h-BNNs类流体/环氧树脂的制备与性能研究毕业论文
2021-11-27 22:29:49
论文总字数:30465字
摘 要
六方氮化硼(h-BN)具有良好的导热性能和绝缘性能,因此被广泛应用于航空航天、电子电工等高端领域。但其作为填料与高分子基体复合时,极易在高分子基体中聚集,影响复合材料的机械性能和导热性能。因此,近年来关于氮化硼改性的研究逐渐增多,目的就是改善氮化硼在高分子基体中的分散性和界面相容性,充分发挥氮化硼的导热性能,制备出高效的导热材料。其中以有机离子长链接枝纳米氮化硼制备氮化硼纳米类流体的改性方法是最佳的方案。氮化硼纳米类流体中的有机离子长链可以与高分子基体相容、帮助纳米氮化硼微粒分散,从而提高复合材料的导热性能、热稳定性和机械性能。本文通过制备氮化硼纳米类流体/环氧树脂复合材料探讨类流体对复合材料导热性、电绝缘性、热稳定性的影响。
本文制备了h-BNNs类流体,分析了h-BNNs类流体的结构形貌、表征了类流体的流变性质。还探讨了不同含量h-BNNs类流体的复合材料的导热性、电绝缘性、热稳定性。主要的研究结果如下:
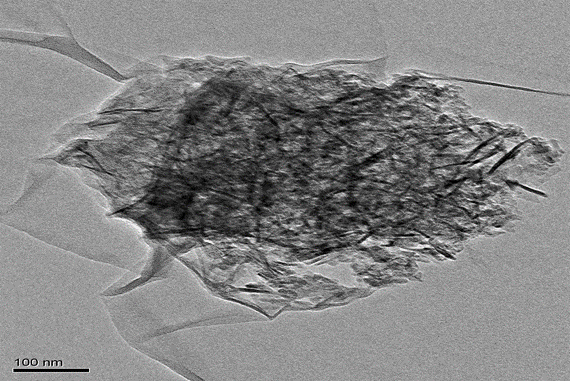
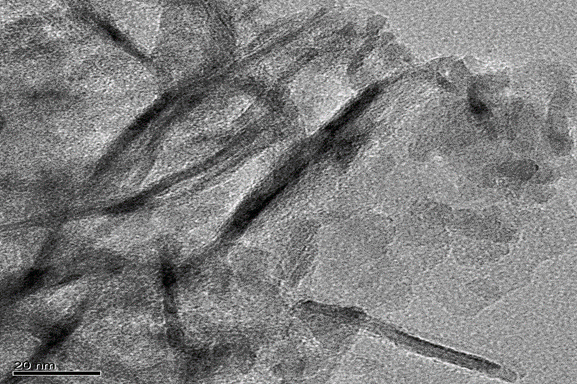
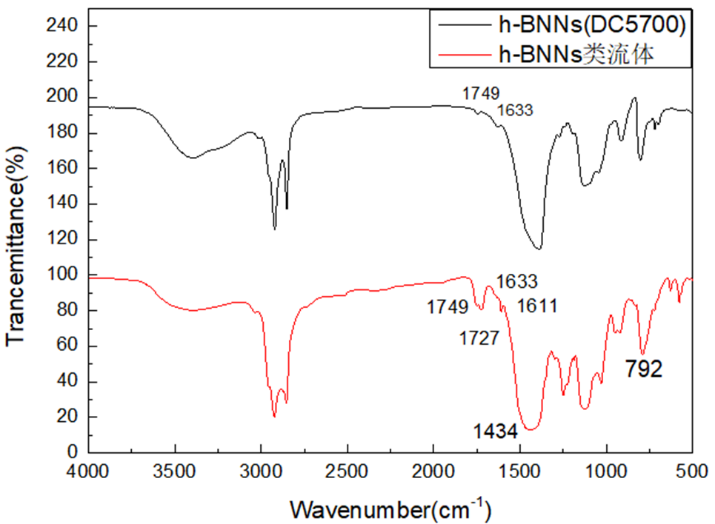
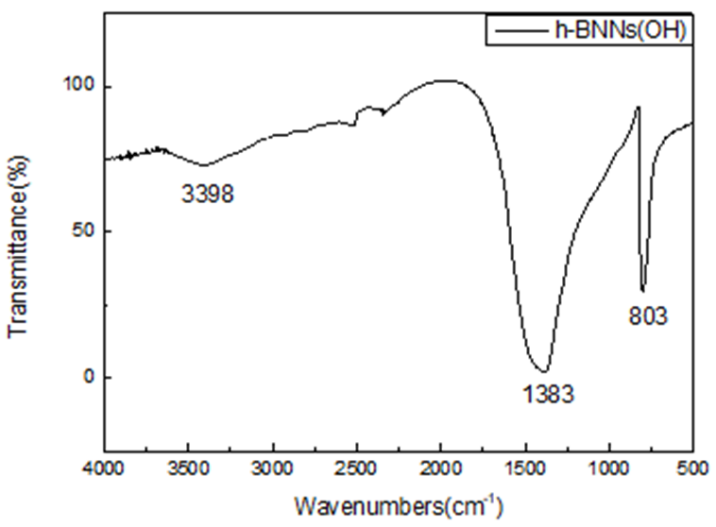
(1)通过h-BNNs类流体TEM图分析得出有机长链基体确实分布在h-BNNs表面,且呈现出包裹的姿态。高放大倍数下,没有发现h-BNNs有明显聚集现象,推测长链基体限制了h-BNNs团聚。红外光谱图分析得知h-BNNs表面成功接枝DC5700,且出现有机长链中苯环结构特征吸收峰,可以推测有机离子长链(NPES)成功与DC5700发生离子交换反应,成功在h-BNNs表面。
(2)h-BNNs类流体常温下具有粘性,其粘度随剪切速率的增大而减小,是典型的“剪切变稀”特征。其储能模量和损耗模量都随温度的增加而变小,在30-50℃的温度区间里下降速率最快,同时损耗模量始终大于储能模量,证明h-BNNs类流体具有流变性质。
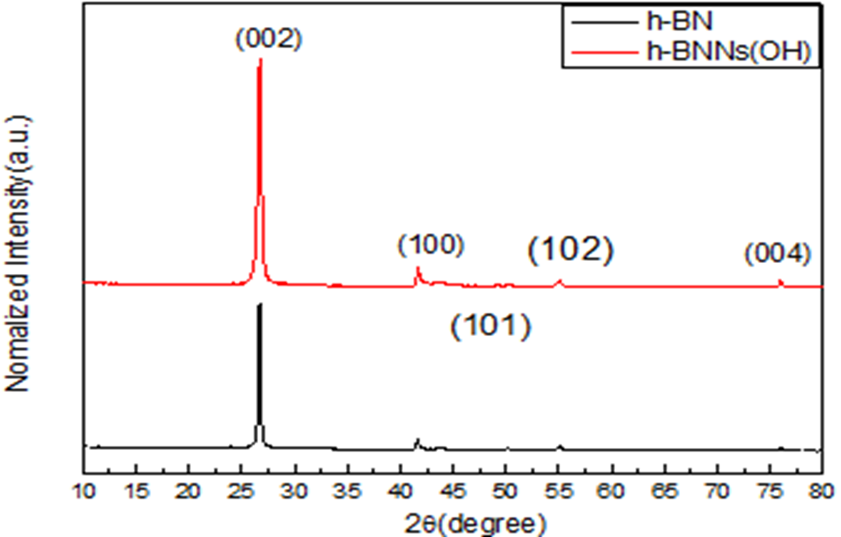
(3)对h-BNNs的改性过程没有影响氮化硼的晶型结构。因此复合材料的导热性随着h-BNNs类流体的比例增加而增大,但并不呈现线性关系。
(4)h-BNNs类流体中的h-BNNs微粒本身有一定的耐热性,而有机长链也兼具良好的热稳定性,故在两者的协同作用下,复合材料的热分解温度有小幅提高。这表明h-BNNs类流体对复合材料的热稳定性有增强作用,且随h-BNNs类流体含量的增加而增加。
(5)h-BNNs类流体对复合材料的电绝缘性有一定程度的影响。随着含量增加,复合材料的体积电阻率有小幅下降趋势;表面电阻率变化不大,总体上保持稳定。虽然复合材料的电绝缘性有所下降,但已基本满足行业使用要求。
关键词:六方氮化硼;h-BNNs类流体;复合材料;导热性;热稳定性
Abstract
Hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) has good thermal conductivity and insulation performance, so it is widely used in aerospace, electrical and electronic fields. However, when it is used as a filler to compound with the polymer matrix, it is easy to accumulate in the polymer matrix, which affects the mechanical properties and thermal conductivity of the composite. Therefore, in recent years, the research on the modification of boron nitride has gradually increased, aiming at improving the dispersibility and interfacial compatibility of boron nitride in the polymer matrix, giving full play to the thermal conductivity of boron nitride, and preparing efficient thermal conductive materials. The best method is to prepare boron nitride nanoscale ionic liquids by organic ion long linked branch boron nitride. The long chains of organic ions in boron nitride nanoscale ionic liquids can be compatible with the polymer matrix and help disperse the boron nitride nanoparticles, thus improving the thermal conductivity, thermal stability and mechanical properties of the composites. The influence of boron nitride nanoscale ionic liquids on the thermal conductivity, electrical insulation and thermal stability of the composite was studied by preparing the nanoscale ionic liquids/epoxy resin composites.
In this paper, h-BNNs ionic liquids are prepared, the structural morphology of h-BNNs ionic liquid is analyzed and the rheological properties of ionic liquids are characterized. The thermal conductivity, electrical insulation and thermal stability of composite materials with different content h-BNNs ionic liquid are also discussed. The main findings are as follows:
(1) Through the analysis of h-BNNs fluid TEM diagram, it is concluded that the organic long-chain substrate is indeed distributed on the surface of h-BNNs, and presents a wrap-around posture. At high magnification, no significant aggregation of h-BNNs was found, and it was assumed that the long-chain substrate limited h-BNNs to reunite. Infrared spectrogram analysis shows that the surface of h-BNNs successfully grafted DC5700, and the appearance of organic long chain of benzene ring structure feature absorption peak,。It can be speculated that the organic ion long chain (NPES) successfully interacted with DC5700 ion exchange, successfully on the surface of h-BNNs.
(2) The h-BNNs ionic liquids are viscous at room temperature, and their viscosity decreases with the increase of shear rate, which is a typical characteristic of "shear thinning". The energy storage modulus and the loss modulus both decrease with the increase of temperature. In the temperature range of 30-50℃, the decline rate is the fastest. Meanwhile, the loss modulus is always greater than the energy storage modulus, which proves that h-BNNs ionic liquids have rheological properties.
(3) The modification process of h-BNNs did not affect the crystal structure of boron nitride. Therefore, the thermal conductivity of composite materials increases with the proportion of h-BNNs ionic liquid, but does not show a linear relationship.
(4) The h-BNNs particles in h-BNNs ionic liquids have a certain heat resistance, and the long chain also has a good thermal stability, so under the synergistic effect of the two, the thermal decomposition temperature of the composite material has a small increase. This shows that h-BNNs ionic liquids have an enhancement effect on the thermal stability of the composite material, and increase with the increase of h-BNNs ionic liquids.
(5) The h-BNNs fluid has a certain degree of influence on the electrical insulation of composite materials. With the increase of the content, the volume resistivity of the composite decreased slightly. The surface resistivity changes little and remains stable on the whole. Although the electrical insulation of the composite material has been reduced, it has basically met the requirements of the industry.
Key words: hexagonal boron nitride; h-BNNs ionic liquid; composites; thermal conductivity; thermal stability
目录
第1章 绪论 1
1.1 研究背景 1
1.2 导热高分子材料分类 2
1.2.1 填充型导热高分子材料 2
1.2.2 影响填充型导热高分子材料导热性能的因素 3
1.3 导热机理 3
1.4 六方氮化硼/高分子基体导热复合材料研究现状 4
1.4.1 h-BN简介 5
1.4.2 六方氮化硼/聚合物导热复合材料 5
1.5 纳米类流体概述 8
1.6 论文研究目的、意义及内容 9
1.6.1 研究目的与意义 9
1.6.2 研究内容 9
第2章 实验部分 10
2.1 实验原料 10
2.2 实验仪器 10
2.3 实验过程 11
2.3.1 h-BNNs类流体的制备 11
2.3.2 h-BNNs类流体/环氧树脂复合材料的制备 11
2.4 测试与表征 11
2.4.1 h-BNNs类流体对比测试与表征 11
2.4.2 h-BNNs类流体/环氧树脂复合材料性能测试 12
2.5 实验设计材料的应用前景以及优势 12
2.6 设计材料性能预测 13
第3章 结果与讨论 15
3.1 h-BNNs类流体的测试与表征 15
3.1.1 h-BNNs类流体微观形貌 15
3.1.2 h-BNNs类流体红外光谱分析 15
3.1.3 XRD分析 16
3.1.4 h-BNNs类流体流变形分析 17
3.1.5 类流体DSC对比分析 18
3.2 h-BNNs类流体环氧树脂复合材料性能测试 19
3.2.1 复合材料的微观形貌 20
3.2.2 复合材料的导热性 21
3.2.3 复合材料的热稳定性 23
3.2.4 复合材料的电绝缘性 23
3.3 设计实验的可行性分析 24
3.4 课题的实验设计基础 24
第4章 结论与展望 26
4.1 结论 26
4.2 展望 26
参考文献 28
致 谢 30
第1章 绪论
1.1 研究背景
在科技时代,各行各业对导热复合材料的需求量变得越来越大,从高端领域例如航空航天、化工工程等方面到电子科技领域例如电子工程、微电子封装等都有应用。尤其是近年来通信技术的飞速发展,我们的生活越来越依赖电子设备。电子科技的发展直接推动了电子器件大规模生产,同时也推动了电子产业革命。电子设备在高功率运行期间难免会产生多余的热量,为了延长电子器件的使用寿命,必须使用高热导率材料将热量高效快速地排出至外界环境。因此,目前如何制备出快速高效导热性能的电子器件材料是一个非常严峻的问题。
众所周知,传统的导热材料例如金属(银、铜、铁等)、金属氧化物(氧化铝、氧化镁等)、金属氮化物(氮化铝)以及陶瓷等非金属材料在当今社会的应用市场中受限。金属以及金属氧化物等导热材料的优势和劣势都十分明显,它们具有出色的导热性能;但是其化学稳定性和电绝缘性能较差始终是人们头疼的问题,这使得它们的应用领域十分受限,而且运输及保存过程也是十分讲究;陶瓷等非金属材料也表现出不俗的导热性能,但是也存在着笨重、易碎、运输成本高的劣势。因此,近年来人们逐渐把视线聚集到高分子材料中来。人们看重其优异的加工性能、低成本、轻巧的特点,最主要是其绝佳的电绝缘性,已经成为电子元件散热材料的不二之选。其中又以环氧树脂为主,因为其重量轻、成本低、介电性能优异以及良好的耐化学腐蚀等优势,目前被广泛应用于电子封装领域[1]。但高分子材料也存在导热性能不足的缺陷。由于聚合物中的链段结构的无定向分布,链段、链节之间相互纠缠,导致聚合物通常同时具有结晶区域和非结晶区域,这非常不利于聚合物将多余的热量排出到外界环境中,从而限制了其在其他领域的应用。为了扩大高分子材料的应用领域,突破其自身局限,近年来人们一直致力于开发具有高导热性、高绝缘性的高分子基体复合材料。
目前,导热复合材料的制备工艺是以高分子材料为基体,以高导热性填料作为导热介质,将两者均匀混合获得导热性良好的复合材料。除去上文中提到的金属(银、铝等)、陶瓷(氮化铝、碳化硅和氮化硼等)以及石墨烯等材料,在高导热填料的选择上,人们逐渐被二维纳米材料六方氮化硼(h-BN)所吸引。其出色的电绝缘性和高导热性一直为人们所追捧,当六方氮化硼(h-BN)作为填料与聚合物基体复合时,复合材料不仅获得氮化硼的导热性能,还可以保留自身固有的性质。因此,六方氮化硼复合材料被广泛应用于微电子封装等领域,利用其高导热高散热的特性,将电子元件中多余的热量导出,以此来延长电子元件的使用寿命和提高其工作效率。
请支付后下载全文,论文总字数:30465字
相关图片展示:
您可能感兴趣的文章
- 在200至300℃的温度下纤维素的水热降解外文翻译资料
- 对O-酰基肟光敏交联剂和丙烯酸丁酯组成的压敏胶一系列光聚合与光降解过程的直接流变学测量外文翻译资料
- 热和紫外线诱导的环氧/环氧丙烯酸酯胶粘剂的制备及其性能外文翻译资料
- 基于光敏可逆固液转换的可调光聚合物胶粘剂外文翻译资料
- 氢氧化物-催化键中近红外吸收的时间演化外文翻译资料
- 利用糖辅助机械力化学剥离技术一步法制备功能化氮化硼纳米片外文翻译资料
- 用于热管理的具有优异力学性能和超高热导率的兼容多功能氮化硼纳米片/聚合物薄膜外文翻译资料
- 油水分离材料用凹土棒复合微球的制备与表征油水分离材料用凹土棒复合微球的制备与表征外文翻译资料
- 单轴拉伸聚乙烯/氮化硼纳米复合薄膜金属状热导率外文翻译资料
- 高导热硅弹性体掺杂石墨烯纳米片和低共熔液体金属合金外文翻译资料




