CNG燃料发动机瞬态性能仿真分析毕业论文
2020-02-18 10:44:48
摘 要
随着全球工业化的发展,汽车保有量提高,石油危机日益严峻。天然气作为一种清洁、高效、储量丰富的替代能源,获得研究者的广泛研究。使用天然气代替传统石油作为汽车能源受到很大欢迎。但是天然气发动机与传统燃料发动机相比有很多不同,需要进行进一步标定研究,天然气组分、稀释等问题也都是CNG发动机进一步应用中需要克服的难点。其中,对天然气发动机的瞬态性能研究是CNG发动机研究的一大重点。
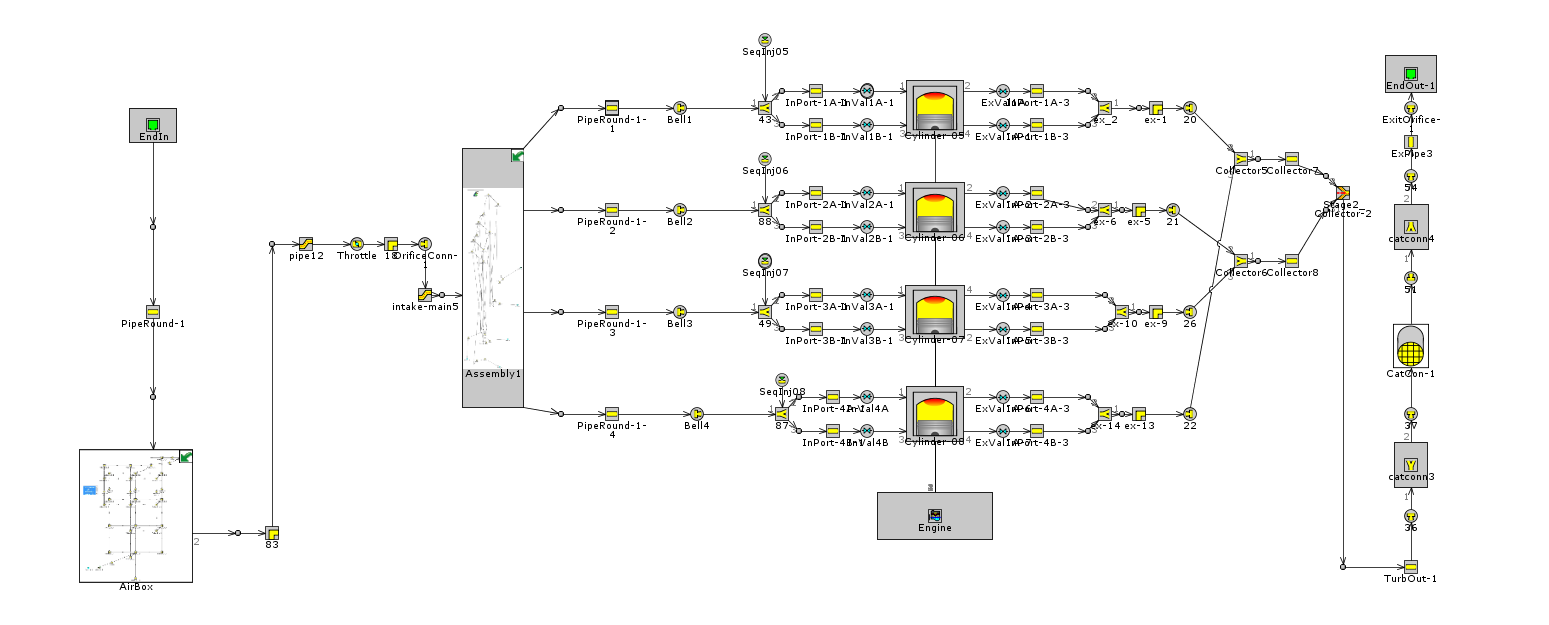
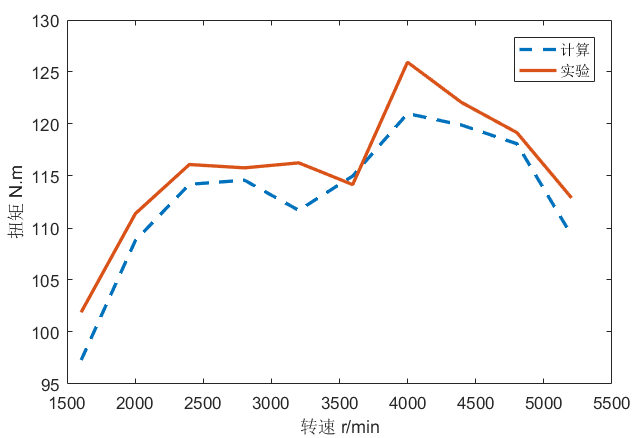
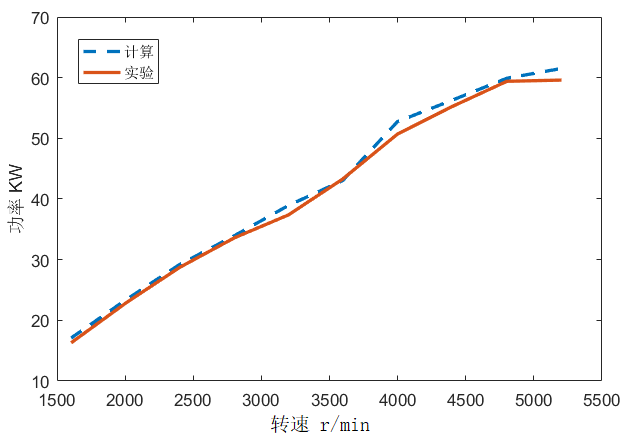
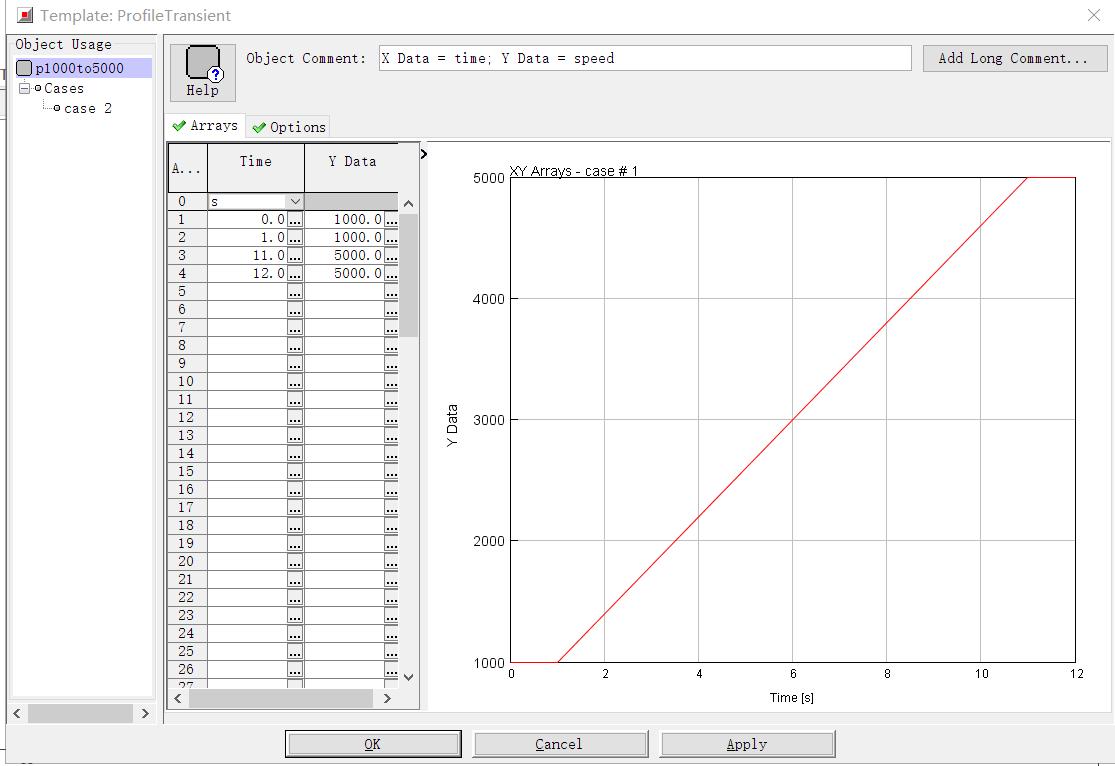
本文综合国内外学者研究成果,选择GT-POWER软件进行天然气发动机瞬态仿真模拟试验。使用GT-POWER建立了CNG发动机仿真模型,进行瞬态工况试验。通过与发动机台架试验进行对比标定,扭矩和功率误差分别为5%和6%,证明模型可用。之后,采用CO2组分为0至16%的五组天然气和Gr、G252种国六基准燃料,进行天然气发动机加减速瞬态工况仿真试验,以研究天然气燃料组分和急加减速时间的改变对CNG发动机经济性和排放性的影响。
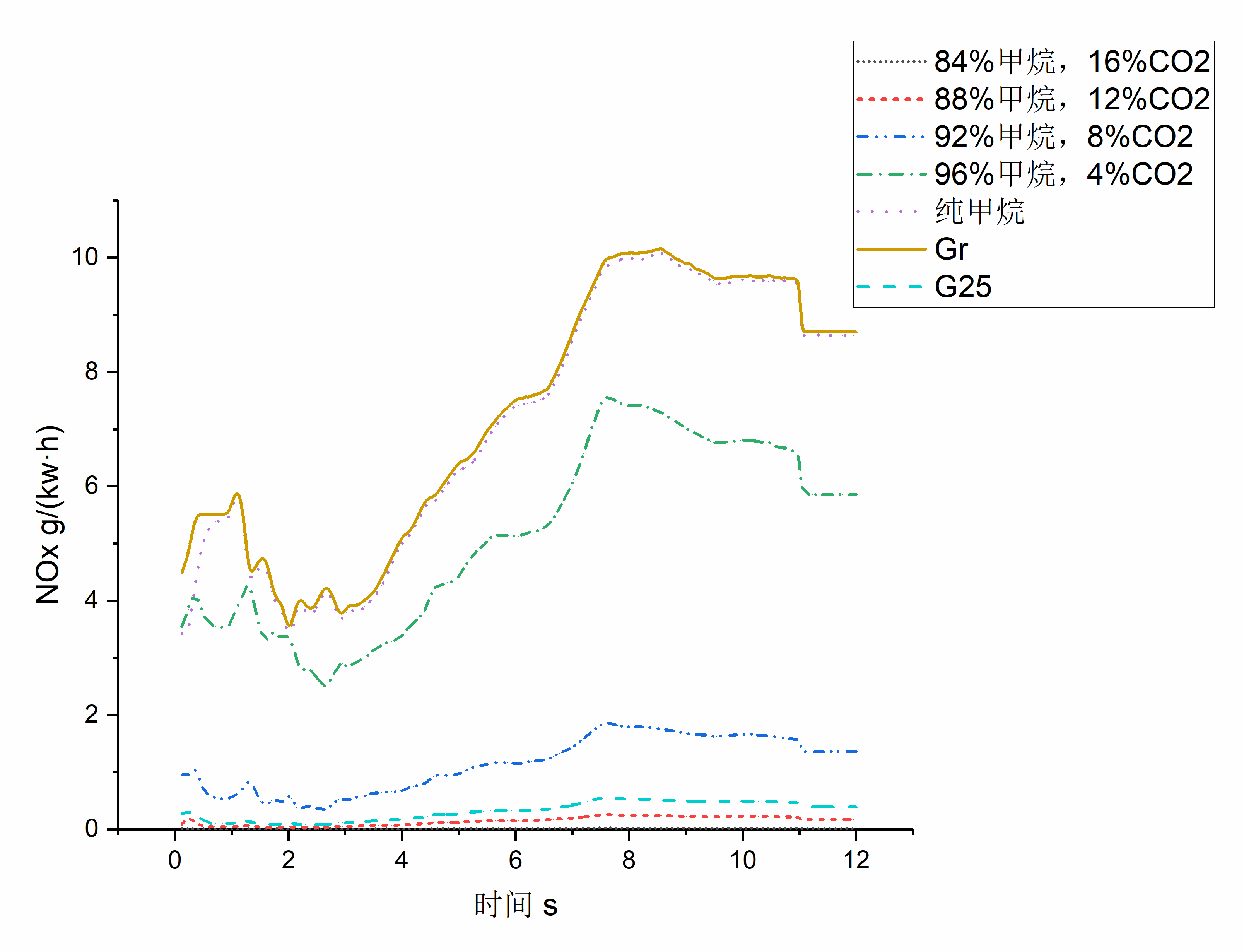
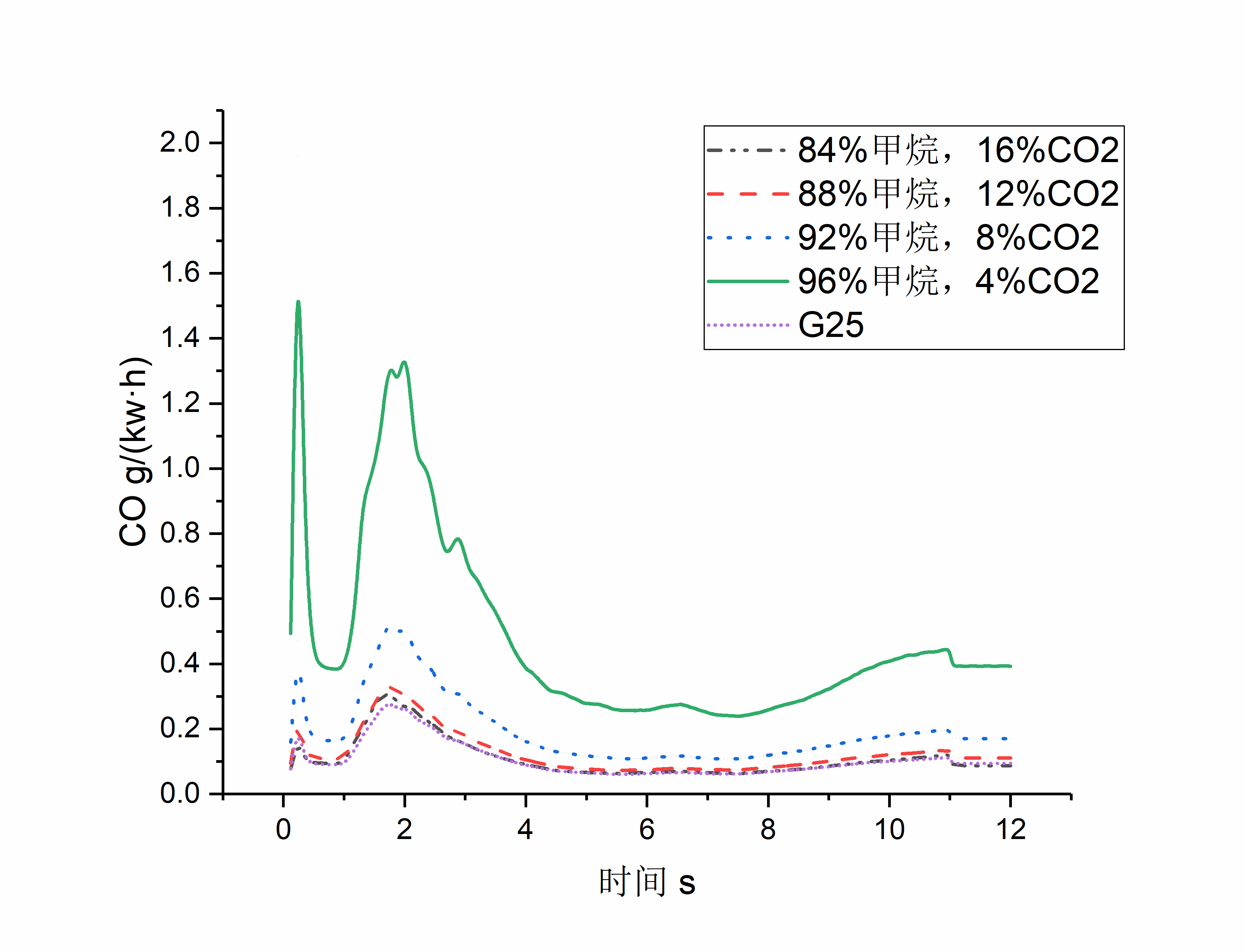
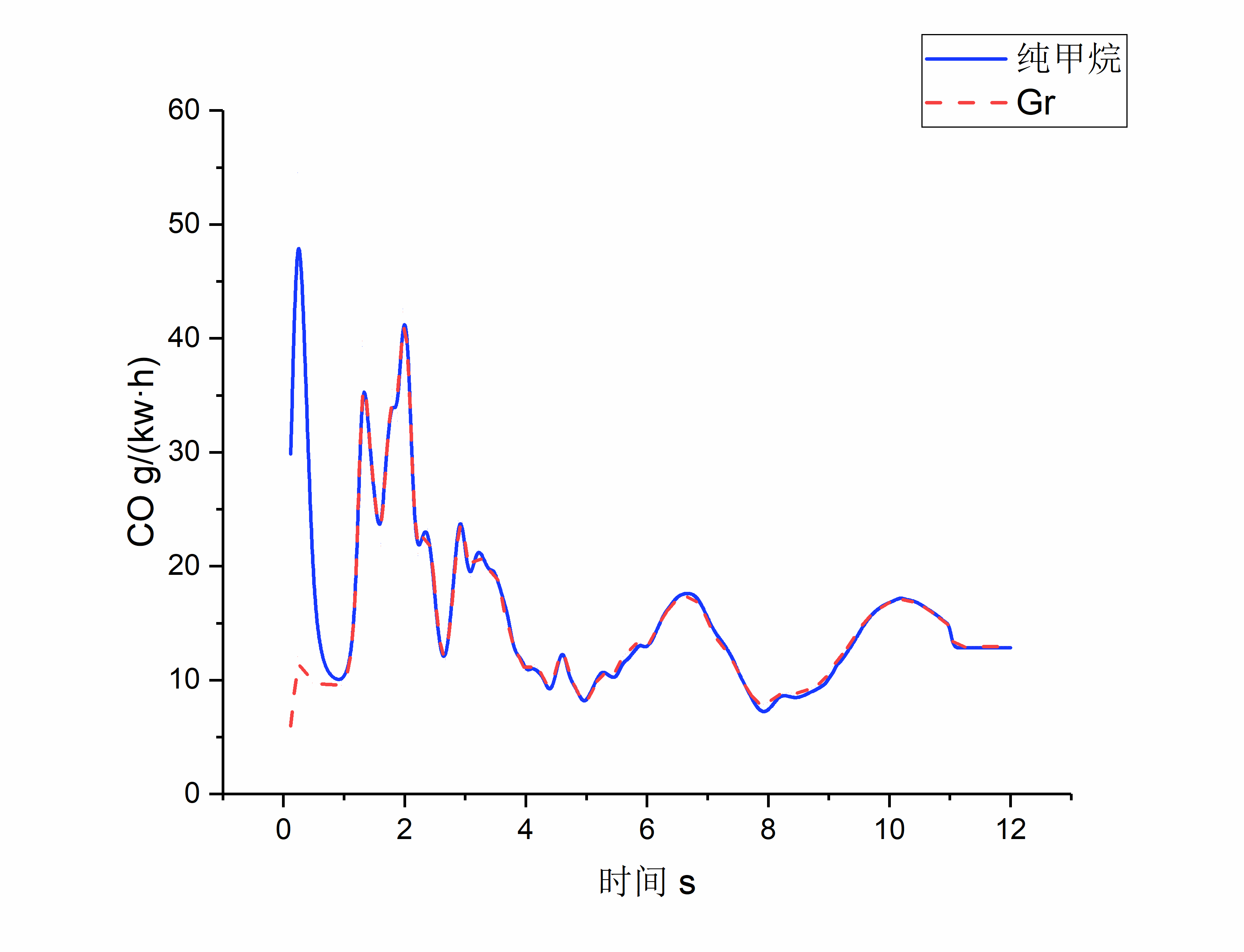
研究发现,改变天然气燃料组分,天然气发动机经济性能和排放性能均会改变,且不同的经济性和排放性指标将会有不同的改变趋势。天然气组分中CO2比例的增加,将导致加减速瞬态工况下天然气发动机NOx排放量和CO排放量减小,但HC排放量急剧增加,CO排放量增加,同时比油耗升高,发动机经济性变差,另外,在天然气组分中添加N2也会有类似效果,但是改变量有所区别。在92%CH4、8%CO2燃料组分时,CNG发动机各项指标均较为优秀,综合表现较好,认为此时天然气组分最佳,并选择此天然气组分进行加减速瞬态仿真试验。
随着发动机加减速进程,发动机经济性和排放性参数按照一定规律变化。在瞬态工况开始阶段,发动机各项参数发生突变,这是由于工况变化的改变。之后发动机经济性和排放性参数恢复正常,并按照一定趋势变化,这主要是由于气缸温度的变化。
选择92%CH4、8%CO2燃料组分的天然气进行发动机急加速、急减速时间对经济性、排放特性影响的研究。研究表明,加减速时间改变,对天然气发动机加减速前期的经济性和排放性影响不大,但会影响到加减速末期的经济性和排放性能。急加速、急减速增加,将使NOx排放减少,但是其余排放参数在加减速末期增加,同时比油耗增加。急加速时间超过10.5s后,在加速阶段末尾,CNG发动机排放性和经济性指标将出现下降;而急减速时间增加,在减速阶段末尾,CNG发动机经济性和排放性指标都将变差。
关键词:CNG发动机,燃料组分,GT-POWER,瞬态工况,仿真
Abstract
With the development of global industrialization, the number of cars has increased and the oil crisis has become more and more severe. As a clean, efficient, and abundant alternative energy source, natural gas has been widely studied by researchers. The use of natural gas rather than traditional oil as the energy source of cars is very popular. However, there are many differences between natural gas engines and traditional fuel engines. Further calibration studies are needed. Natural gas components and dilutions are also difficult to overcome in further application of CNG engine. Among these studies, the study of transient performance of natural gas engines is a major focus of CNG engine research.
Based on the research results of domestic and foreign scholars, GT-POWER software was selected for the simulation test of natural gas engine transient simulation. This paper uses GT-POWER to establish a CNG engine simulation model for transient operating conditions. The torque and power errors were 5% and 6% respectively, compared to the engine bench test, demonstrating that the model is reliable. Then, five sets of natural gas with CO2 composition from 0 to 16% and Gr and G25 from the Six National Standard fuels are used to simulate the acceleration and deceleration transient conditions of natural gas engine,to study the influence of changes in natural gas fuel composition and rapid acceleration and deceleration time on the economic characteristics and emissions of CNG engines.
The study found that changing the natural gas fuel composition will change the economic performance and emissions of natural gas engine, and different economic and emission indicators will have different trends. The increase of CO2 ratio in natural gas components will lead to a decrease in NOx emissions and CO emissions of natural gas engines during acceleration and deceleration transient conditions, but HC emissions will increase sharply, CO emissions increase, while fuel economy will increase and engine economy will deteriorate. In addition, adding N2 to the natural gas component will have a similar effect, but the amount of change is different. When in 92% CH4, 8% CO2 fuel composition, the CNG engine indicators are relatively the best, and the overall performance is better than other. It is considered that the natural gas component is the best at this time, and this natural gas component is selected for acceleration and deceleration transient simulation test.
As the engine accelerates and decelerates, engine economic and emission parameters change according to certain rules. At the beginning of the transient condition, the engine parameters are abruptly changed due to changes in operating conditions. After that, the engine economic and emission parameters returned to normal and changed according to certain trends, mainly due to changes in cylinder temperature.
Natural gas with 92% CH4 and 8% CO2 fuel components was selected to study the effects of engine acceleration and deceleration time on economy and emission characteristics. The study shows that the change of acceleration time has little effect on the economic and emission effects on the natural gas engine during the early stage of acceleration and deceleration, but will affect the economic and emission performance at the end of acceleration and deceleration. Accelerated acceleration and deceleration will deduce NOx emissions, but the remaining emission parameters will increase at the end of acceleration and deceleration, and the fuel consumption will increase. After the acceleration time exceeds 10.5s, the emission and economic indicators of CNG engines will decrease at the end of the acceleration phase; while the deceleration time increases, the economic and emission indicators of CNG engines will change at the end of the deceleration phase.
Keywords: CNG engine, fuel composition, GT-POWER, transient condition, simulation
目录
摘要
Abstract
第1章 绪论 1
1.1 CNG发动机的介绍和应用前景 1
1.2 关于CNG发动机瞬态分析的国内外研究总结 3
1.3 本文的主要研究方法 5
第2章 仿真模型和实验参数的确定 6
2.1 GT-POWER软件介绍 6
2.2 利用GT-POWER建立发动机仿真模型 6
2.3 仿真试验燃料选择 9
2.4 本章小结 10
第3章 加速工况下CNG发动机瞬态性能分析 11
3.1燃料组分对发动机瞬态性能的影响 11
3.1.1 发动机排放性分析 12
3.1.2 发动机经济性分析 16
3.2 急加速时间对发动机瞬态性能的影响 17
3.2.1 发动机排放性分析 17
3.2.2 发动机经济性分析 19
3.3 本章小结 20
第4章 减速工况下CNG发动机瞬态性能分析 21
4.1 燃料组分对发动机瞬态性能的影响 21
4.1.1 发动机排放性分析 21
4.1.2 发动机经济性分析 24
4.2 急减速时间对发动机瞬态性能的影响 25
4.2.1 发动机排放性分析 25
4.2.2 发动机经济性分析 28
4.3 本章小结 28
第5章 结论和展望 30
5.1 结论 30
5.2 展望 30
致谢 34
参考文献 32
第1章 绪论
1.1 CNG发动机的介绍和应用前景
近年来,全球工业化迅速发展,汽车保有量提高,导致各国对石油资源的消耗量越来越大,石油危机成为世界各国亟待解决的一大难题。据国家统计局报道,2017年我国煤炭、石油两种能源合计占比达79.2%,能源结构单一。且石油资源消费量高但生产量低,供应依赖进口。图1-1为2016年中国一次能源消费结构图。
图1-1 2016年中国一次能源消费结构
我国石油对外依存度连年增长,从2000年的30%,到2009年已经突破了世界公认的50%的警戒线。然而形势依然恶化,在2011年,中国超过美国,成为世界最大的石油进口国和消费国,据外界估计到2020年我国的石油对外依存度将达到惊人的70%[1]。图1-2展示了我国近年来的石油对外依存度及其预测数据。
对石油资源的依赖对我国环境造成了严重的负面影响,同时,石油资源对外依存度过高也不利于我国安全战略。因此,必须尽快寻找一种清洁、储量大的替代能源来代替石油,来缓解我国面临的能源压力,平稳地度过能源危机。
在各种替代能源中,天然气(natural gas)具有清洁高效、储量丰富、比热较高、污染较少等优点,因此受到研究者的关注[3]。
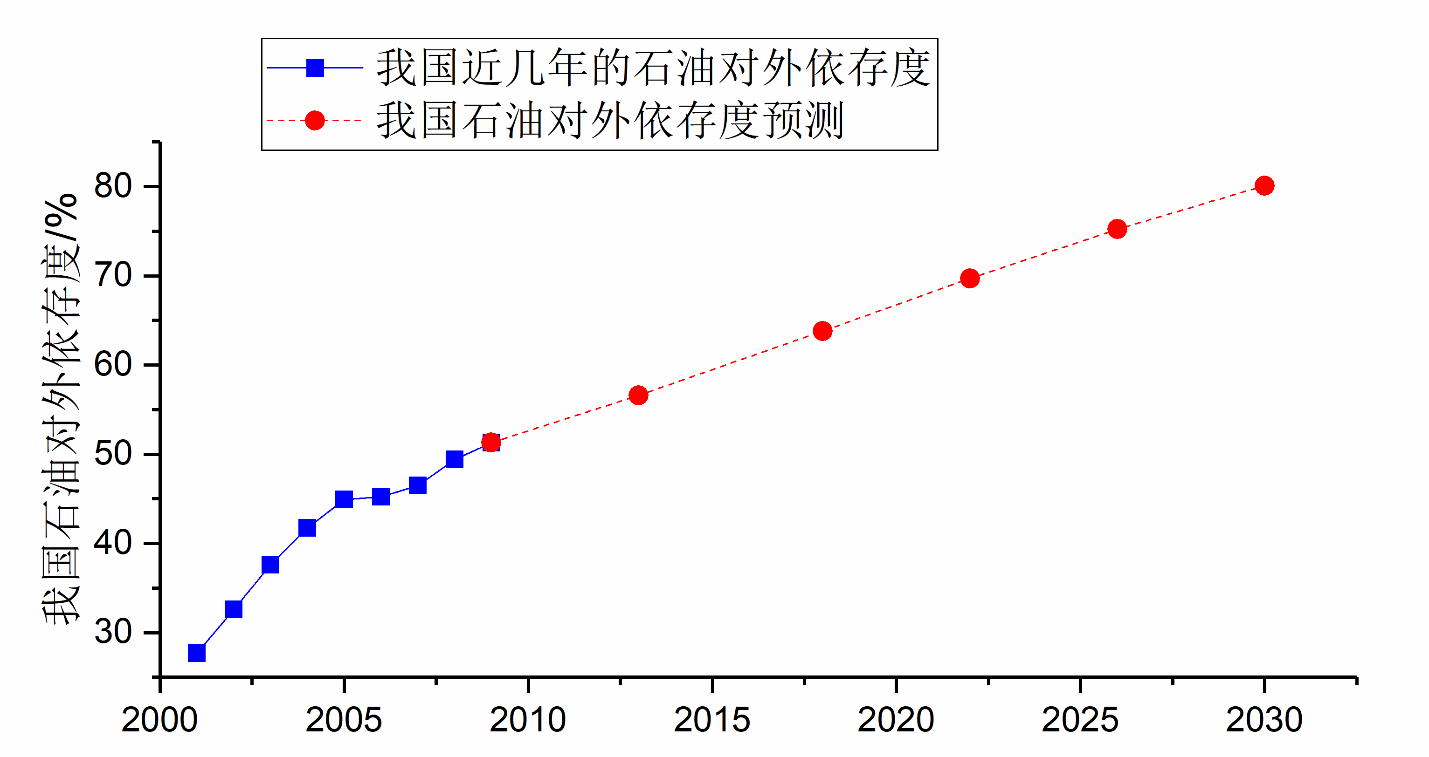 图1-2 我国近几年的石油对外依存度及其预测[2]
图1-2 我国近几年的石油对外依存度及其预测[2]
天然气是指天然蕴藏在地层中的烃类和非烃类气体的混合物。其主要组分为甲烷,含量在约70%~90%之间,此外还含有乙烷、丙烷、丁烷等烃类物质和CO2、N2、H2S等非烃类物质。
天然气的组分随其产地和季节的不同有较大变化。天然气组分如表1-1所示[4]。
组分 | 一般情况 | 最大值 | 最小值 |
甲烷 | 87.3% | 92.8% | 79.0% |
乙烷 | 7.1% | 10.3% | 3.8% |
丙烷 | 1.8% | 3.3% | 0.4% |
丁烷 | 0.7% | 1.2% | 0.1% |
氮气 | 2.2% | 8.7% | 0.5% |
二氧化碳 | 0.9% | 2.5% | 0.2% |
表1-1 天然气的组分[4]
与传统燃料发动机相比,天然气发动机有颇多优势。它具有高辛烷值,因此适用于压缩比较高的发动机。它具有高自燃温度,因此需要较强能量源以实现燃烧,即通过电热塞,火花塞或先导液体燃料。它可以与空气迅速混合,形成均匀的空气燃料混合气,在发动机气缸内部有效燃烧,大幅度减少有害气体排放[5]。
另外,天然气还有较为清洁的优点。天然气的成分中87%为甲烷,因此其燃烧后的废气排放量相比于传统发动机将有很大降低。其中,SO2排放量相比于柴油机可降低90%,碳烟排放量可降低93%;相对于汽油机,在燃烧较好的情况下,CO排放量可降低97%,NOx排放量则可降低39% [6]。
不过,天然气的使用也存在一些待解决的问题。试验研究结果表明同排量的CNG发动机与柴油机相比,其动力性将会下降,因此如果不对CNG发动机进行标定调整,将会影响到发动机动力性能的发挥 [7]。
学术研究中一般将天然气分为压缩天然气(CNG)、液化天然气(LNG)、吸附天然气(ANG)和近临界流体(NCF)四大类[8]。天然气汽车也可以分为以上四种类型。其中,压缩天然气(compressed natural gas, 简称CNG)一般指将天然气压缩并并以气态存储,这种方式成本、效益均较为理想,同时绿色环保,是一种理想的发动机替代燃料。
1.2 关于CNG发动机瞬态分析的国内外研究总结
以上是毕业论文大纲或资料介绍,该课题完整毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、程序设计、图纸设计等资料请添加微信获取,微信号:bysjorg。
相关图片展示: