日光温室地下蓄热系统的温室内热量传递过程研究毕业论文
2020-05-22 21:11:29
摘 要
日光温室由于其良好的采光和保温性能,越来越受到设施农业的青睐。日光温室分为被动式日光温室和主动式日光温室。被动式日光温室借助土壤和围护材料的蓄热和保温特性,在没有外部加热的条件下,以日光为能量来源,为植物在恶劣环境下提供满足其生长需求的环境。相对于主动式日光温室,被动式日光温室所占的土地资源更少,初期投资以及运行维护成本更低。特别是在小规模应用中,被动式日光温室具有相对更高的经济优势,因此被动式日光温室在农业生产领域得到广泛使用。
本文介绍了自20世纪60年代以来国内外学者对日光温室的研究情况,包括研究方法、所建立的温室数学模型和计算机软件模拟模型等等。日光温室内环境是一个相当复杂的系统,具有高度非线性、强耦合、大时延的特点,所要考虑的变量参数很多。针对日光温室复杂的内环境,本文运用热力学、传热学、计算流体力学的基本相关理论,拟建适用于无植物条件下日光温室热环境的三维模型,并利用计算流体力学软件Fluent对其进行数值模拟研究,考虑太阳辐射和地下蓄热影响情况下,得出日光温室内空气温度场的分布情况,分析日光温室内的热量传递过程。得出的结果为实际实践提供一定的参考指导作用。
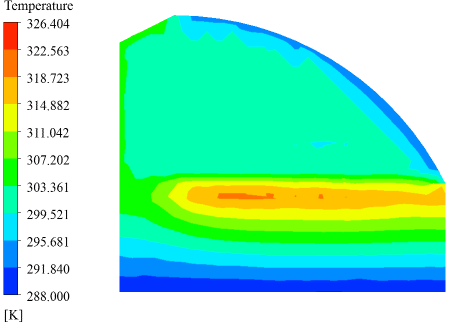
基于模拟结果,本文分析了不通风条件下不同光照强度下日光温室内环境的温度场、压力场和速度场的分布情况,得出以下结论:日光温室内温度最高的区域出现在土壤表面附近,不同强度的太阳辐射不会改变整体的温度分布情况,只是温度值大小存在差异;温室内压力最大值出现在在温室顶部,并且沿着重力方向至土壤表面呈递减趋势,类似于辐射对温度分布的影响,不同强度的太阳辐射并不会改变整体的压力分布趋势,只会影响压力值的大小;不同于温度和压力的分布,温室内的速度分布具有一定的不规律性,随着太阳辐射的增强,整体空气流动速度却有所下降。在通风条件下,温室内外的空气直接进行热交换,从而影响温室内的温度,除此之外,温室通风更主要的是使温室内的空气温度和压力分布更为均匀,避免了温室内的局部温度过高或过低的问题,更有利于作物的生长。
关键词:日光温室;计算流体力学;热量传递过程
HEAT TRANSFER PROCESS IN THE SOLAR GREENHOUSE WITH UNDERGROUND HEAT STORAGE SYSTEM
Abstract
Solar Greenhouse is increasingly favored in agricultural facilities for its excellent lighting performance and thermal insulation properties. It has two types of passive and active. With the storage and insulation properties of soil and the building envelope materials in passive solar greenhouse, in the absence of external heating conditions, use sunlight as energy source, to meet the growing demand for plants in harsh environments. With respect to the active greenhouse, passive solar greenhouse occupies fewer land area, lower initial investment as well as operation and maintenance costs. Especially in small scale applications, passive solar greenhouse has a relatively higher economic advantage, so that passive solar greenhouse in the agricultural production field has been widely used.
In this paper, studies of solar greenhouse done by scholars from home and abroad since 1960s are introduced, including research methods, mathematical models and computer software simulation models and so on. Environment in sunlight greenhouse is a very complex system with the characteristics of highly nonlinear, strong coupling and large delay. There are many variables and parameters need to be considered. For the complex internal environment in the solar greenhouse, this paper establishes a three-dimensional model about the thermal environment of solar greenhouse under non-plant conditions bases on the theory of Thermodynamics, Heat Transfer and Computational Fluid Dynamics, and use software of Computational Fluid Dynamics for numerical simulation study. Considering the influence of solar radiation and underground heat storage case, get the distribution of different air temperature field in solar greenhouse, analyze the heat transfer process inside the solar greenhouse. The results obtained provide a reference guide for the actual practice.
Based on simulation results, this paper analyzes the distribution of temperature, pressure and velocity in greenhouse on the condition of without ventilation. And we can draw the conclusions: the highest temperature regions in the solar greenhouse appears near the surface of the soil, different intensities of solar radiation does not change the overall temperature distribution, but the numerical value of temperature is different. The maximum pressure regions in the solar greenhouse appears at the top of greenhouse, and showed a decreasing trend to the soil surface on the direction of gravity. Similar to the effects of radiation on the temperature distribution of the different intensity of solar radiation and won’t change the overall trend of the pressure distribution but affect the numerical value of pressure. Unlike the distribution of temperature and pressure, velocity distribution inside the greenhouse is irregular and with the enhancement of the solar radiation, the overall air velocity has declined. In ventilation, air inside and outside greenhouse exchange heat directly and affect the temperature inside the greenhouse. In addition, greenhouse ventilation makes air temperature and pressure inside the greenhouse more evenly distributed and avoid the problem that local temperature becomes too high or too low in the greenhouse which is more conducive to the growth of crops.
Key words: solar greenhouse; Computational Fluid Dynamics; heat transfer process
目 录
摘要 I
Abstract II
第一章 绪论 1
1.1 课题背景和研究意义 1
1.2 日光温室及其原理和研究发展状况 1
1.2.1 日光温室及其原理 1
1.2.2 日光温室研究发展状况 2
1.3本章小结 5
第二章 温室理论模型和数值模拟数学模型 6
2.1 日光温室参数变量说明 6
2.2 日光温室模型 7
2.3 日光温室内热量传递过程分析 8
2.4 日光温室内环境模型的简化 9
2.5 日光温室数学模型 10
2.5.1 热量传递 10
2.5.2 数值计算基本方程 11
2.6本章小结 11
第三章 模型构建及日光温室内热量传递过程的CFD模拟 13
3.1 模型构建 13
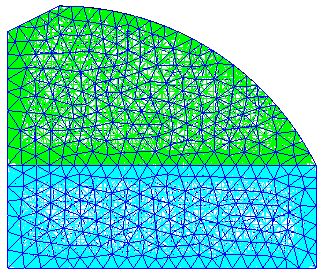
3.2 网格划分 14
3.3 边界条件的确定 14
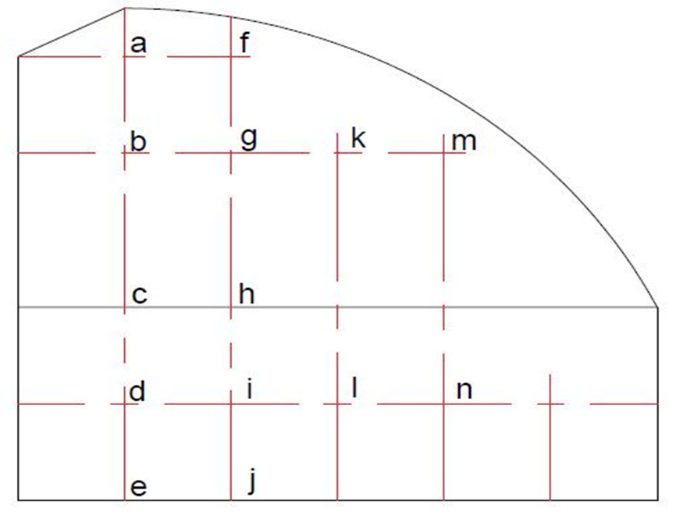
3.4 网格独立性验证 15
3.5 无通风条件下模拟结果 23
3.6 不同通风条件下模拟结果 27
3.6.1 只在后屋面中央开设通风口模拟结果 27
3.6.2 在西墙上部和东墙底部各开设通风口模拟结果 32
3.6.3 在后屋面中央和东墙底部各开设通风口模拟结果 36
3.7本章小结 40
第四章 结论与讨论 41
4.1 结论 41
4.2 讨论 41
参考文献 42
致谢 45
第一章 绪论
1.1 课题背景和研究意义
日光温室主要是在恶劣的环境条件下,建立适当的热湿内环境,以满足各种喜温作物的生长需求。同时,温室能够保护作物免除过冷和过热气候的影响,又可抵御恶劣自然灾害、虫害的侵害。此外,日光温室兼具良好的经济、社会和环境效益,使得日光温室近年来在我国迅速发展,研究学者也日益趋多。日光温室对太阳能的利用通常是被动的,通过温室结构的优化、新型材料的采用、后墙等蓄热能力的增强来达到保温性与采光性的提高要求[1-6],然而这些调控手段对于日光温室内环境的温度的调节是有限的,对于有些喜温作物来说,仍不能满足其要求。研究主动的太阳能利用的日光温室系统,对温室内部热量传递过程进行研究和分析,有利于对温室内部设备的排布进行优化热设计[7]。日光温室的研究发展意在外界多变的自然气候条件下,建立一个更为稳定、可靠、可控、节能、高效益的适合作物生长的小气候环境。鉴于日光温室系统的复杂性和参数变量的繁多性和多变性,计算流体力学(CFD)的发展为日光温室的数字化研究提供了重要的手段。
为了更好的研究温室热环境及日光温室内的热量传递过程,本文拟建了无植物条件下的三维被动式日光温室模型,然后通过CFD模拟,对日光温室内环境的温度场、压力场和速度场的分布情况进行分析、讨论并得出结论,有利于优化实际日光温室的建设及温室内部设备的排布,也能够为实际过程中的研究和生产提供一定的理论指导依据和建议。
1.2 日光温室及其原理和研究发展状况
1.2.1 日光温室及其原理
日光温室是园艺设施的一种,它采用透光覆盖材料作为全部或部分围护结构,具有充分采光、严密保温或补充加温、对空气对流等性能的良好设备。在日光温室中,可以人为的对设施内环境要素(光照强度、室内温度、空气湿度、土壤含水量和二氧化碳浓度等)进行有效的调控,按照日光温室内作物的需要为其提供适宜甚至更好的栽植培育条件,以部分有效或全部有效地克服外界不利环境条件对作物生长产生的影响,使得光照辐射资源、人力资源和土地资源得到最大化的科学合理利用,从而提高劳动生产率和作物在不适宜生长季节的优质产出率,显著地提高经济效益和生态效益。
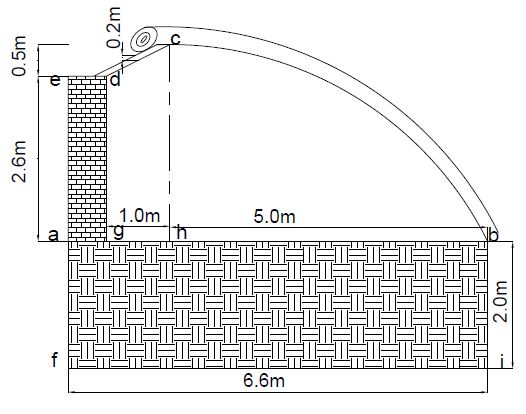
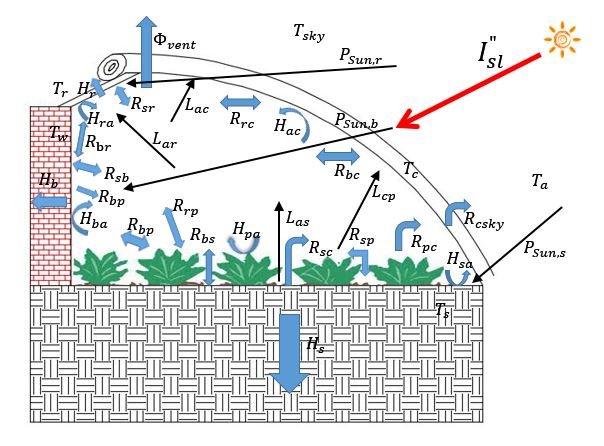
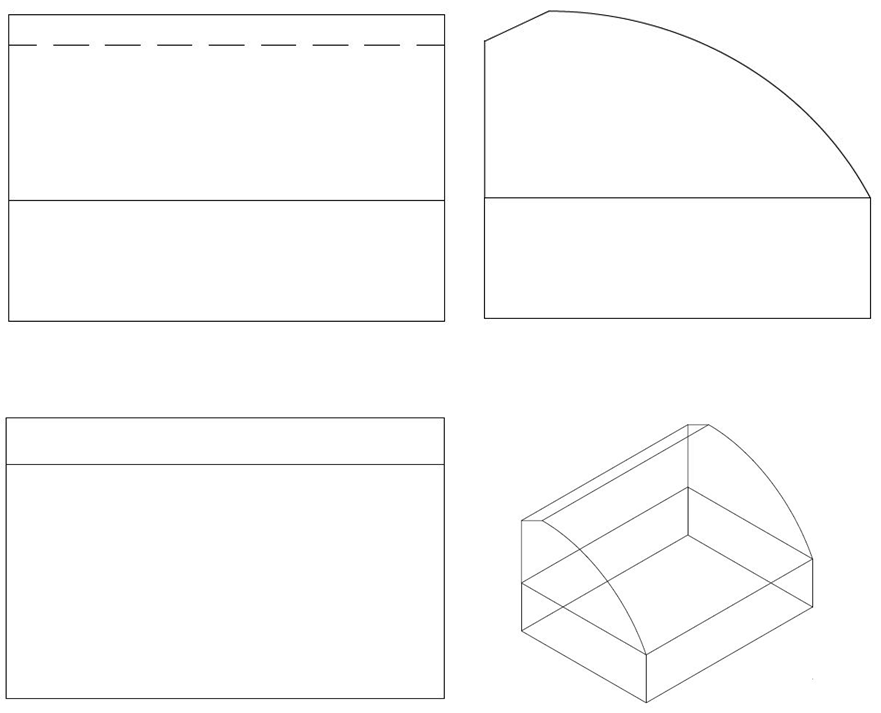
相关图片展示: