十字交叉口街谷交通污染物传播的传播规律毕业论文
2020-04-12 09:01:03
摘 要
随着城市的快速发展,越来越多的机动车除了给人们生活带来便利以外,也难免会造成交通拥堵和环境污染的问题。在此背景下,许多学者将目光投向了城市的一个复杂空间结构的基本组成空间——城市街谷,了解和掌握城市街谷风环境、污染物分布特性和规律,在改善城市环境质量,给城市居民提供一个健康安全的生活环境,提高人们的生活质量等方面具有重要的意义和价值。本文主要采用数值模拟的方法对道路十字交叉口内的污染分布状况进行研究。
本文针对十字路口空间的情况建立一个简化的十字路口模型,在街谷道路上设置了两个污染源,采用FLUENT作为研究工具,选取 RNG K-ε湍流模型进行数值模拟计算。模拟不同风速情况下和不同风向情况下污染物的扩散情况来得到结论,本文的主要工作如下:
本文首先对众多研究人员的结果进行综述,内容包括对城市街谷空间污染物分布,风热环境对于街道峡谷内部污染物扩散的影响,街道几何形状及建筑排布十字交叉口污染物扩散影响的分析等研究成果,之后运用CFD进行十字路口街谷的数值模拟,分析风速与风向这两个主要影响因素对污染物扩散的作用。
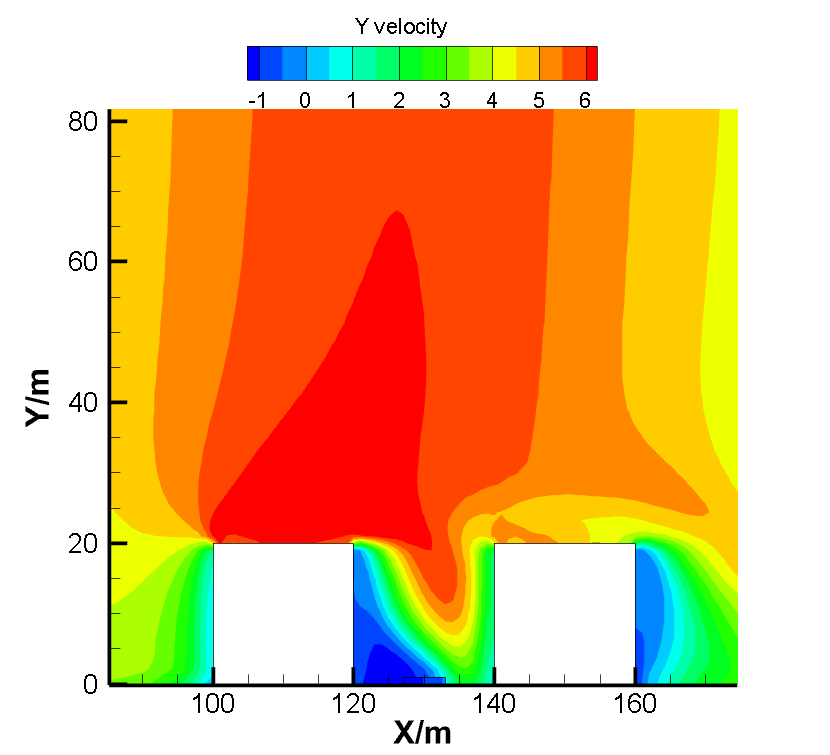
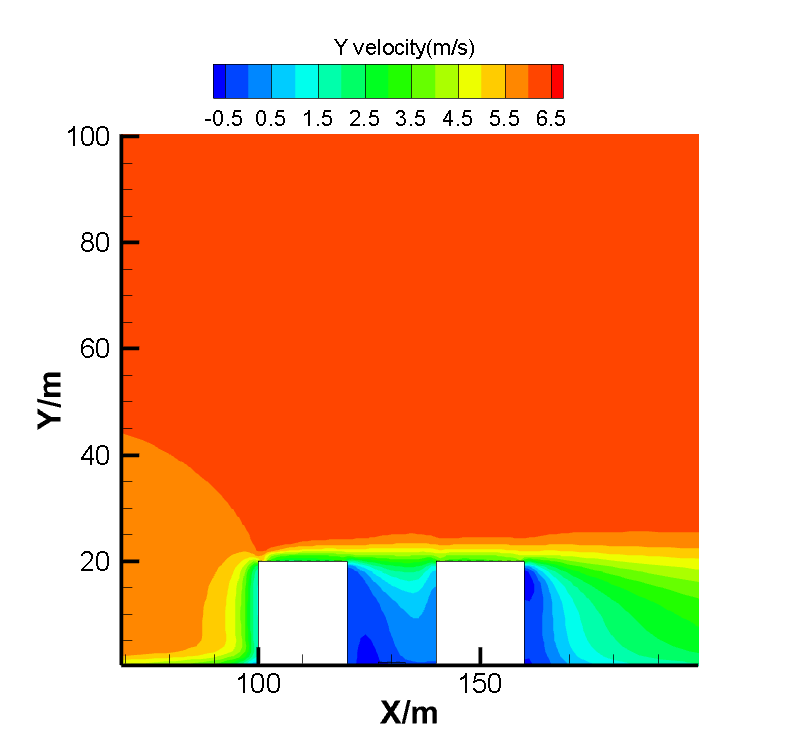
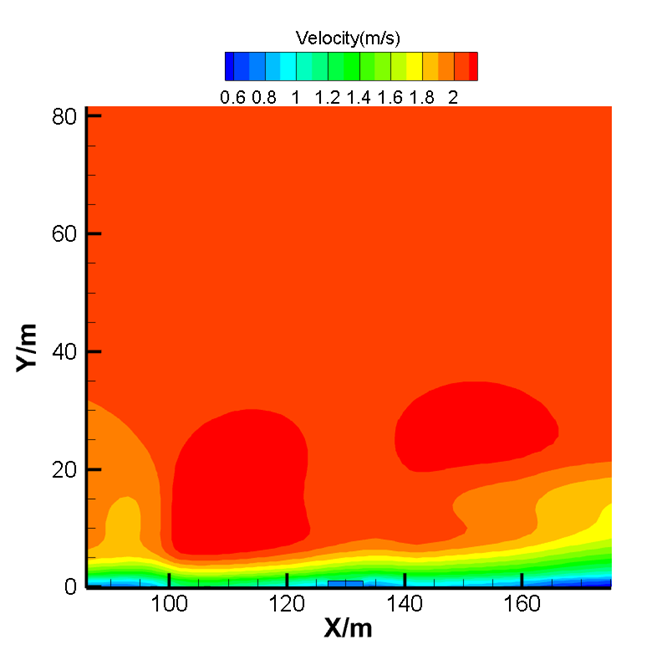
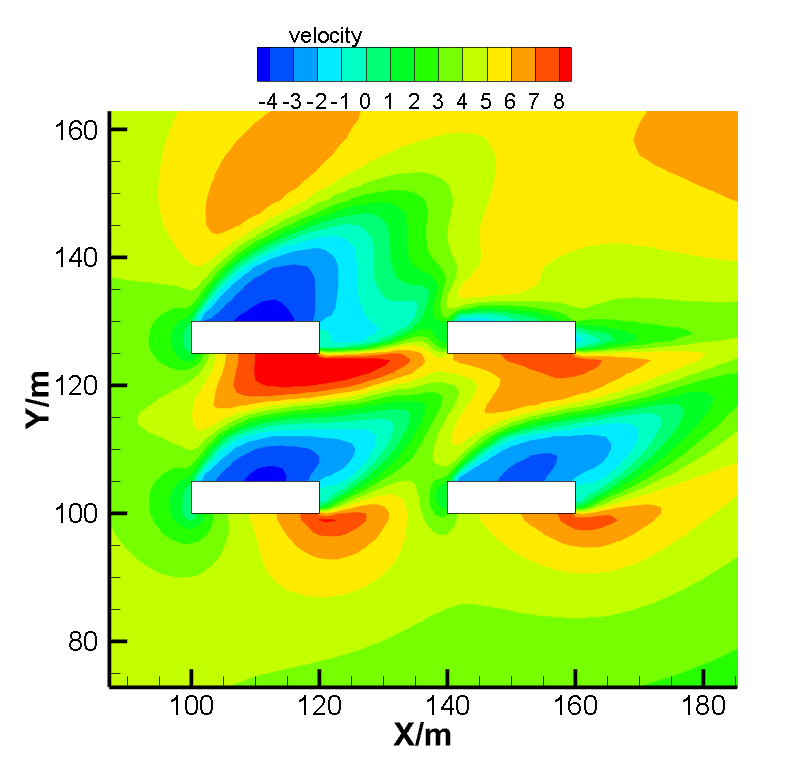
结果表明,在来流风沿风向进入街谷内,来流风会将污染物沿风向从上游带到下游处。同时位于上游建筑物的遮挡作用会对气流产生更大的影响,会遮挡气流导致污染物的聚集,不利于街谷内污染物的扩散。风向的变化会导致污染在不同的位置产生积聚,上游建筑的背风侧是污染物的主要积聚区域。风速的增加会降低街谷中污染物浓度,并且使污染物更快的扩散出去,降低其影响。污染物位于地面0.5m高处,随着高度的增加,污染物的扩散情况越好,污染物浓度越低,下风处距离街谷区域越远,污染物浓度越低,空气流场越接近开阔空间状态。
文章结尾处提出本次研究的没有考虑到一些因素,希望未来有机会更深入的进行针对十字路口空间污染物扩散的研究,并且能够结合实际情况,得到更为准确和具有说服力的结论。最后表达了对于未来计算流体力学发展的一些期望。
关键词:十字路口;街道峡谷;污染物扩散;数值模拟;CFD
Abstract
With the development of the city, the number of motor vehicles in the city has always maintained an increasing trend. In addition to increasing the convenience of people's lives, more and more vehicles will inevitably cause traffic jams and environmental pollution. Under this background, many scholars have paid their attention to the basic components of a complex spatial structure of cities—the city streets canyons. It is significant to understand and master the wind environment of urban street and canyon, and the distribution characteristics and laws of pollutants, because it has important academic and application value in creating a comfortable urban microclimate, alleviating urban air pollution, and protecting pedestrian health and safety. At present, the relevant researches on vehicle exhaust mainly used wind tunnel experiments-numerical simulation. Due to the long period and high cost of wind tunnel tests, this thesis mainly uses numerical simulation methods to study the pollution caused by vehicle exhaust in road intersections.
In this thesis, a simplified intersection model is established for the situation of crossroad space. Two pollution species are set inside the street canyon to represent the status of the exhaust emissions of the traffic. At the same time, the RNG K-turbulence model in FLUENT is used for numerical simulation. The conclusion is reached by simulating the diffusion of pollutants under different wind speeds and under different wind directions. The main tasks of this thesis are as follows:
This thesis firstly concludes the space pollutants of many researchers on city street canyons, and distribution, influence of wind and heat environment on the diffusion of pollutants inside street canyons, analysis of street geometry and influence of pollutant diffusion at cross intersections of building layout, etc., and then using CFD to perform modeling calculations at cross streets canyons. Analyze the role of two major influencing factors, wind speed and wind direction, on the dispersion of pollutants.
As the result, inside the windward street canyon, the wind will carry upstream pollutants to the downstream street canyon. At the same time, the upstream buildings have a greater impact on the air flow, which will block the air flow and lead to the accumulation of pollutants. Different wind directions can lead to accumulation of pollution in different locations. The leeward side of upstream buildings is the main area of accumulation of pollutants. Set the pollutants to 0.5m above the ground. Higher speed will lead to less pollutant. As the height increases, the better the diffusion of pollutants, the lower the concentration of pollutants, the farther the downwind distance from the street canyon area, the lower the concentration of pollutants, the more the air flow field becomes. It will keep decline until it is similar to open space atmosphere.
In the end, this thesis did not consider some factors. It is hoped that there will be more researches on the diffusion of pollutants at crossroads in the future and there are some prospects for the future development of computational fluid dynamics.
Key words:crossroads;street canyon;pollution dispersion;numerical simulation.
目 录
摘 要 II
Abstract III
1 绪 论 1
1.1 研究背景及意义 1
1.1.1研究背景 1
1.1.2研究意义 2
1.2研究方法 2
1.3国内外研究现状 3
1.4 本文研究内容 5
2 街谷污染物传播的基础理论 6
2.1 城市微气候 6
2.2 CFD数值模拟原理 7
2.2.1流体力学微分方程的离散化方法 7
2.3 街道峡谷污染物扩散的数值模型 8
2.3.1基本假设 8
2.3.2数学模型 9
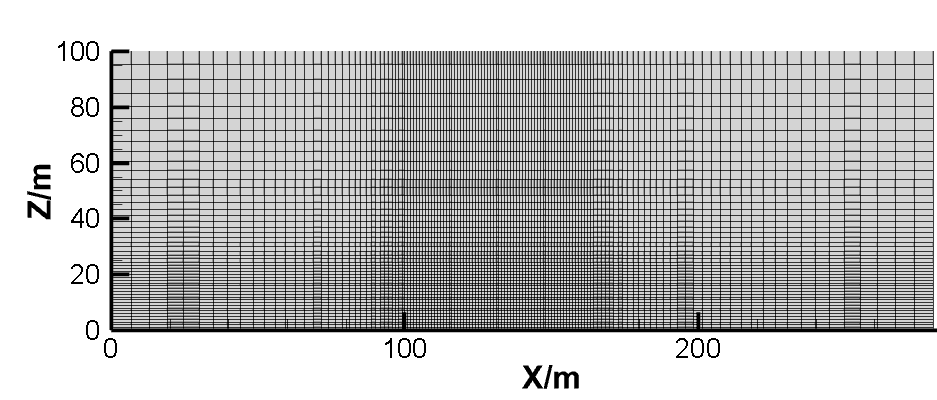
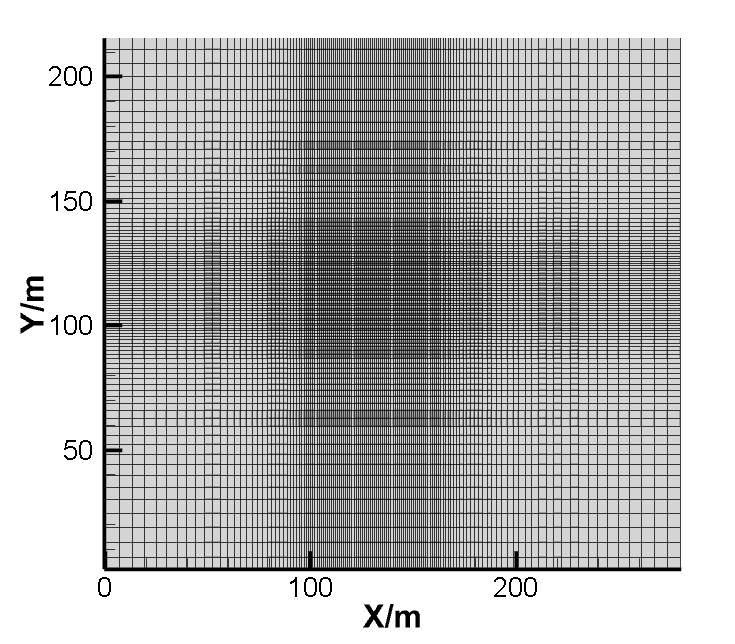
2.3.3 网格划分原则 11
3 十字路口街谷污染物数值模拟及结果分析 13
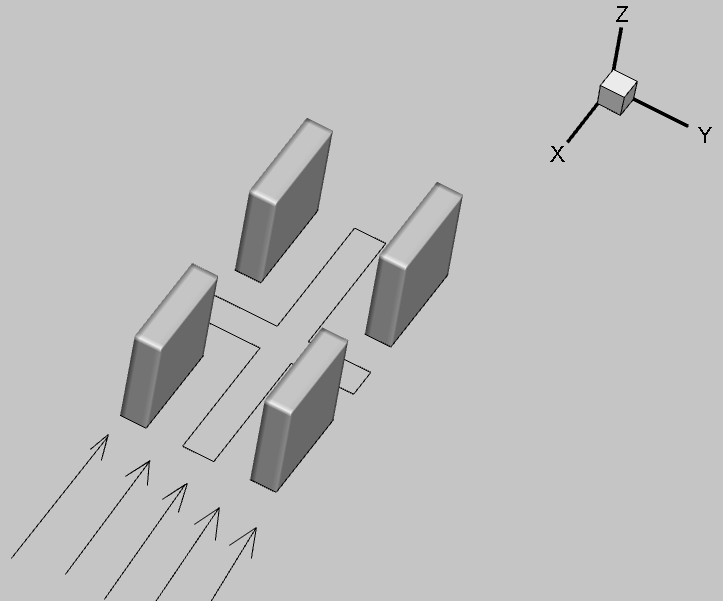
3.1 几何模型 13
以上是毕业论文大纲或资料介绍,该课题完整毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、程序设计、图纸设计等资料请添加微信获取,微信号:bysjorg。
相关图片展示: