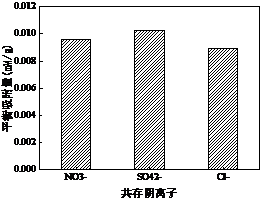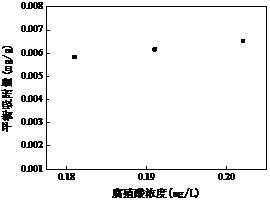水合氧化锆陶粒复合材料的制备及除磷性能研究毕业论文
2020-04-18 19:43:18
摘 要
一直以来,磷是造成水体富营养化和水生态环境破坏的主要污染物。随着国家进一步严格控制总磷的排放,相关的除磷技术研究显得十分重要。本文以高温煅烧后的陶粒为载体,使用共沉淀法将水合氧化锆负载在陶粒上,形成了水合氧化锆/陶粒复合材料,并研究了其除磷性能。采用X射线衍射(XRD)、扫描电镜(SEM)和傅里叶变换红外光谱(FT-IR)等方法表征了复合材料的物理化学性能,考察了溶液pH、共存阴离子、腐殖酸等对复合材料除磷性能的影响。实验结果表明,pH对吸附效果影响显著,并在pH=3时,吸附效果最佳;离子强度对吸附效果的影响较小,但是,腐殖酸的存在会使复合材料的吸附性能降低。磷在水和氧化锆/陶粒复合材料上的吸附过程满足Freundlich等温吸附模式,与拟二级动力学模型匹配。
关键词:陶粒 水合氧化锆 除磷
Preparation and Phosphorus Removal Properties of Hydrated Zirconia/Ceramsite Composites
Abstract
Phosphorus has always been a major pollutant resulting in eutrophication of water body and environment destruction. With the further strict control of total phosphorus emission by the state, the related research on phosphorus removal technology is very important. In this paper, hydrated zirconia/ceramsite composites were prepared by co-precipitation method using calcined ceramsite as carrier, and their phosphorus removal properties were studied. In this paper, zirconia hydrate/ceramsite composites were prepared by co-precipitation method, using ceramsite calcined at high temperature as carrier, and their phosphorus removal properties were studied. X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) were used Characterization and characterization of physical and chemical properties of composites. The effect of various factors on the phosphorus removal performance of the composites were investigated. These factors include solution pH, humic acid, coexisting anions, etc. PH has a significant effect on the adsorption effect, and when pH=3, the adsorption effect is the best. The experimental outcome point to the composite has the best adsorption effect at pH 3, and the ionic strength and coexisting anions have little influence on the adsorption effect, but the existence of humic acid will reduce the adsorption performance of the composite. The adsorption process of phosphorus on water and zirconia/ceramsite composites satisfies Langmuir isothermal adsorption model, which matches the pseudo-second-order kinetic model.
Key Words:ceramsite;hydrated zirconia;phosphorus removal
目录
摘 要 I
Abstract II
第一章 绪论 1
1.1磷的来源与危害 1
1.2 磷的处理方法 1
1.3 吸附剂 2
1.4 负载型纳米吸附剂 3
1.5研究内容 4
1.5.1本课题研究问题 4
1.5.2拟采用的研究手段 4
第二章 实验部分 5
2.1 实验试剂及仪器设备 5
2.2 水合氧化锆/陶粒复合材料的制备 6
2.3 材料表征 6
2.3.1 XRD 表征 6
2.3.2 SEM 表征 6
2.3.3 红外表征 6
2.4 磷吸附实验 7
2.4.1 磷溶液的配制与测定 7
2.4.2 磷标准曲线的绘制 7
2.5 吸附实验 8
2.5.1 pH的影响 8
2.5.2 离子强度的影响 8
2.5.3 共存阴离子的影响 8
2.5.4 腐殖酸的影响 8
2.5.5吸附动力学实验 8
2.5.6吸附等温吸附实验 9
第三章 结果与讨论 10
3.1 材料分析 10
3.1.1 XRD分析 10
3.1.2 SEM分析 10
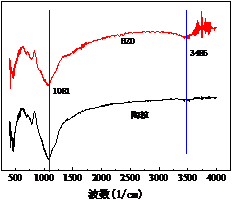
3.1.3 红外分析 11
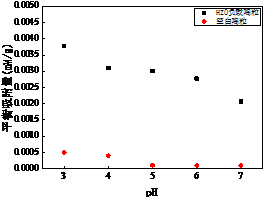
3.2 pH对吸附效果的影响 12
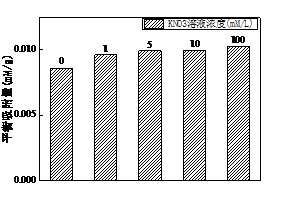
3.3 离子强度对吸附效果的影响 13
3.4共存阴离子对吸附效果的影响 14
3.5 腐殖酸对吸附效果的影响 15
3.6 吸附动力学 16
3.7 吸附等温线 18
第四章 研究结论与展望 21
4.1 研究结论 21
4.2 研究展望 21
参考文献 22
致谢 27
第一章 绪论
1.1磷的来源与危害
磷是一种有限的资源,它稀少且不可再生,是人类生活不可缺少的资源。磷通常来源于人类和动物产生的废弃物、食品加工废水、工业废水、农用土地径流和家用清洁剂[1、2]。在水和废水中,磷以正磷酸盐、多磷酸盐和有机磷的形式存在,多磷酸盐和有机磷通过水解或微生物活化转化为正磷酸盐[3、4]。由于它们对无机颗粒的强吸附性,它们也会吸附在水中的颗粒物/沉积物上。
磷被认为是淡水中潜在的限制性营养元素,过量的磷会对人类和环境康造成危害[4]。
以上是毕业论文大纲或资料介绍,该课题完整毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、程序设计、图纸设计等资料请添加微信获取,微信号:bysjorg。
相关图片展示: