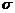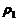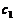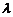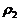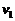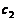倾斜下热管传热性能的实验研究毕业论文
2020-04-15 20:17:28
摘 要
摘要:本文首先介绍了热管的一些基本结构与特性,然后进一步说明重力热管的结构与特性,总结了当前对重力热管传热极限以及倾角对传热极限的影响进展。然后总结了从中得到的一些实验思路的启发。接着对实验装置进行介绍,初步分析了实验装置的一些设计原则,具体分析了热管实验的套管设计,冷却水系统的设计以及导热油系统的设计。在实验装置设计完成后,提出了实验的一些基本流程以及一些基本思路。接着对实验装置以及数据的合理性进行评估,从而分析了不同情况下热管传热量的误差,验证了所得数据的合理性。在完成实验过程后,通过对实验数据的初步分析可得,热管的传热量随着热管油流量,导热油的进口温度,热管的水流量的增加而增加。在完成上述分析之后,重点分析了倾斜角度下热管的传热性能,经过分析可得,热管的传热性能随着倾斜角度的增加,总体呈现先增加后减少的趋势。
关键词:热管 倾斜角度 导热油 冷却水 传热量
Abstract
Abstract:This paper first introduces some basic structure and characteristics of heat pipe, then further explains the structure and characteristics of gravity heat pipe, summarizes the current heat transfer limit of gravity heat pipe and the influence of inclination on the heat transfer limit progress.Then some experimental ideas are summarized.Then the experimental device is introduced, some design principles of the experimental device are preliminarily analyzed, and the design of heat pipe test casing, cooling water system and heat conduction oil system is specifically analyzed.After the design of the experimental device is completed, some basic flow and some basic ideas of the experiment are put forward.Then, the rationality of the experimental equipment and data was evaluated, and the error of heat pipe heat transfer under different conditions was analyzed to verify the rationality of the obtained data.After the completion of the experimental process, through the preliminary analysis of the experimental data, it can be concluded that the heat transfer of the heat pipe increases with the oil flow rate of the heat pipe, the inlet temperature of the heat conduction oil, and the water flow rate of the heat pipe.After completing the above analysis, the heat transfer performance of the heat pipe at the inclined Angle was emphatically analyzed. Through the analysis, it can be found that the heat transfer performance of the heat pipe increases first and then decreases with the increase of the inclined Angle.
Keywords: heat pipe; tilt Angle; heat conduction; oil cooling water; heat transf
符号表
名称 | 符号 | 名称 | 符号 |
温度 | T | 水侧传热量 | Q1 |
导热油进口温度 | t1 | 油侧传热量 | Q2 |
导热油出口温度 | t2 | 误差 |
|
冷却水进口温度 | t3 | 定性温度 | tm |
冷却水出口温度 | t4 | 定性长度 | dm |
导热油密度 |
| 热流密度 | q |
导热油比热容 |
| 导热系数 |
|
冷却水密度 |
| 导热油流量 |
|
冷却水比热容 |
| 冷却水流量 |
|
目 录
摘要...............................................................I
Abstract...........................................................II
符号表............................................................Ⅲ
第一章 绪论
1.1 引言..........................................................1
1.2 热管简介......................................................1
1.2.1热管基本特性.............................................1
1.2.2重力热管一般特性.........................................2
1.3 热管传热性能..................................................4
1.3.1热管传热性能研究概况.....................................4
1.3.2热管传热极限研究概况.....................................4
1.3.3倾角对传热性能的研究.....................................5
1.4 本课题的研究手段和拟解决的问题................................6
- 实验平台设计
2.1 实验台设计....................................................7
2.1.1热管实验台的结构设计.....................................7
2.1.2热管与套管的尺寸设计.....................................8
2.1.3实验管路的设计...........................................8
2.1.4导热油系统的设计.........................................9
2.1.5冷却水系统的设计........................................10
2.2 实验规划.....................................................10
2.2.1实验的流程介绍..........................................10
2.2.2实验过程记录与监控......................................11
第三章 数据误差分析
3.1 误差来源.....................................................13
3.2 导热油的性质.................................................13
3.2.1导热油的比热容..........................................13
3.2.2导热油的密度............................................14
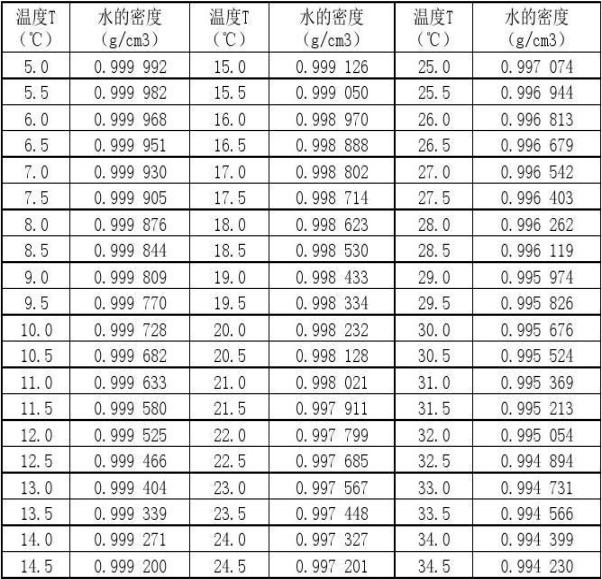
3.3 冷却水的性质................................................14
3.4 传热量的误差计算............................................15
3.4.1油侧传热量的误差计算....................................15
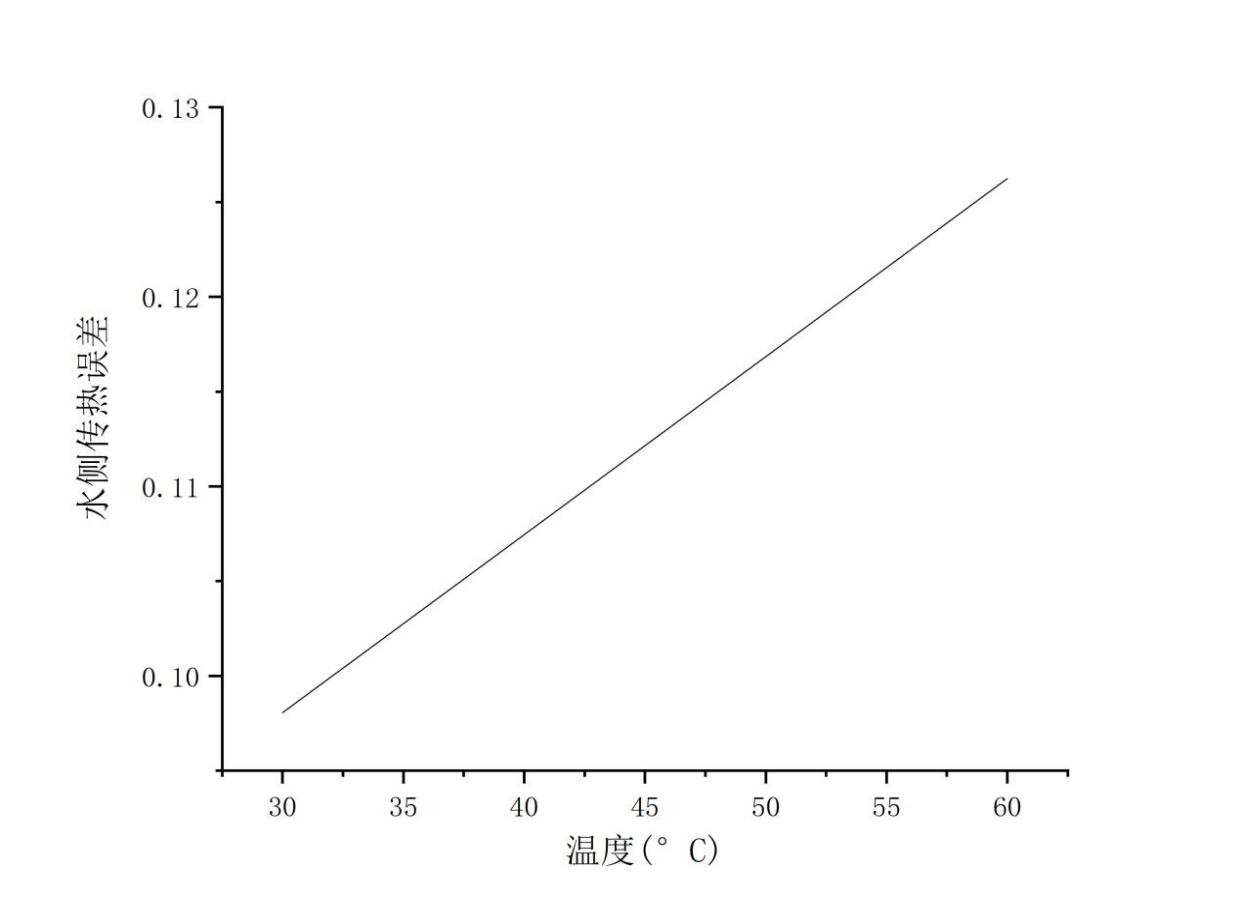
3.4.2水侧传热量的误差计算....................................16
3.5 误差曲线.....................................................17
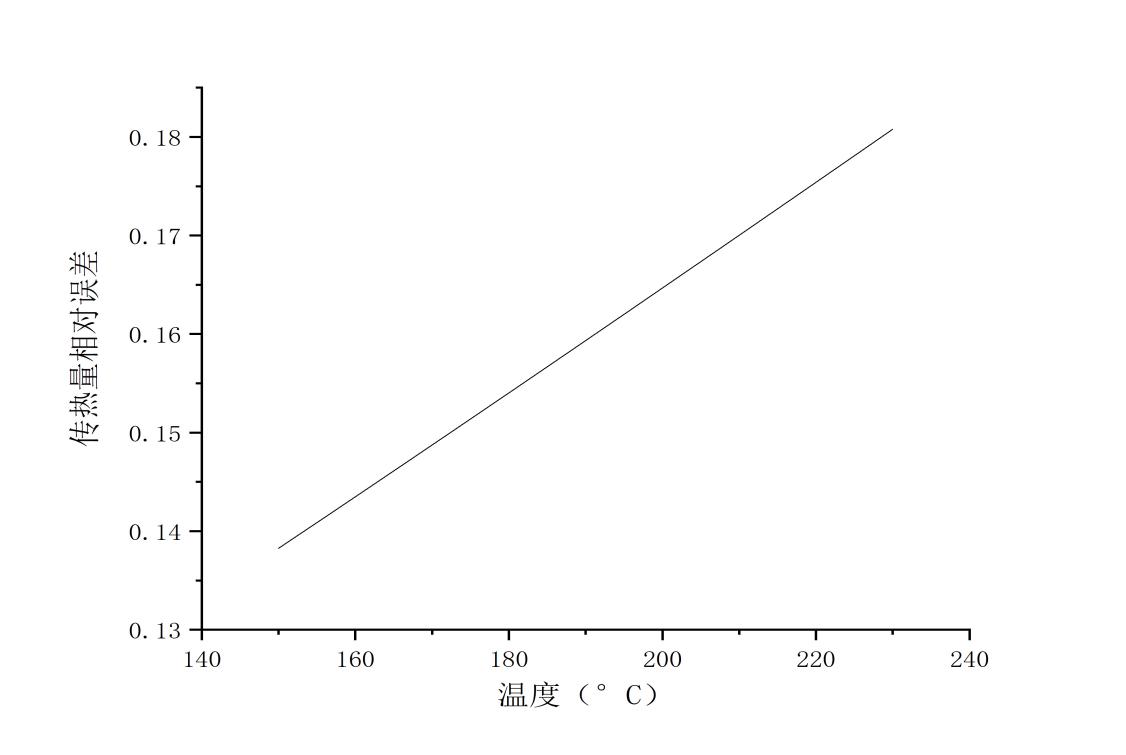
3.5.1油侧传热量的误差曲线....................................17
3.5.2水侧传热量的误差曲线....................................18
第四章 数据分析
4.1 传热量的影响因素...............................................21
4.1.1传热量与套管油进温度的关系..............................21
4.1.2传热量与套管油流量的关系................................22
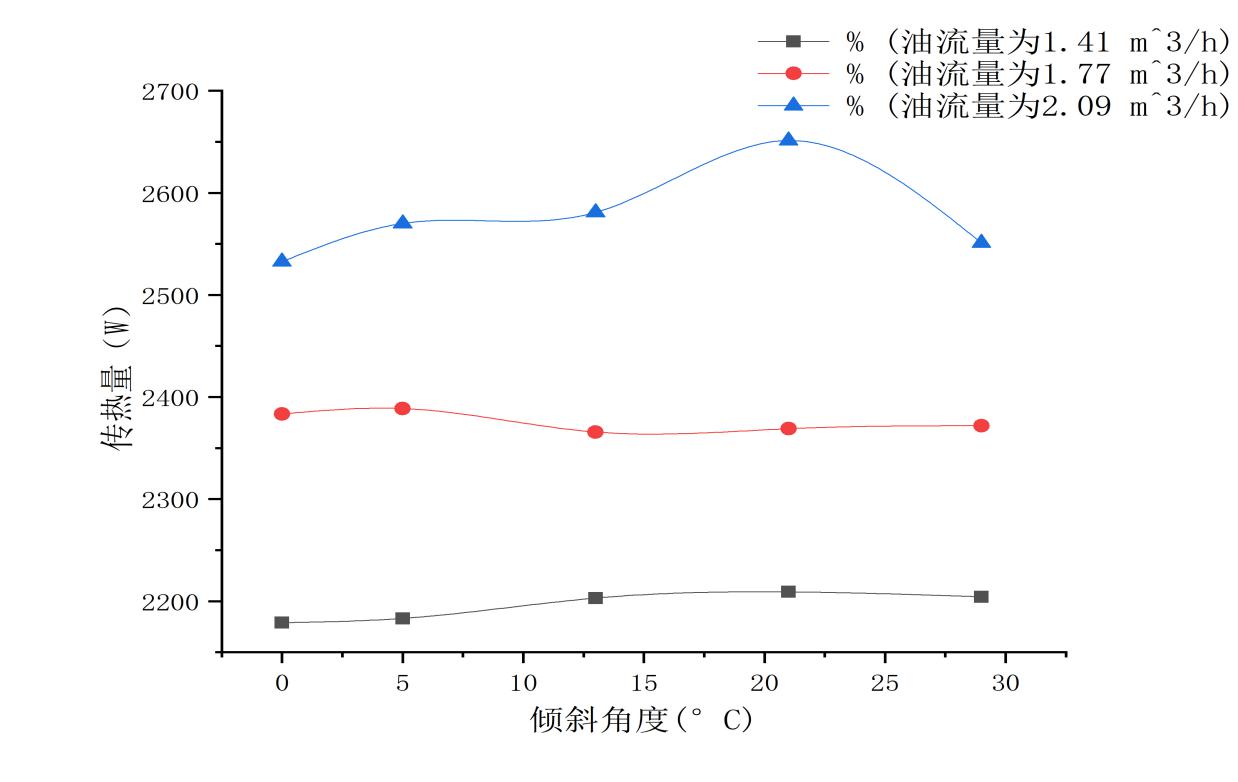
4.1.3传热量与倾角的关系......................................22
4.2 热管倾斜下的传热性能.........................................24
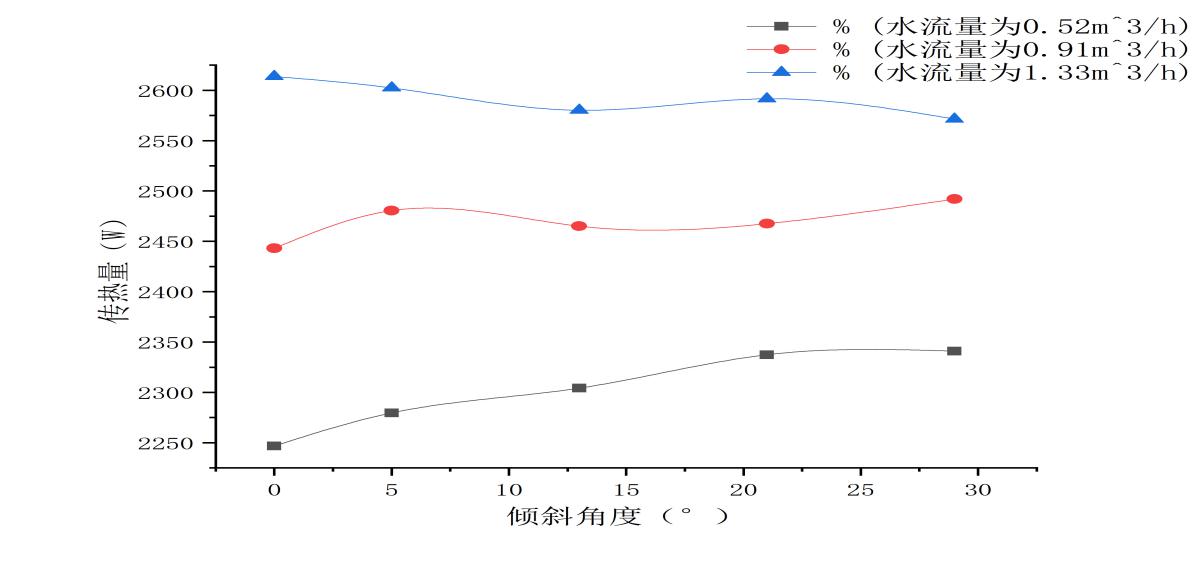
4.2.1热管传热量在不同油流量下的变化比较......................24
4.2.2热管传热量在不同水流量下的变化比较......................26
4.3 传热量的热平衡分析...........................................27
参考文献.........................................................28
致谢.......................................................... ...31
第一章 绪论
1.1 引言
电子及相关产业的发展方向有两大趋势。一方面,需要不断小型化和集成化;另一方面,它还需要在高频率和高速连续运行[1]。因此,无论上述哪种趋势,都对设备的散热条件提出了更高的要求,所以电子设备的散热处理技术已经成为制约电子行业小型化发展的瓶颈[2]。一般来说,电子设备的工作温度必须在一定的范围内,才能保证其正常运行。一旦超过温度范围,精密电子设备的工作性能和使用寿命将大大降低[3]。为了保证电子设备不超过允许的温度范围,有必要解决电子设备局部热流密度随时间变化过大的问题。虽然风机散热可以有效解决部分问题,但风机散热需要足够的空间来布置风机,且存在噪声大等缺点。我们可以考虑热管的传热[4]。除电子工业的应用外,我国工业余热资源的回收率仅为33.5%[5]。相当一部分热量没有被利用完,造成能源浪费,能源效率降低,可见我国工业企业在能源利用方面具有很大的潜力。重力热管具有结构简单、制造方便、成本低、性能优异、工作可靠等等优良特性、在相关领域的性能表现良好,其应用日益增多,在各行各业中发挥了巨大的优势[6-7]。
1.2 热管简介
以上是毕业论文大纲或资料介绍,该课题完整毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、程序设计、图纸设计等资料请添加微信获取,微信号:bysjorg。
相关图片展示: