纤维增强橡胶复合材料界面疲劳损伤模型研究毕业论文
2020-05-28 07:01:20
摘 要
纤维增强橡胶复合材料性能优越,在工业领域得到广泛使用。复合材料界面在往复荷载作用下易产生疲劳损伤,对其宏观性能有重要的影响。因此,界面疲劳损伤预测方法研究已经成为复合材料领域的研究重点。本文总结已有界面疲劳裂纹扩展模型,并基于剪切筒模型预测界面的疲劳损伤。主要工作和结论如下:
(1)归纳已有的几种界面疲劳裂纹扩展模型,比较其的优缺点。基于Paris公式的界面疲劳裂纹计算方法,在计算裂纹尖端应力时会产生奇异性。基于Miner公式的线性疲劳损伤方法在计算复杂条件下的疲劳过程时,误差较大。基于非线性疲劳损伤模型的计算方法能够克服应力奇异性并且适合复杂的疲劳问题。
(2)基于剪切筒模型,建立了纤维增强复合材料的细观力学模型,求得界面剪应力分布的理论解。结果表明,剪应力沿界面变化并不明显,可以近似假设界面剪应力均匀相等。
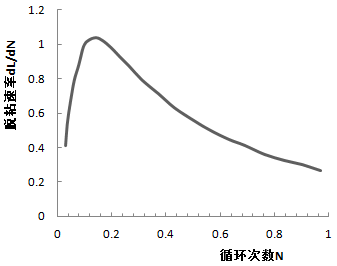
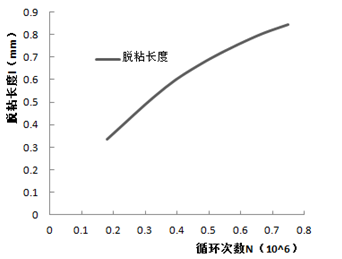
(3)基于Paris裂纹扩展准则,在细观力学模型的基础之上得到了界面疲劳裂纹扩展速率,扩展长度随循环加载次数的变化。
(4)采用两种不同的疲劳裂纹扩展模型来计算裂纹扩展速率。发现基于两种模型的疲劳裂纹扩展总体趋势相同,裂纹长度都随着疲劳次数的增加而不断增加。但是,基于Paris公式的疲劳裂纹扩展速率逐渐减小,而基于非线性疲劳损伤准则的疲劳裂纹速扩展速率不断增大。原因可能是基于Paris公式的计算中裂纹出现钝化。因此,需根据实验裂纹发展趋势选择合适的计算模型。
关键词:纤维增强 橡胶复合材料 界面脱粘 疲劳损伤 模型
ABSTRACT
Fiber-reinforced rubber composites have been widely used in many fields because of the superior performance. The fatigue damage of composite interfaces under cyclic loading has influence on the macroscopic properties of composites. So the prediction of interface fatigue damage has become a research focus in the field of composites. This thesis summarizes the existing fatigue crack propagation models of interface, and predicts the fatigue crack propagation of the interface based on the shear cylinder model. The main works and conclusions are as follows:
(1) The existing several fatigue crack propagation models of interface were summarized. The advantages and disadvantages of the models were compared. The method based on the formula of Paris will encounter singularity in the calculation of the crack tip stress. The method based on Miner formula is not accurate for those complex problems. The method based on the nonlinear fatigue damage model can overcome the stress singularity and is suitable for complex fatigue problems.
(2) A mesoscopic mechanics model of fiber reinforced composites was established based on the shear cylinder model. The analytical solution of the distribution of interfacial shear stress was obtained. The shear stresses along the interface are approximately equal. So it is assumed that the interface shear stresses are uniform.
(3) The relationship between the growth rate and length of interfacial fatigue crack and numbers of cyclic loading was obtained based on the Paris law and the mesoscopic mechanics model of composites. The influence of material parameters on the above quantity was discussed.
(4) Two models of fatigue crack propagation were used to predict the crack propagation rate, respectively. The overall trends of fatigue crack propagation based on the two models are same. The fatigue crack lengths are increased with the increase of numbers of fatigue loads. The fatigue crack growth rate calculated based on Paris law is decreased with the increase of numbers of fatigue loads. However, the fatigue crack growth rate calculated based on the nonlinear fatigue damage model is increased with the increase of numbers of fatigue loads. This is because the crack blunting would occur when Paris law is used. So, it is necessary to select appropriate model according to the experimental results of crack development.
Keywords: Fiber reinforced; Rubber compound material; Interfacial debonding; Fatigue damage model.
目录
摘要 II
ABSTRACT III
目录 V
第一章 绪论 1
1.1 选题依据和课题背景 1
1.2 复合材料力学理论研究现状 1
1.2.1 细观力学 1
1.2.2 宏观力学 2
1.2.3 复合材料强度理论 2
1.3 纤维增强橡胶复合材料疲劳强化现象及损伤模型 3
1.4 纤维增强橡胶复合材料中界面破坏问题 4
1.5 纤维增强橡胶复合材料裂纹研究现状及进展 4
1.6 目前研究工作存在的不足 4
1.7 本文的研究内容和方法 5
第二章 细观力学模型 6
2.1 现有界面疲劳脱粘和扩展准则比较 6
2.1.1 基于Pairs公式的界面疲劳脱粘准则 6
2.1.2 Miner线性疲劳损伤模型 7
2.1.3非线性疲劳损伤模型 7
2.1.3.1 损伤变量的定义 8
2.1.3.2 S-N疲劳方程的理论推导 8
2.1.3.3疲劳损伤方程的建立 9
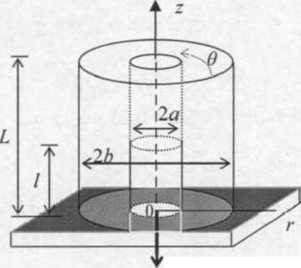
第三章 基于剪切筒模型的疲劳损伤解析 10
3.1 力学模型建立 10
3.1.1 剪切筒模型 10
3.1.2 外加循环载荷型 10
3.2 界面疲劳脱粘的解析分析 11
3.2.1 基本方程 11
3.2.2 脱粘区应力分量的求解 10
3.2.3 粘结区应力分量的求解 15
3.3 两种疲劳脱粘与扩展方法的计算结果与比较 17
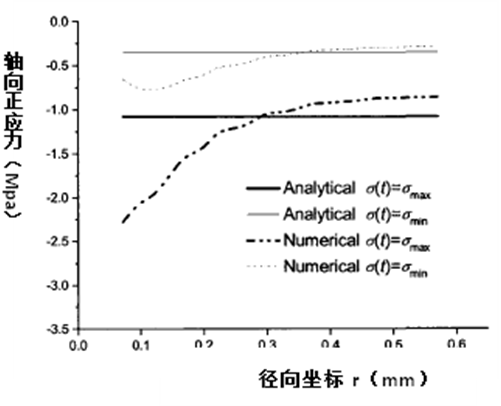
3.3.1 基于Pairs公式的界面疲劳脱粘准则的解析与数值分析结果比较 17
3.3.2 基于非线性疲劳损伤准则的疲劳脱粘与扩展 20
3.3.3 两种疲劳脱粘与扩展方法的比较 22
3.4 几何和材料参数对界面疲劳脱粘的影响 23
3.4.1 几何尺寸的影响 23
3.4.2 弹性模量的影响 25
第四章 结论 28
4.1 结论 28
参考文献 29
致 谢 32
第一章 绪论
1.1 选题依据和课题背景
纤维增强橡胶复合材料是一种以纤维为增强项、橡胶为基体制成的,是轮胎等结构体的重要组成材料。近些年来,人们一直关注着纤维增强橡胶复合材料的理论研究进展,但到目前为止,人们仍然不能够为纤维增强橡胶复合材料的疲劳损伤模型和寿命预测提供有价值的信息[1-2]。
纤维增强橡胶复合材料一般有三种可能会发生破坏,一是橡胶开裂,二是纤维断裂,三是纤维与橡胶界面发生了脱粘。一旦在外载作用下产生裂纹后,然后会在各相间继续扩大[3]。
纤维增强橡胶复合材料的使用寿命高低,主要取决于纤维和橡胶基体间界面相的力学性能。所以可以通过界面设计,来显著提高材料的整体力学性能。随着对纤维增强橡胶复合材料宏观、细观,甚至微观构造及其特性深入研究,纤维增强橡胶复合材料的界面破坏机理与力学行为已成为现代力学、材料科学和物理学的前沿课题之一。了解界面相对材料宏观力学性能影响之后,根据物理、化学相容性原理与服役环境要求对密封复合材料界面相进行增效设计,可以充分展示纤维的优点、提高纤维增强橡胶复合材料的力学性能。
1.2 纤维增强橡胶复合材料的力学理论研究现状
纤维增强橡胶复合材料包含多种组分,其宏观特征与组分的细观结构特征相关[4-5]。复合材料力学包含了两个部分,一是宏观力学,二是细观力学[6-8]。宏观力学假设材料质地相同且均布,即忽略了某些组分材料造成的不均匀性;细观力学则要考虑复合材料中不均匀的组分。
1.2.1 细观力学
复合材料的细观力学是以各个阶段复合材料的物理性质为核心[4-5]。纤维增强橡胶复合材料,它的纤维和橡胶是基本单元,但是这些基本单元虽然性质不同,但都是均匀分布的。为了得到纤维增强橡胶复合材料的细观应力应变场,一般要考虑纤维整体的排布方式和体积分数、纤维和橡胶的力学性能(包括纤维和橡胶之间的相互作用)等条件[9-11]。
1.2.2 宏观力学
纤维增强橡胶复合材料的宏观力学是把材料看成是由一些宏观均匀连续体组成,并且这些连续体是各向异性的,但是无法深入探究细观层次上各组分相的变形及材料承受疲劳损伤时产生的行为[4-11]。
1.2.3 复合材料强度理论
宏观强度理论主要有四大理论,最大应力、最大应变、Tsai-Hill、Tsai-Wu张量等。细观强度理论是综合了各相的复合来形成的。这种复合有为两大方面:混合效应和协同效应[5]。
纤维增强橡胶复合材料的混合效应是组分材料特性的线性叠加,从而表明了复合材料的力学特性,是“平均化”思想。混合效应和刚度问题有很大的联系,与此对应的力学模型和基本定律达到了成熟的地步。
相关图片展示: