TC4-0.5Fe合金的悬浮熔炼及固溶时效对其组织和性能的影响毕业论文
2020-07-06 18:16:46
摘 要
关键字:钛合金 悬浮熔炼 热处理 显微组织 力学性能
ABSTRACT
TC4 alloy has many advantages, such as small density, high specific strength and good histocompatibility, etc. it is widely used in the field of aviation, ocean and medicine. But in use, its strong plastic matching can not meet the requirements of high requirement structure. It is often modified by adding alloy elements, and the best strength is achieved through heat treatment. Plastic matching.
The addition of alloying element Fe as a beta stable element can improve the hot workability of titanium alloy and improve its plasticity and toughness. In the experiment, the alloy ingot was rolled by vacuum suspension smelting, and the alloy was rolled. The alloy structure was controlled by the heat treatment method of solid solution and aging in the beta phase region. Finally, the structure with good comprehensive performance was obtained. Metallographic observation and XRD were used to study the relationship between the size of the secondary phase and the tensile strength and hardness of the beta grains and the alpha phase content.
The experimental study shows that when the solution temperature reaches the point of transformation, the alloy structure changes into lamellar structure, and only one phase and beta phase exist in the alloy. With the aging temperature from 500 to 560, the original beta grain size of the alloy increased from 580 to 1029 m, the width of the secondary phase increased from 0.94 to 1.63 m, and the tensile strength of the alloy decreased from 985.29MPa to 877.26MPa, and the plasticity of the alloy increased and the hardness increased. At the temperature of 520, the alloy reaches the best strength plastic matching.
Key words: titanium alloy, suspension melting, heat treatment, microstructure, mechanical properties
目录
摘 要
ABSTRACT
第一章 文献综述
1.1 引言
1.2 钛合金概述
1.2.1 钛及钛合金的应用和前景
1.2.2 钛及钛合金的组织和性能
1.2.3 TC4钛合金介绍
1.3 合金元素对钛及钛合金的作用和影响
1.3.1 铁(Fe)元素的作用
1.3.2 钒(V)元素的作用
1.3.1 铝(Al)元素的作用
1.3.2 其他元素的作用
1.4 钛合金的应用与发展
1.4.1 钛合金在航空航天业的应用
1.4.2 钛合金在海洋工业的应用
1.4.3 钛合金在车辆建筑中的应用
1.4.4 钛合金在医疗器械中的应用
1.5 钛合金的熔炼技术
1.6 组织形态对力学性能的影响
1.7 课题研究的现状与近况
1.8 课题研究的内容与方法
第二章 实验内容
2.1 实验材料与仪器
2.1.1 实验材料及规格
2.1.2 实验仪器及规格
2.2 实验内容
2.2.1 熔炼过程
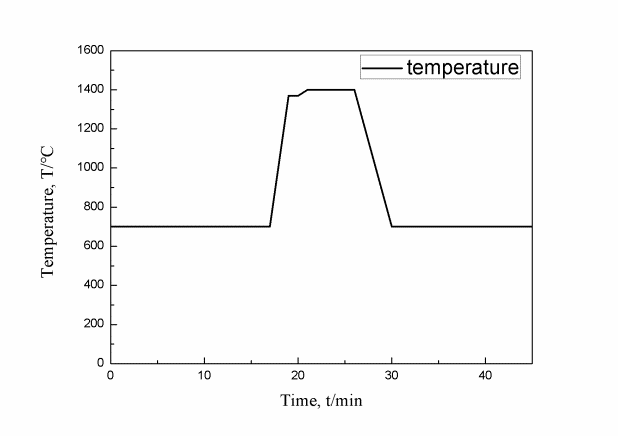
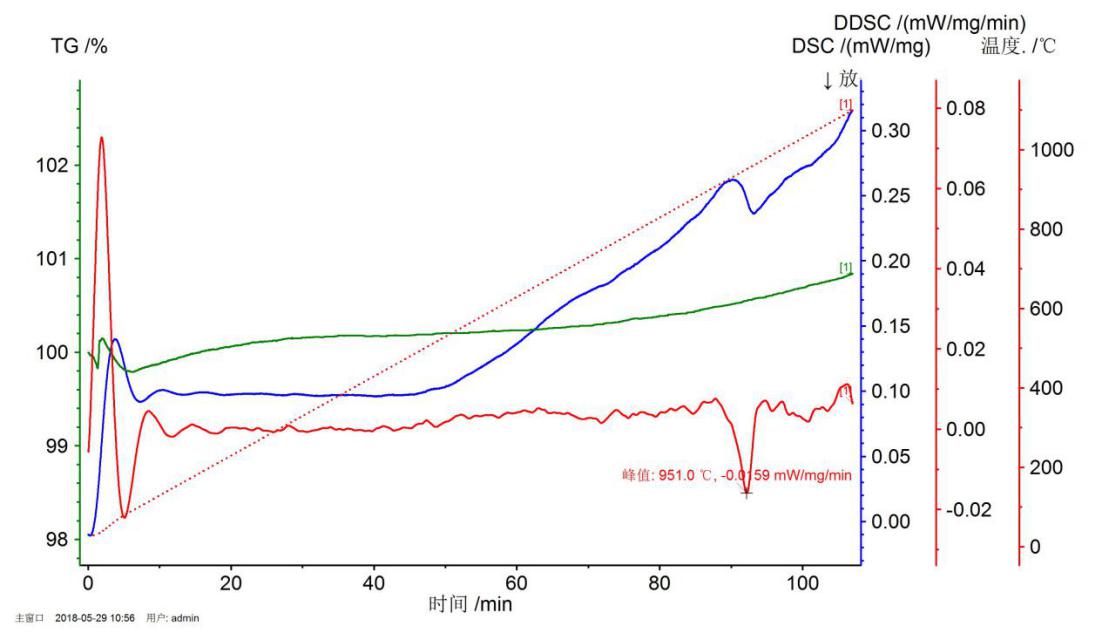
2.2.2 相变点的测定
2.2.3 制定热处理工艺
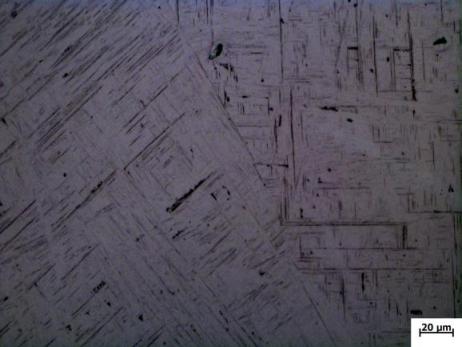
2.2.4 金相观察
2.2.5 XRD检测分析
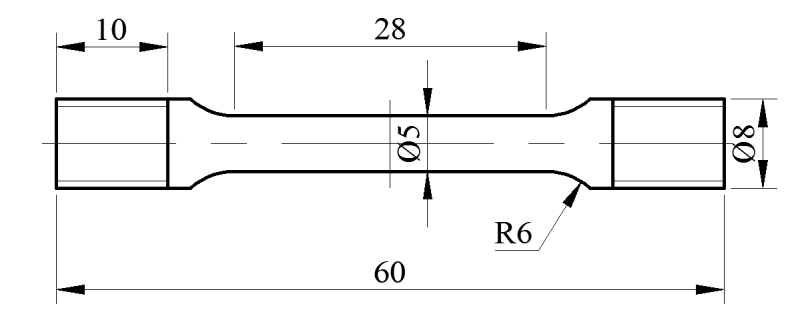
2.2.6 拉伸测试
2.2.7 断口形貌测试
2.2.8 硬度测试
第三章 实验结果的讨论与分析
3.1 悬浮熔炼测定
3.2 合金相变点的测定
3.3 热处理后合金组织分析
3.4 XRD衍射图分析
3.5 热处理后合金的拉伸性能
3.6 拉伸断口形貌
3.7 热处理后的合金硬度
第四章 结论与总结
参考文献
致 谢
第一章 文献综述
1.1 引言
在20世纪50年代,第三次科技革命带起了全世界经济的飞速发展,其中航天业、海洋工程、生物医疗最为迅速的发展了起来,为了能够满足各行各业的需求,人们开始大力研发各种金属和合金。作为被开发出的新型结构金属之一,钛和钛合金相比于其他金属拥有更好的性能,迅速得到人们的青睐,短时间内成为了最重要的新型材料之一 [1]。
在1954年,人们研制出一种新型的钛合金,该合金相比于其他钛合金更加优质,很快便成为了使用量最大的合金,人们将该合金命名为Ti-6Al-4V合金。
由于TC4合金的性能优秀,目前许多钛合金都在TC4合金上的基础上进行研究。人们也在研究如何将TC4合金向着更加经济实用的方向发展。
我国是一个拥有丰富钛资源的大国,在目前已经探测到的钛矿中,我国的储量约占全世界的四成,丰富的资源极便于提高了我国钛工业发展的进度。但是由于我国改革开放较晚,我国在钛工业上起步相比于发达国家较慢,钛和钛合金的研究仍然任重道远,因此我们还需要将更多的投入和经理用在开发和改良钛合金上。
相关图片展示: