石墨烯导热膜的制备及其性能研究毕业论文
2020-04-21 17:03:10
摘 要
石墨烯晶格结构为蜂窝状,并且碳原子呈单层紧密排列,碳原子之间的间距为0.142 nm,每个碳原子均以sp2杂化形式与其他碳原子相连。石墨烯由于其本身特有的高电子迁移率,良好的化学稳定性和机械性能,使其在众多领域都有良好的发展,尤其是因为石墨烯具有超高的理论导热率,使其成为散热材料新的研究方向。
本课题研究的石墨烯导热膜是一种新型的导热材料,具有优异的导热性能、机械性能和柔性,3000~5000 W/(m·k)的高导热系数,高达100 MPa的模量。石墨烯导热膜不仅可以解决智能手机散热越来越高的问题,而且石墨烯导热膜在航空航天,热管理领域俊具有潜在的应用价值。
本实验以氧化石墨溶液为原料,通过旋蒸法制备液晶相氧化石墨烯分散液,并研究其性质。再利用涂覆法制备石墨烯膜,进一步通过不同的升温梯度对其进行还原,探究膜的制备条件对其导热性能的影响。
关键词:氧化石墨烯 石墨烯 石墨烯导热膜 涂覆法
Preparation and Properties of Graphene Thermal Conductive Films
Abstract
The graphene lattice structure is honeycomb, and the carbon atoms are closely arranged in a single layer. The spacing between the carbon atoms is 0.142 nm, and each carbon atom is connected to other carbon atoms in the sp2 hybrid form. Graphene has developed well in many fields due to its unique high electron mobility, good chemical stability and mechanical properties, especially because graphene has an ultra-high theoretical thermal conductivity, making it a heat-dissipating material. New research directions.
The graphene thermal conductive film studied in this subject is a new type of thermal conductive material with excellent thermal conductivity, mechanical properties and flexibility, high thermal conductivity of 3000~5000 W/(m·k) and modulus of up to 100 MPa. Graphene heat-conducting film can not only solve the problem of higher and higher heat dissipation of smart phones, but also has potential application value in the field of aerospace and thermal management.
In this experiment, the graphite oxide solution was used as a raw material, and the liquid crystal phase graphene oxide dispersion was prepared by a rotary evaporation method, and its properties were studied. The graphene film was prepared by coating method, and further reduced by different temperature gradients to explore the influence of the preparation conditions of the film on its thermal conductivity.
Keywords: graphene oxide graphene graphene heat conductive film Coating method
目 录
摘要 I
ABSTRACT II
第一章 前 言 5
1.1石墨烯概述 5
1.1.1石墨烯的简介 5
1.1.2石墨烯的性质 5
1.2 石墨烯薄膜的制备方法 6
1.3.1 旋涂法制备石墨烯薄膜 6
1.3.2 真空抽滤法制备石墨烯薄膜 6
1.3.3 化学气相沉积法制备石墨烯薄膜 7
1.3.4 其他方法制备石墨烯薄膜 7
1.3 石墨烯的应用 8
1.3.1 复合材料 8
1.3.2 储能材料 8
1.3.3 薄膜材料 9
1.3.4 电子器件 9
1.5 本课题研究意义和主要内容 9
1.5.1 研究意义 9
1.5.2 研究内容 10
第二章 实验部分 11
2.1主要试剂和实验仪器 11
2.2 实验步骤 11
2.2.1 制取18g/L的氧化石墨烯溶液 11
2.2.2 刮膜 11
2.2.3 烧膜(还原) 11
2.2.4 制备液晶相氧化石墨烯分散液 12
第三章 结果与讨论 13
3.1 制备液晶相氧化石墨烯分散液 13
3.1.1 氧化石墨烯液晶相的形成 14
3.1.2 旋蒸过程是否会使氧化石墨烯发生堆叠 16
3.2制备还原石墨烯膜 17
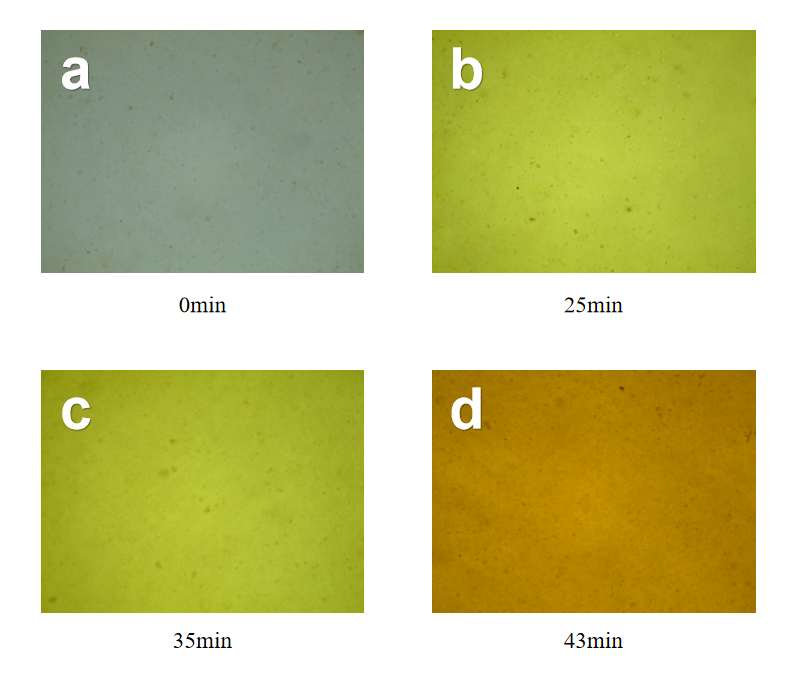
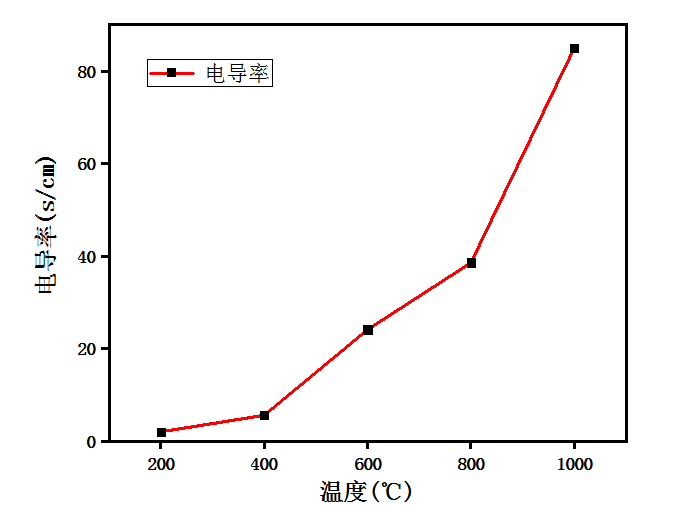
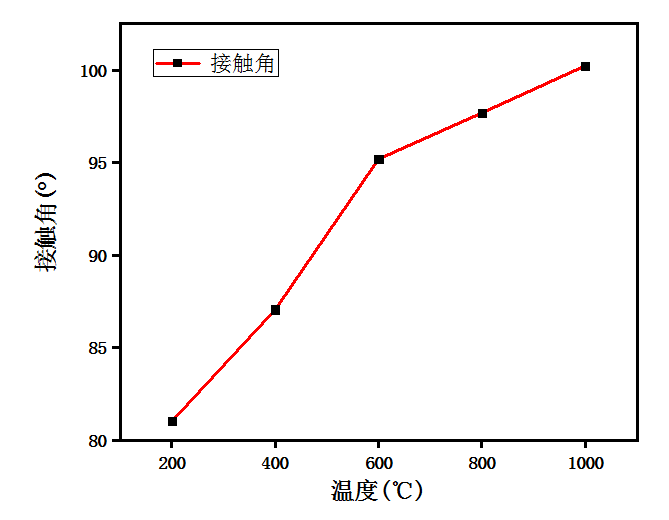
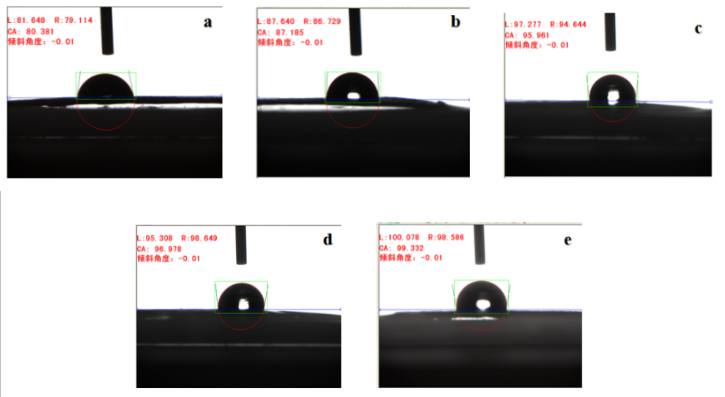
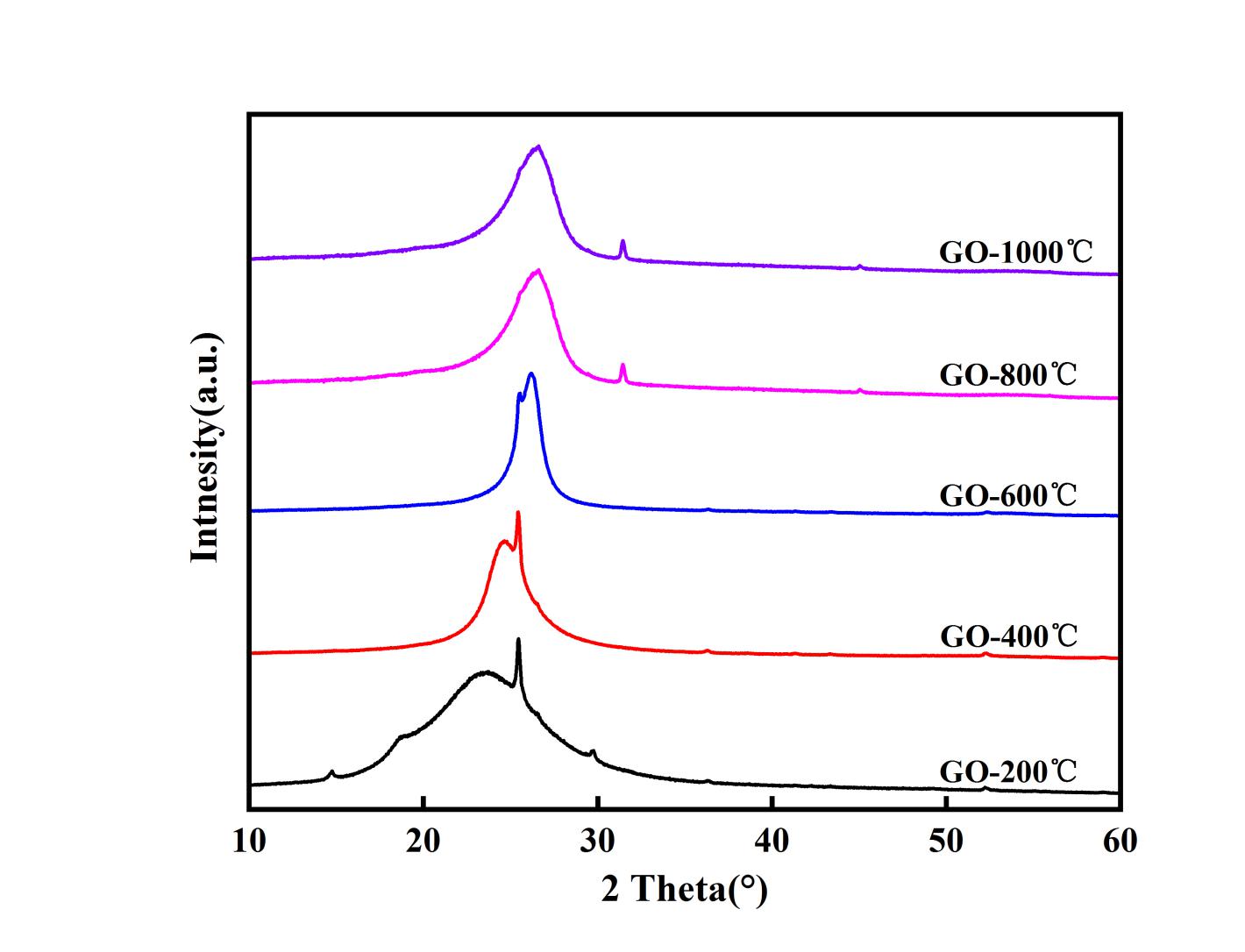
3.2.1 温度对还原石墨烯膜导电性的影响 17
3.2.2探究还原温度对氧化石墨烯还原的影响: 17
3.4 X射线衍射(XRD) 20
第四章 总结与展望 22
4.1总结 22
4.2展望 22
参考文献 23
致谢 25
第一章 前 言
1.1石墨烯概述
1.1.1石墨烯的简介
2004年,英国曼彻斯特大学物理学家安德鲁·盖姆(Andre Geim)与康斯坦丁·诺沃肖洛夫(Konstantin Novoselov),成功制备出几个原子层的石墨烯和单层石墨烯,并成功研究了它们的电子性质证实了“石墨烯”的存在,二人也因 “在二维石墨烯材料方面的突破性研究”而获得2010年诺贝尔物理学奖[1]。
石墨烯的独特结构与其各种各样的优异的性能相匹配,使其在航天材料领域,微电子领域,新能源领域,等领域被广泛的使用[2]。
相关图片展示:
您可能感兴趣的文章
- 用于甲醇制烯烃反应的SAPO-34/ZSM-5复合催化剂的原位水热结晶合成外文翻译资料
- 硫化氢在活体的化学发光探针成像外文翻译资料
- 全色发射型ESIPT荧光团对某些酸及其共轭碱负离子识别的颜色变化外文翻译资料
- 一种用于成像神经元细胞和海马组织中NMDA受体附近内源性ONOO-的双光子荧光探针外文翻译资料
- 表面功能化的Ui0-66/pebax基超薄复合中控纤维气体分离膜外文翻译资料
- 金属有机框架中的可逆调节对本二酚/醌反应:固态固定化分子开关外文翻译资料
- 二维MXene薄片的尺寸相关物理和电化学性质外文翻译资料
- 将制甲烷的Co催化剂转化为产甲醇的In@Co催化剂外文翻译资料
- MXene分子筛膜用于高效气体分离外文翻译资料
- 模板导向合成具有排列通道和增强药物有效荷载的立方环糊精聚合物外文翻译资料




