太阳能高温吸收器实验研究毕业论文
2020-04-15 20:29:40
摘 要
随着化石燃料的日渐消减,能源供给的缺口不断加大,新能源普及应用势在必行。太阳能高温热利用作为新能源应用的研究路线,逐渐成为世界范围研究热点。太阳能热利用的核心环节就是太阳能接收器的研制。本文对课题组研制的太阳能高温吸收器的核心部件异型高温热管进行传热性能实验研究,主要研究内容和结果如下:
(1)基于热管与压力容器设计准则对异型高温热管进行设计。采用金属钠作为异型高温热管工质,充液量为220g,充液率40%;采用椭圆型封头作为高温热管吸热面,有利于减少热应力,减少吸热面厚度;以双层20目金属丝网作为异型高温热管吸液芯。对设计的异型高温热管进行热应力模拟,最大热应力为8.52MPa,其结构能够满足750℃使用条件。
(2)利用电加热炉对异型高温热管进行实验研究,考察了自然冷却条件下异型高温热管的启动及均温性能。当加热功率在3kW~5kW时,启动时间在79min~27min,各加热功率情况下启动过程图线相似表现出其启动过程的稳定,随加热功率增大启动时间减少量变小,热板段温度变化率峰值与理论转变温度处相重合,热管启动过程符合平面前锋启动模型。热管均温性能良好,整体轴向温差随着加热过程的进行逐渐减小并稳定。随着功率的增加,热管段轴向温差变化范围在50℃~75℃,热板段吸热面与冷凝面温差在200℃左右。热管径向均温性能良好,热板冷凝面温差在3kW~5kW功率下基本维持在0℃~20℃,热管段径向温差逐渐稳定至0℃~20℃。
(3)利用Trace Pro软件建立太阳能模拟器聚光系统光源分布,并对异型高温热管进行光学仿真。结果表明标准椭圆型封头结构具有良好的聚光能力,吸收光通量为平板底面的1.15倍以上,标准椭圆封头结构底面单点光通量最小值为3.2×10-4W/sr大于平板底面1.5×10-4W/sr,最大值为7.8e5W/sr小于平板底面的8.5e5W/sr,较少形成聚焦点,光学分布更均匀。
关键词:太阳能 异型高温热管 实验研究 光学仿真
The experimental research on the high temperature solar receiver
ABSTRACT
With the decline of fossil fuels, the gap in energy supply is increasing, and the popularization of new energy sources is imperative. As a research route for new energy applications, solar high-temperature heat utilization has gradually become a worldwide research hotspot. The sophistication of solar heat utilization is the development of solar energy receiver. In this paper, the heat transfer performance of the special-shaped high-temperature heat pipe, which is the core component of the solar high-temperature absorber developed by our research group, is experimentally studied. The main research contents are as follows:
(1) Design of special-shaped high-temperature heat pipes based on heat pipe and pressure vessel design criteria. Sodium metal is used as working fluid of special-shaped high-temperature heat pipe, the filling capacity is 220g, and the filling rate is 40%. Elliptical head is used as the heat absorbing surface of high-temperature heat pipe, which is conducive to reducing thermal stress and thickness of heat absorbing surface. Double-layer 20 mesh metal wire mesh is used as the liquid absorbing core of special-shaped high-temperature heat pipe. Thermal stress model simulation of shaped high temperature heat pipes, the maximum thermal stress is 8.52MPa, and its structure can meet the service conditions of 750℃.
(2) Experimental study on heat transfer performance of a profiled high temperature heat pipe using an electric heating furnace, the start-up and average temperature performance of the special-shaped high-temperature heat pipe at different heating power under natural cooling conditions are investigated. When the heating power is 3kW~5kW, the starting time is 79min~27min, and as the heating power increases, the startup time decreases. The heat pipe has good uniform temperature performance, and the overall axial temperature difference decreases gradually with the heating process. With the increase of power, the axial temperature difference of the heat pipe section ranges from 50℃~75℃, and the temperature difference between the heat absorbing surface and the condensation surface of the hot plate section ranges from 200℃~250℃. Heat pipe has good radial temperature uniformity. The temperature difference of the condensation surface of the hot plate is maintained at 0℃~20℃, at 3kW~5kW power, and the radial temperature difference of the heat pipe section is gradually stabilized to 0℃~20℃.
(3) Trace Pro software is used to establish the distribution of light source in the concentrating system of solar simulator, and to simulate the optical characteristics of the special high temperature heat pipe. The results show that the standard elliptical head structure possesses good focusing capability. The absorbable light flux is more than 1.15 times of that of the flat bottom. The minimum single point light flux of the standard elliptical head structure is 3.2×10-4, which is larger than 1.5×10-4 of the flat bottom, and the maximum value is 7.8e5, which is less than 8.5e5 of the flat bottom.
Keywords: solar energy; high temperature special-shape heat pipe; experiment research; optics emulation
目录
摘 要 I
ABSTRACT III
目录 1
第一章 绪论 1
1.1 研究背景和意义 1
1.2 太阳能高温吸收器的研究进展 2
1.2.1 直接照射式接收器 2
1.2.2 间接受热式高温吸收器 4
1.3 研究内容及方法 9
1.3.1 主要研究内容 9
1.3.2 技术路线 10
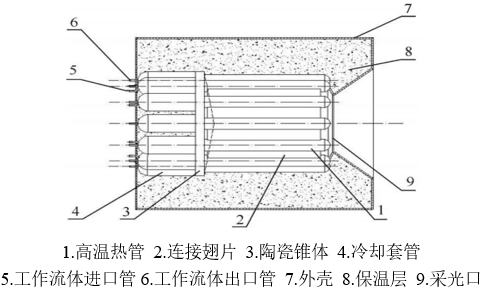
第二章 太阳能高温吸收器的研制 11
2.1 太阳能高温吸收器 11
2.2 异型高温热管结构设计 12
2.2.1 热管工质 12
2.2.2 壳体材料 13
2.2.3 吸液芯的选取 14
2.2.4 结构计算 15
2.3 应力分析 16
2.3.1 模型建立及网格划分 16
2.3.2 边界条件与载荷参数设定 17
2.3.3 求解及应力评估 18
2.4 本章小结 20
第三章 异型高温热管传热性能的实验研究 22
3.1 引言 22
3.2 异型高温热管实验系统 22
3.2.1 实验装置 22
3.2.2 实验测试条件 23
3.3 异型高温热管传热性能分析 24
3.3.1 启动性能 24
3.3.2 均温性能 30
3.4 本章小结 33
第四章 基于太阳能模拟器下的异型高温热管光学仿真 35
4.1 引言 35
4.2 太阳能模拟器系统介绍及光源建立 35
4.2.1 实验装置 35
4.2.2 基于模拟器的光源模型建立 35
4.3 聚光特性分析 37
4.3.1 标准椭圆封头结构底面 37
4.3.2 平板底面 38
4.3.3 坎德拉图 38
4.4 本章小结 40
第五章 结论与展望 41
5.1 主要结论 41
5.2 展望 42
5.3 经济性评价 42
5.3.1 投资估算 42
5.3.2 资金筹措 42
5.3.3 所需费用明细 42
参考文献 44
致谢 48
第一章 绪论
1.1 研究背景和意义
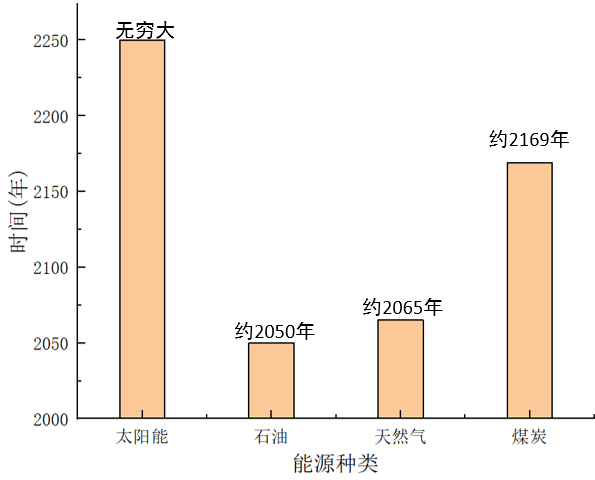
能源危机的概念已经逐步深入人心,据统计:石油的可使用量在1180~1510亿吨左右,以1995年世界石油开采总量33亿吨为标准计算,石油能源总量大约在2050年耗尽;天然气可应用总量大约在14万兆立方米,以年天然气开采总量在2300兆立方米为标准预计,天然气能源总量将要在2065年左右耗尽;探明的煤储备总量在5600亿吨左右,以1995年世界煤炭开采总量大约为33亿吨为标准预估,煤炭能源总量预计在2169年左右耗尽[1] ,如图1-1所示。化石能源衰减已成必然,新能源的利用与普及势在必行。
以上是毕业论文大纲或资料介绍,该课题完整毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、程序设计、图纸设计等资料请添加微信获取,微信号:bysjorg。
相关图片展示: