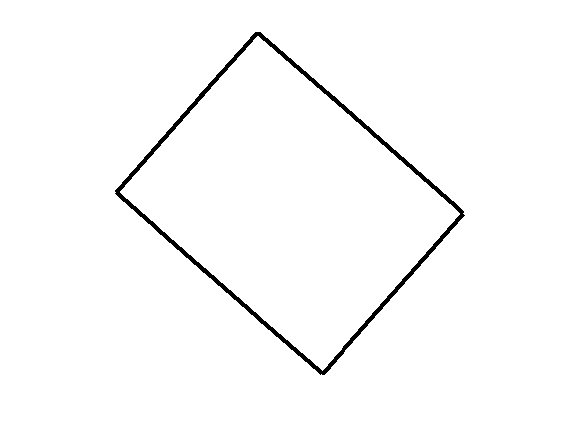
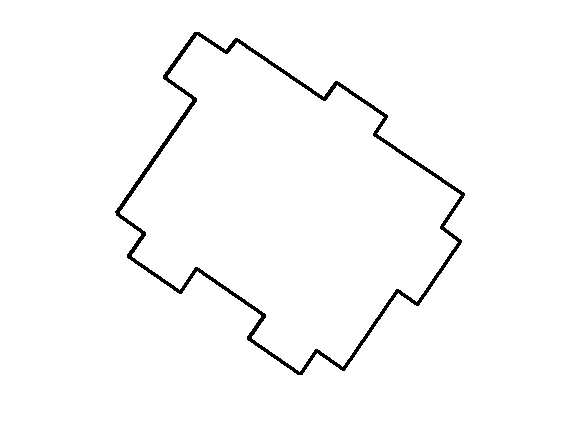
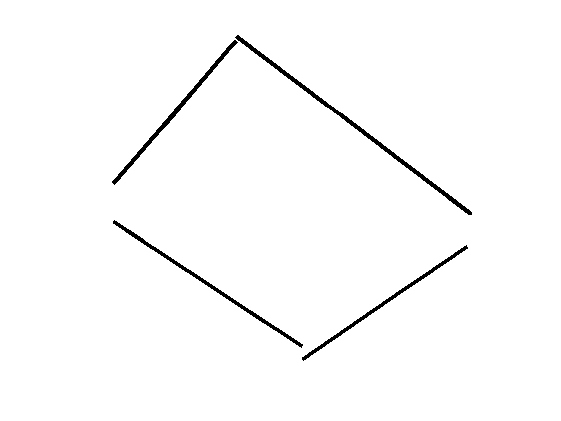
相关图片展示: