一种γ-聚谷氨酸-透明质酸水凝胶皮肤的制备毕业论文
2020-06-12 20:20:46
摘 要
皮肤组织工程已成为目前解决皮肤缺损和功能重建问题的先进技术,其中仿生支架材料的选择及构建是皮肤组织工程的核心要素。水凝胶作为一种高含水量的软湿材料,已成为皮肤组织工程支架材料研究的热点。该研究选取生物相容性较好且生物可降解的生物大分子γ-聚谷氨酸(γ-PGA)和透明质酸(HA)为主体材料,分别模拟皮肤组织中蛋白质和多糖为主的细胞外基质组分,通过分子修饰GMA,使用紫外光交联手段构建原位成型水凝胶。该水凝胶的成胶时间、溶胀性能可控、力学性能优良,亲水性较好,具有适合皮肤细胞生长、增值的三维网络多孔结构,有利于细胞生长、增值和迁移。通过将采用上述方法和材料制得之水凝胶应用于3D打印,又可赋予水凝胶皮肤复杂的外形和内部结构,进行批量化生产和个性化生产,为解决皮肤大面积损伤缺失和机械损伤提供了一个很好的思路。
关键词:皮肤组织工程 γ-聚谷氨酸 透明质酸 水凝胶 光引发
The preparation of a γ-polyglutamic acid-hyaluronic acid hydrogel skin
Abstract
Skin tissue engineering has become the current advanced technology to solve the problem of skin defect and function reconstruction, including selection of biomimetic scaffold materials and building elements is the core of the skin tissue engineering. Hydrogel as a soft wet materials of high water content, has become the hot topics in the study of skin tissue engineering scaffold material. The study selection has good biological compatibility and biodegradable macromolecular γ- poly glutamic acid (γ- PGA) and hyaluronic acid (HA) as the main materials, respectively mimicking skin extracellular matrix (ECM) components of the structure of collagen and hyaluronic acid, through the modification of methyl glycidyl ester of acrylic acid, UV curing method is used to build water in situ gel. The gelation time and swelling properties of the hydrogel can be controlled, the mechanical properties are excellent, the hydrophilicity is better, and the porous structure of the three-dimensional network satisfying the growth of the skin cells is provided, which provides a highly bionic three-dimensional microenvironment for cell growth, increment and migration. By applying the hydrogels prepared using the methods and materials described above to 3D printing, the hydrogel skin can be given a complex shape and internal structure, mass production and personalized production. In order to solve the problem of large area damage and mechanical damage Damage provides a good idea.
Key words: Skin tissue engineering; γ-polyglutamic acid; Hyaluronic acid; Hydrogel; Light initiation
目录
摘要 I
Abstract II
第一章 绪论 1
1.1前言 1
1.2水凝胶简介 1
1.2.1水凝胶的性质和相关优势 1
1.2.2组织工程水凝胶皮肤的发展现状 2
1.2.3组织工程水凝胶皮肤在创面修复中的临床应用现状 4
1.3γ-聚谷氨酸和透明质酸 5
1.3.1 γ-聚谷氨酸的性质和合成方法 5
1.3.2 γ-聚谷氨酸的应用 5
1.3.3透明质酸的合成和应用 6
1.3.4透明质酸的结构和性质 6
1.4研究意义和目的 7
第二章 实验部分 8
2.1实验试剂及设备 8
2.1.1实验试剂 8
2.1.2仪器与设备 8
2.2水凝胶的合成 8
2.2.1γ-聚谷氨酸改性 9
2.2.2透明质酸的改性 9
2.2.3水凝胶的制备 9
2.3水凝胶的表征 9
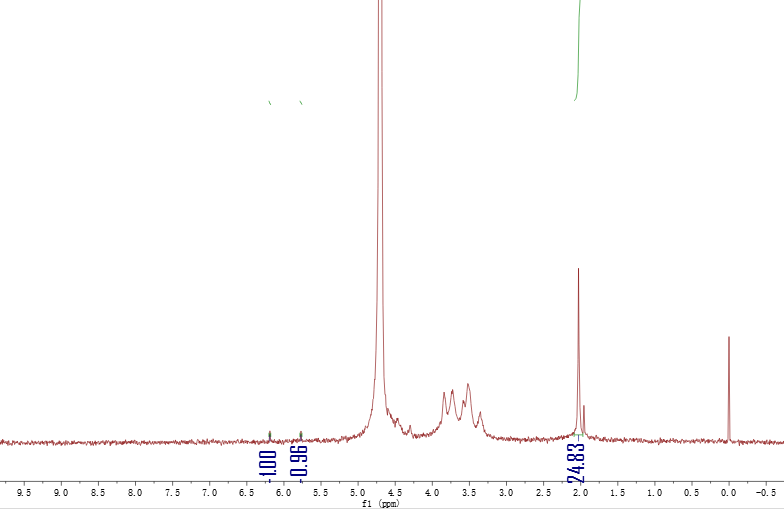
2.3.1核磁共振(HNMR) 9
2.3.2水凝胶成胶时间表征 10
2.3.3水凝胶的溶胀性能测试 10
2.3.4水凝胶的降解性能测试 10
2.3.5水凝胶的形貌表征 11
2.3.6水凝胶的亲水性 11
第三章 结果与讨论 12
3.1结果 12
3.1.1 HA-GMA和γ-PGA-GMA的表征和接枝率计算 12
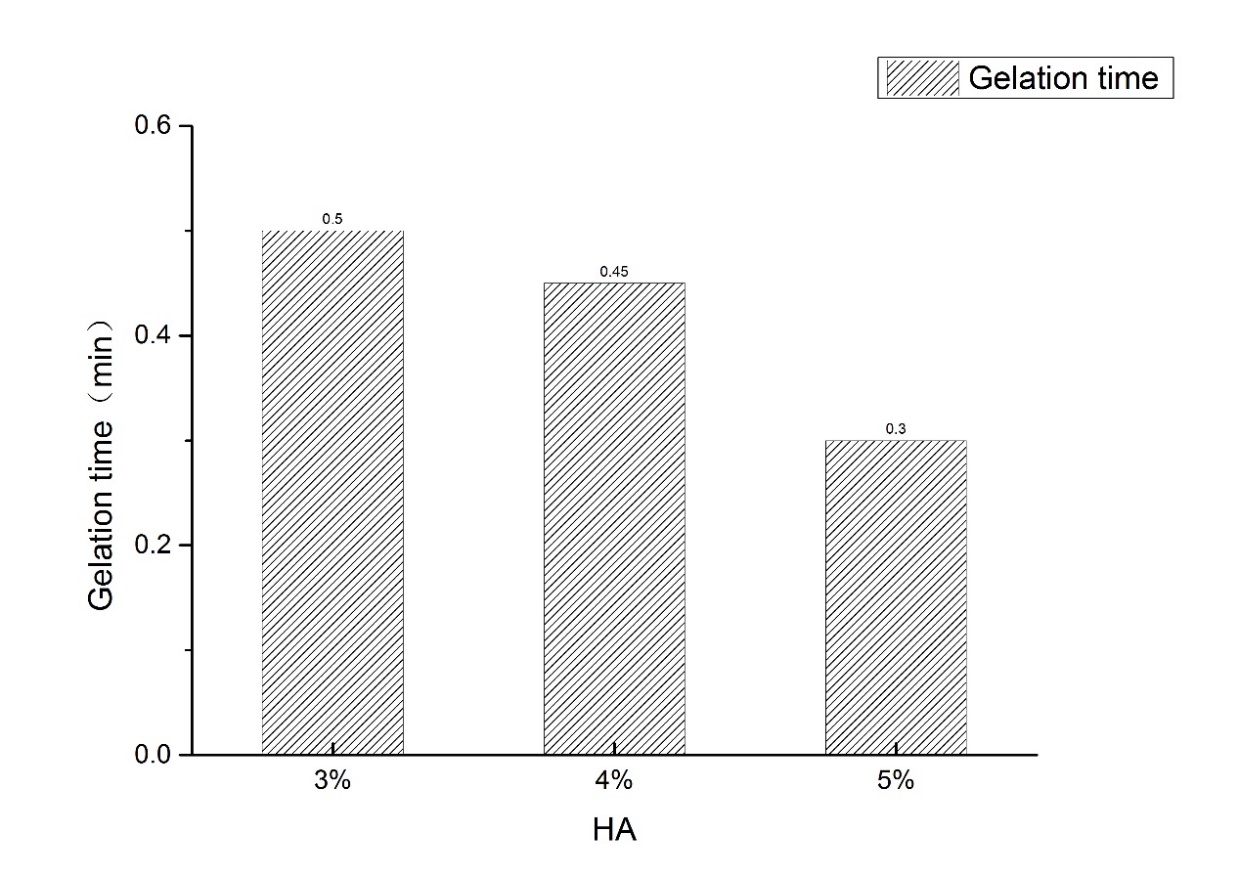
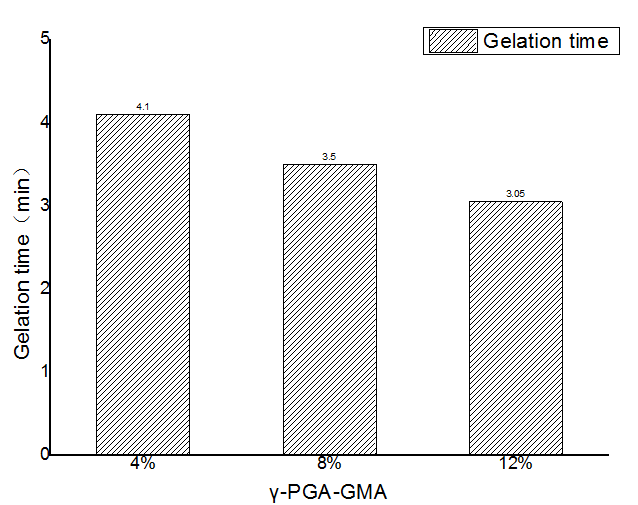
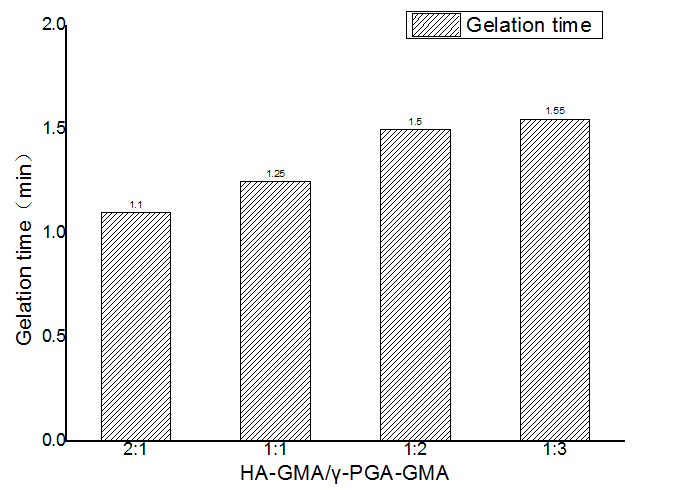
3.1.2水凝胶成胶时间 14
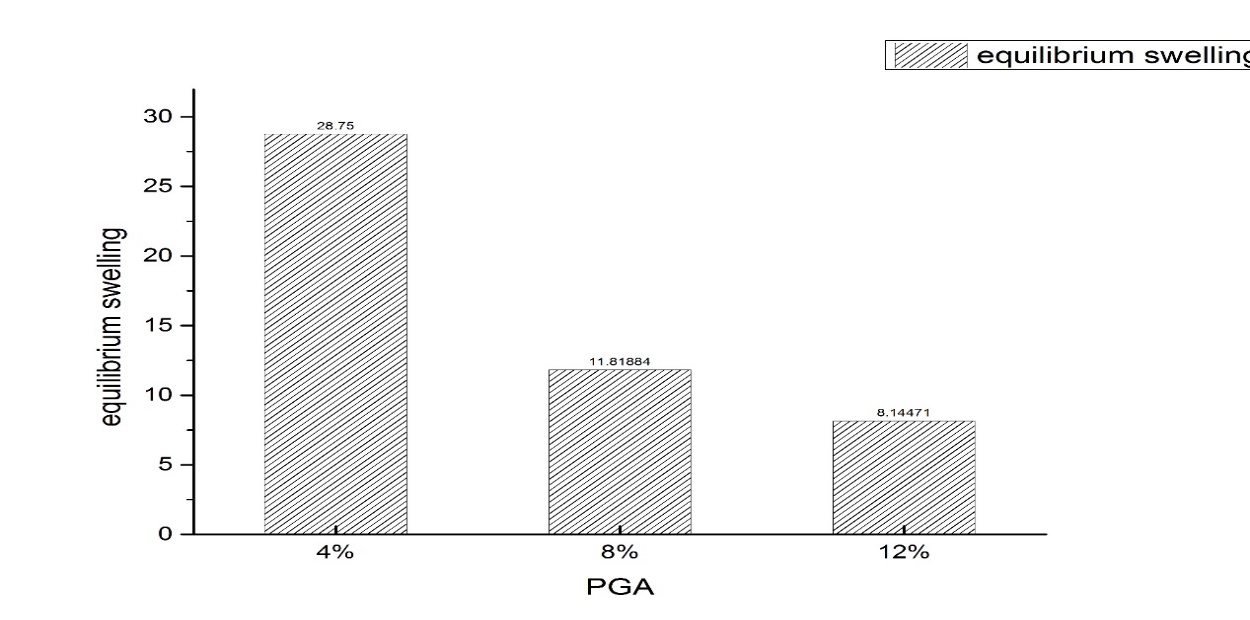
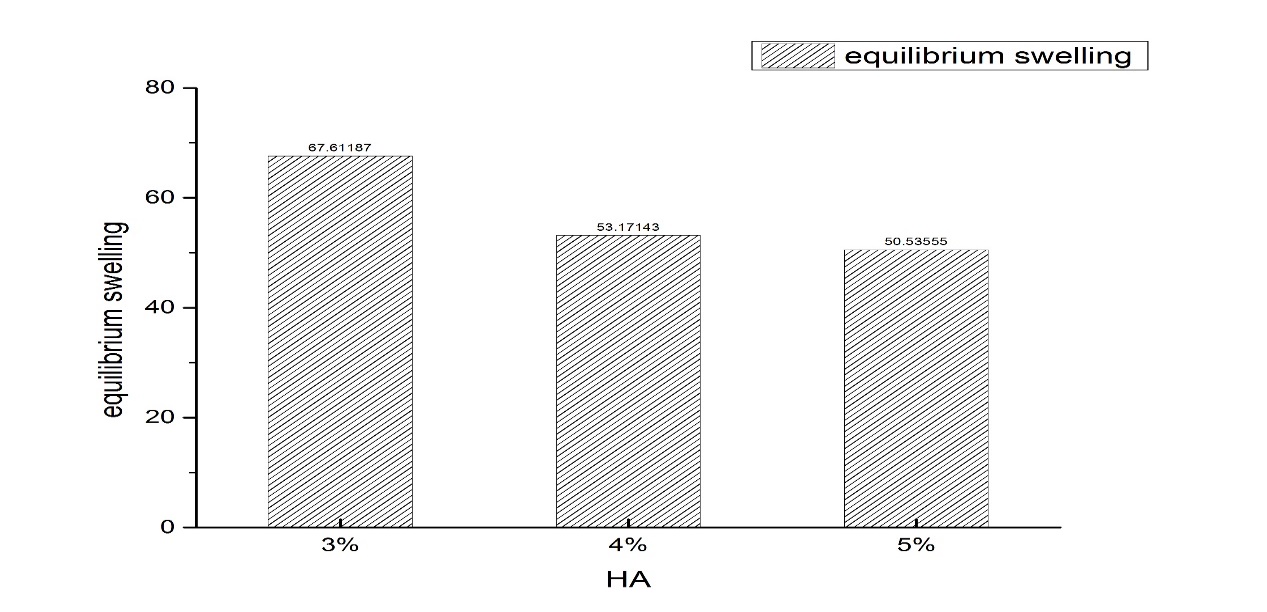
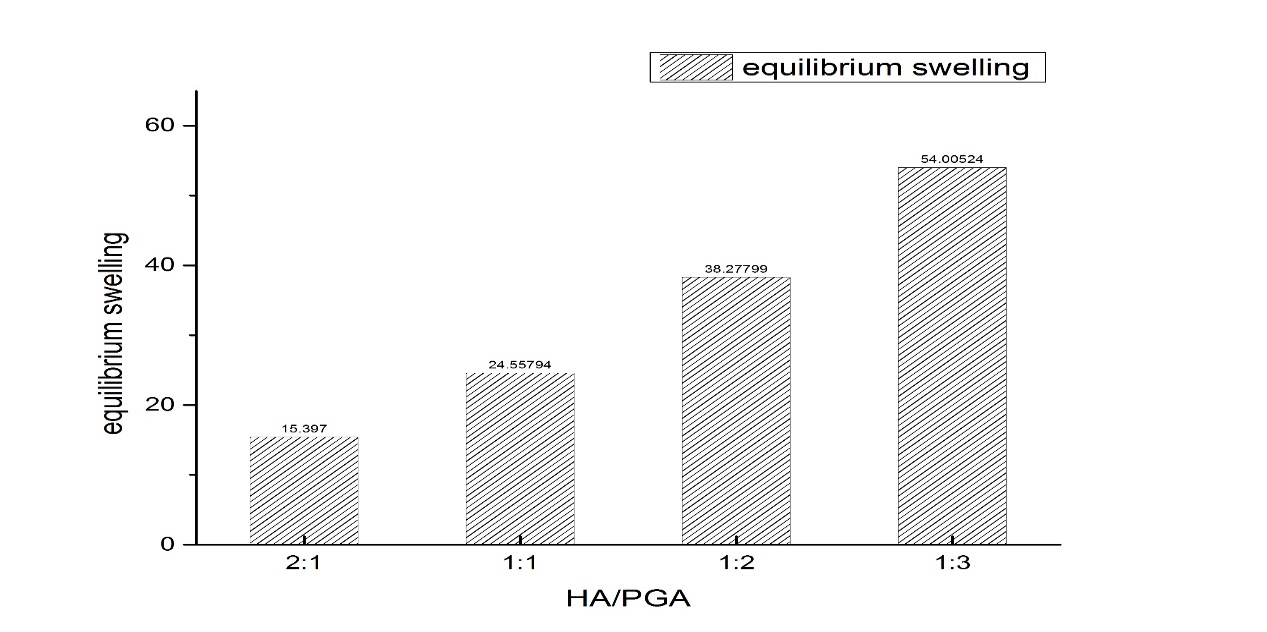
3.1.3水凝胶的平衡溶胀系数 16
3.1.4水凝胶的降解表征 18
3.1.5水凝胶的形貌表征 18
3.1.6水凝胶的亲水性 20
3.2讨论 21
3.2.1对实验原理的讨论 21
3.2.2对实验结果的讨论 23
第四章 结论与展望 24
参考文献 25
致 谢 28
第一章 绪论
1.1 前言
一直以来,如何治疗大面积的皮肤损伤一直困扰着相关的医护人员。皮肤感染、没有可供移植的皮肤及换药时给患者造成的二次损伤是皮肤损伤领域经常出现的问题。目前在治疗过程中,通常都是通过自体皮瓣或者皮片移植进行修复,但自体皮瓣或皮片数量有限,所以人们现在越来越青睐于人造皮肤。而随着组织工程研究的深入,人造皮肤的发展也备受瞩目。目前组织工程相关技术的关键在于制备皮肤支架,而由于3D打印能够对产品内外部结构形态进行精确控制,所以3D打印有望被用来制备与自然皮肤有相似结构和组分的人造皮肤,帮助创伤愈合。虽然3D打印在组织工程中具有独特的优势,但目前仍存在一些问题,比如相关皮肤支架透气性较差、力学强度较弱、无法进行自我修复。所以研究可用于3D打印生物材料的相关性质,对治疗皮肤损伤、器官修复意义重大。而水凝胶特别是光引发型使用聚氨基酸和多糖类材料制备的水凝胶为组织工程人造皮肤打开了一个新方向。
1.2 水凝胶简介
1.2.1 水凝胶的性质和相关优势
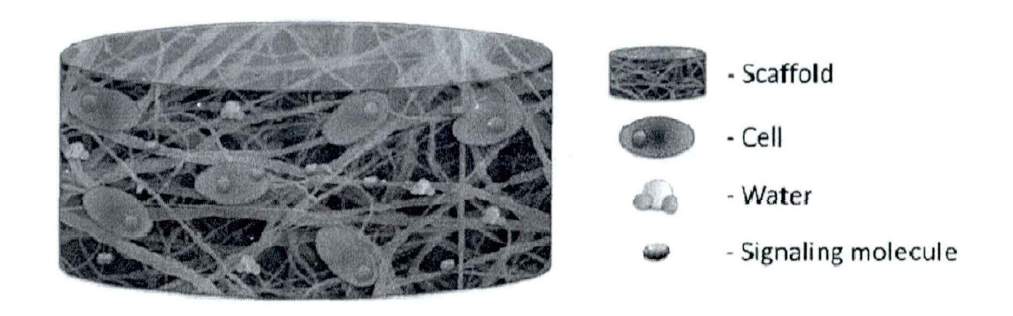
水凝胶是一种三维网状结构的化合物,可以通过接枝共聚、水溶性的高分子交联或者通过单体进行交联形成,由共价键、氢键等分子间作用力而聚合在一起。由于水凝胶本身具有亲水性基团,所以能够大量吸水而发生溶胀,水的含量能够达到水凝胶干重的10%~20%,甚至数千倍。水凝胶的网络结构可见图1-1[1]。
相关图片展示: