光响应金属有机骨架材料的制备及性能研究毕业论文
2020-04-22 19:47:15
摘 要
实现高效吸附分离的核心是吸附剂在吸/脱附过程中孔径可以根据需要进行调节,传统吸附剂无法满足生产需求的原因之一是吸附剂的孔径不可调。
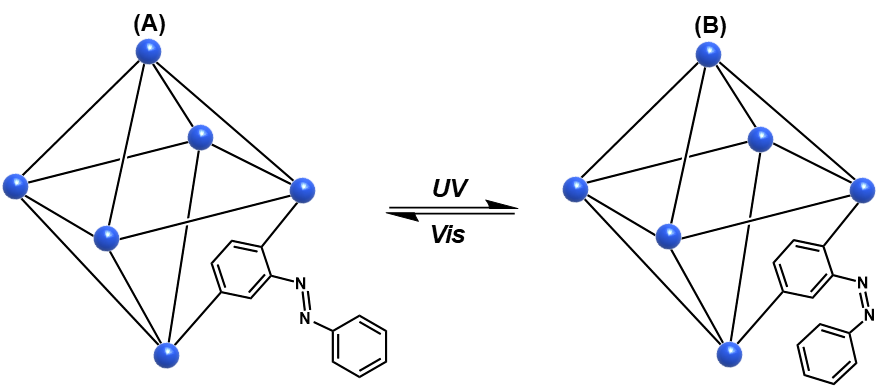
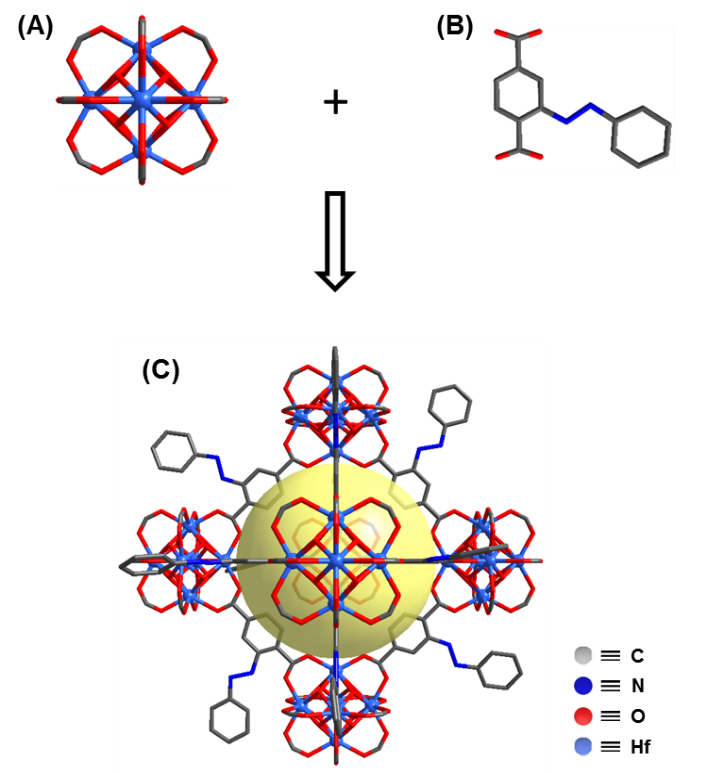
本文开发出一种新型光响应吸附材料MOF-azo,该材料以2–(苯基二氮烯基)对苯二甲酸为配体,Hf基金属簇为次级结构单元。通过改变光照条件可以实现MOF-azo自身性质的改变,从而满足吸/脱附过程中的不同要求,实现高效选择性吸/脱附。
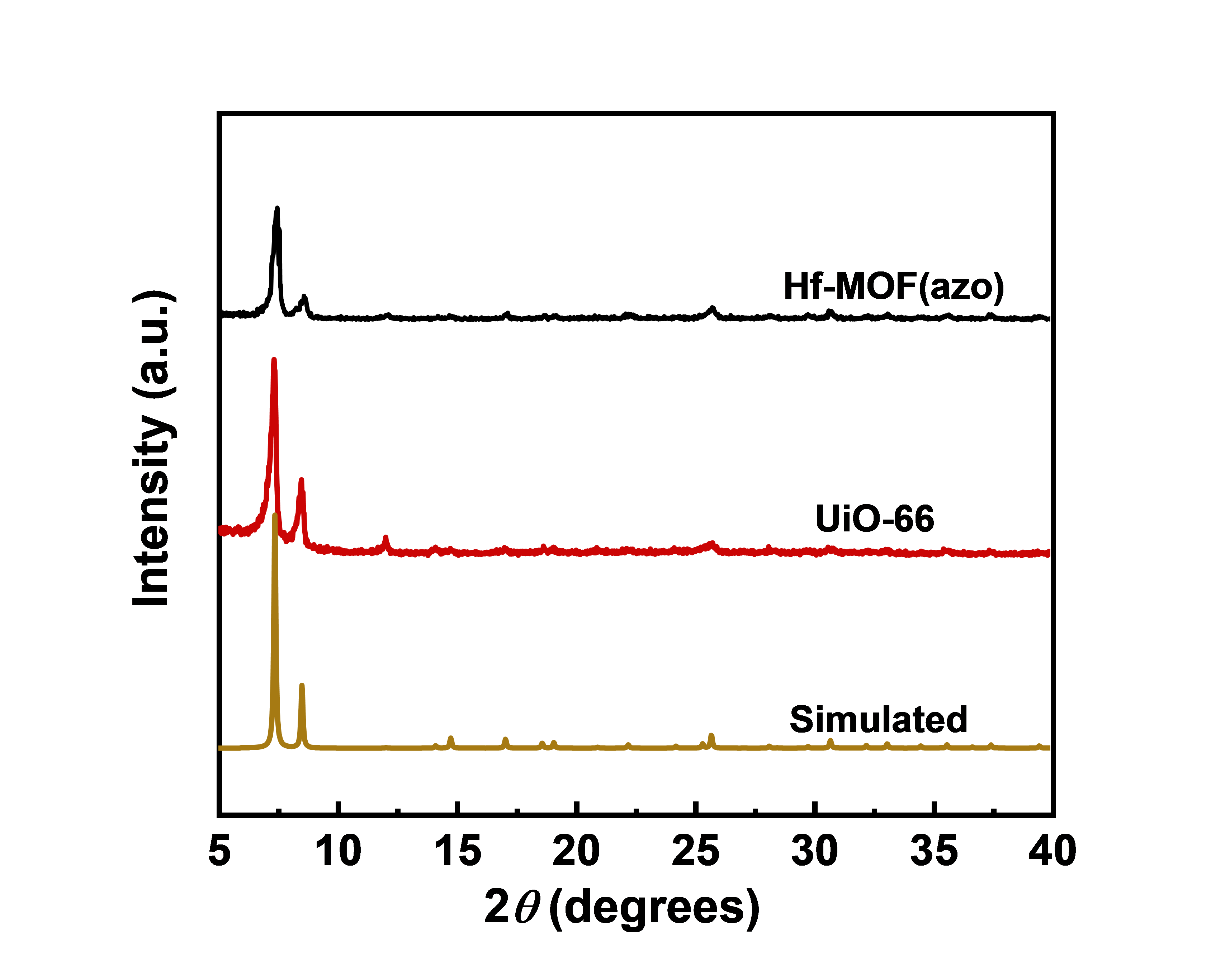
利用多种测试分析手段对MOF-azo的结构和形貌进行了分析和表征,验证了其光响应性能,评价了其对气体的吸附性能。通过红外光谱、X射线衍射、核磁共振、N2吸附-脱附等表征,证明了得合成的新材料MOF-azo纯度较高,且吸附能力较强;利用热重分析法,探究表明材料的热稳定性能相对较高;通过紫外-可见光谱的研究,证明MOF-azo具有良好的光响应性能,能够实现其结构在紫外/可见光照射下的可逆性转化。
关键词:吸附剂 光响应 高效吸/脱附
Preparation and Properties of Photoresponsive Metal-Organic Framework Materials
ABSTRACT
The core of achieving high-efficiency adsorption separation is that the pore size of the adsorbent can be adjusted as needed during the absorption/desorption process. The pore size of the adsorbent is not adjustable is one of the reasons why the conventional adsorbent cannot meet the production demand.
In this paper, a new type of photoresponsive adsorbent MOF-azo was developed, which is based on 2–(phenyldiazenyl) dicarboxybenzene and Hf-based metal clusters as secondary structural units. By changing the lighting conditions, the properties of MOF-azo can be changed to meet the different requirements in the adsorption/desorption process, enabling efficient selective absorption/desorption.
The structure and morphology of MOF-azo were analyzed and characterized by various test and analysis methods. The photoresponse performance was verified and its adsorption performance on gas was evaluated. Characterization by infrared spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction, nuclear magnetic resonance, N2 adsorption-desorption, etc., proved that the new synthetic material MOF-azo has high purity and strong adsorption capacity; using thermogravimetric analysis, the heat of the material is revealed. The stability is relatively high. The UV-Vis spectroscopy study proves that MOF-azo has good photoresponsive performance and can achieve reversible transformation of its structure under UV/Vis irradiation.
Key words: adsorbent;light response;high efficiency absorption/desorption
目录
摘要 I
ABSTRACT II
目录 i
第一章 1
1.1 1
1.1.1 1
1.1.2 金属有机骨架材料的分类 3
4
1.1.4 5
6
1.2.1 6
1.2.2 7
1.2.3 8
1.2.4 9
1.3 9
1.3.1 研究目的 9
1.3.2 研究内容 10
11
2.1 11
2.2 11
2.3 样品的制备 12
2.3.1配体2–(苯基二氮烯基)对苯二甲酸的合成 12
2.3.2 13
2.4 样品MOF-azo的表征 13
2.4.1 13
2.4.2 13
2.4.3 13
2.4.4 14
2.4.5 14
2.4.6 14
2.4.7 14
2.5 14
2.6 14
第三章 MOF-azo的表征及分析 15
3.1 15
3.1.1 16
3.1.2 16
3.1.3 17
3.1.4 样品热重分析 18
3.2 19
3.3 19
第四章 结论与展望 21
4.1 结论 21
4.2 展望 21
参考文献 22
致谢 26
第一章
1.1
1.1.1
)是20世纪末出现的一种新型多孔材料。它将过渡区金属(金属离子或簇)作为节点,有机配体作为骨架通过配位作用相互连接从而形成的形成具有分子内孔隙的聚合物,因此又被称作多孔配位聚合物()[1-3]。由于其结构的多样性、大的比较面积、丰富的物理化学条件以及温和的合成条件[4],近年来。
在20世纪初期,传统的无机和碳质材料是多孔材料主要构成。
沸石分子筛,一种具有吸附性能、催化性能及离子交换性能的晶态铝硅酸金属盐的水合物,在当时是无机材料的代表。早期人们采用最多的是天然分子筛,它有良好的孔道结构和高的水热稳定性,在当时被作为吸附剂应用到许多工业生产过程中。随着研究的推进,科研者开发出一批新型的人造分子筛如,ZSM-5等。
活性炭在早1901年就被发明,最早投入实际应用中是在第一次世界大战期间,在防毒面具中使用来过滤有害物质,是一种碳质人造材料。制造活性炭的材料来源广泛,木材、兽骨等富含碳元素的材料经高温碳化、活化后便可制得。普通的活性炭已经具有很大比的表面积,一般位于500~1700 m2/g之间,在其活化过程中形成的许多微孔结构,又赋予它更加优良的吸附性能,在环保业被大规模使用,且大小不同的微孔还可以做到一定的选择性吸附。然而,工业水平的不断提高导致传统的多孔材料的吸附量及吸附速率已无法满足日益增长的生产需求。
相关图片展示:

您可能感兴趣的文章
- 用于甲醇制烯烃反应的SAPO-34/ZSM-5复合催化剂的原位水热结晶合成外文翻译资料
- 硫化氢在活体的化学发光探针成像外文翻译资料
- 全色发射型ESIPT荧光团对某些酸及其共轭碱负离子识别的颜色变化外文翻译资料
- 一种用于成像神经元细胞和海马组织中NMDA受体附近内源性ONOO-的双光子荧光探针外文翻译资料
- 表面功能化的Ui0-66/pebax基超薄复合中控纤维气体分离膜外文翻译资料
- 金属有机框架中的可逆调节对本二酚/醌反应:固态固定化分子开关外文翻译资料
- 二维MXene薄片的尺寸相关物理和电化学性质外文翻译资料
- 将制甲烷的Co催化剂转化为产甲醇的In@Co催化剂外文翻译资料
- MXene分子筛膜用于高效气体分离外文翻译资料
- 模板导向合成具有排列通道和增强药物有效荷载的立方环糊精聚合物外文翻译资料




