Lan-826对不锈钢酸洗过程中钝化行为的影响毕业论文
2020-07-11 17:58:59
摘 要
不锈钢因其良好的耐腐蚀性和外观在生活中应用极其广泛。然而在不锈钢使用过程中,需要对其进行酸洗处理,以去除表面氧化层,便于它的后续利用。本课题主要通过静态失重法探究316与304两种常用不锈钢在柠檬酸酸洗中的腐蚀行为,通过动态失重法和电化学极化曲线研究加入缓蚀剂对酸洗过程的影响,主要包括缓蚀剂浓度和酸洗温度。结果表明,316与304不锈钢的腐蚀速率随着温度的升高而加快,随着酸洗时间的延长而加快,304不锈钢的腐蚀速率始终高于316不锈钢。温度越高,缓蚀剂对316与304不锈钢的钝化行为影响越弱,腐蚀速率越高;缓蚀剂浓度越高,缓蚀剂对316与304不锈钢钝化行为的影响越强,腐蚀速率越低。
关键词:不锈钢 柠檬酸洗 缓蚀剂 钝化 腐蚀
Effect of Lan-826 on the corrosion behavior of stainless steel during pickling
Abstract
Stainless steel is widely used in daily life due to its good corrosion resistance and appearance. However, in the process of stainless steel using, it needs to be pickling to remove the surface oxidation layer, so as to facilitate its subsequent use. To explore this topic mainly by static weight-loss method in 316 and 316 two common stainless steel on the corrosion behavior of citric acid pickling, through dynamic weight loss method and electrochemical polarization curve to study the effect of adding corrosion inhibitor for acid pickling process, mainly including acid corrosion inhibitor concentration and temperature. The results show that the corrosion rate of 316 and 304 stainless steels increases with the increase of temperature, and increases with the extension of acid cleaning time. The corrosion rate of 304 stainless steels is always higher than 316 stainless steels. The higher the temperature, the weaker the influence of corrosion inhibitor on the passivation behavior of 316 and 304 stainless steel, the higher the corrosion rate. The higher the concentration of corrosion inhibitor, the stronger the influence of corrosion inhibitor on the passivation behavior of 316 and 304 stainless steel, the lower the corrosion rate.
Key words: stainless steel; lemon pickling ;corrosion inhibitor ;passivating ;corrosion
目 录
第一章 绪论····································································································1
1.1研究背景······························································································1
1.2 Lan-826多功能缓蚀剂作用机理·································································1
1.3 多功能缓蚀剂缓蚀性能研究·····································································2
1.4 多功能缓蚀剂性能研究方法·····································································3
1.4.1 腐蚀失重法··················································································3
1.4.2 极化曲线分析法············································································4
1.4.3 电化学阻抗谱分析法······································································4
1.5 新型缓蚀剂的研究·················································································4
1.6 缓蚀剂的评价与筛选··············································································5
1.7 研究目的及意义····················································································6
第二章 实验内容······························································································7
2.1 实验仪器、材料及药品···········································································7
2.2 实验方法·····························································································7
2.2.1 静态腐蚀失重法量腐蚀速率·····························································7
2.2.2动态腐蚀失重法测量腐蚀速率···························································7
2.2.3 极化曲线的测量············································································8
第三章 实验结果与讨论·····················································································9
3.1 316与304不锈钢在柠檬酸中的腐蚀行为·····················································9
3.1.1 不同温度下316与304不锈钢的腐蚀行为···········································9
3.1.2 不同酸洗时间下316与304不锈钢的腐蚀行为·····································9
3.2 316与304不锈钢在含Lan-826柠檬酸中的腐蚀行为·······································10
3.2.1 温度对316与304不锈钢在含Lan-826柠檬酸中腐蚀行为的影响··············10
3.2.2 缓蚀剂浓度对316与304不锈钢在含Lan-826柠檬酸中腐蚀行为的影响····12
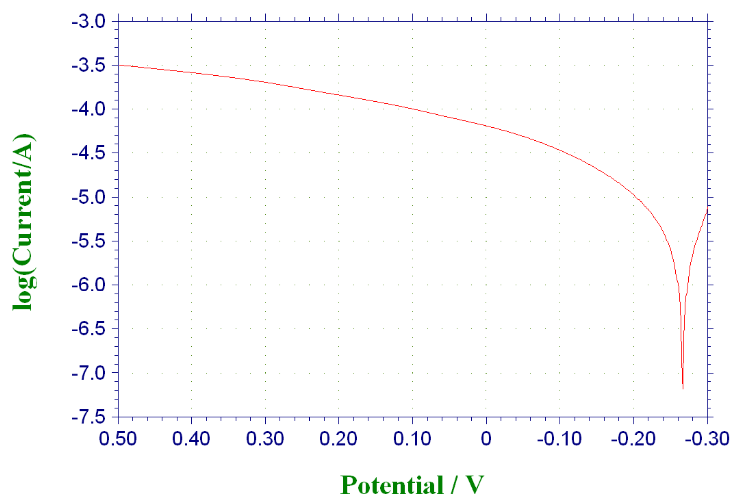
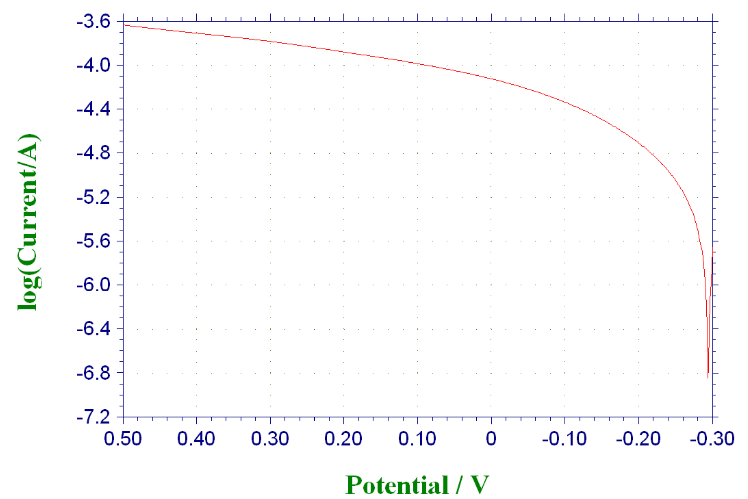
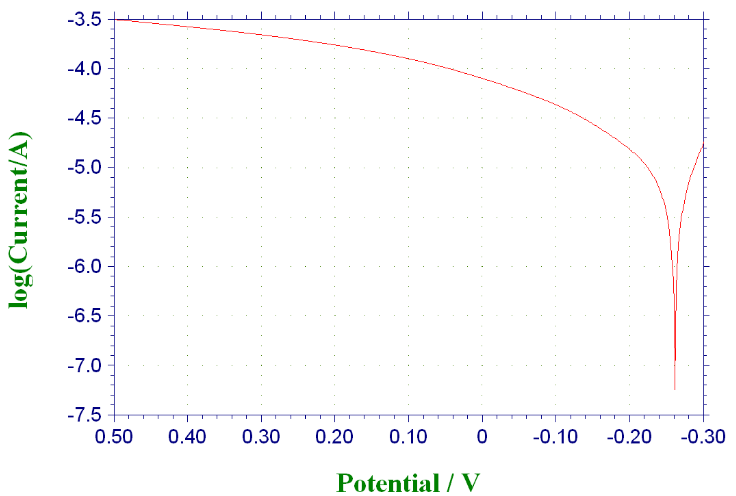
3.3 不同条件下316与304不锈钢的极化曲线···················································13
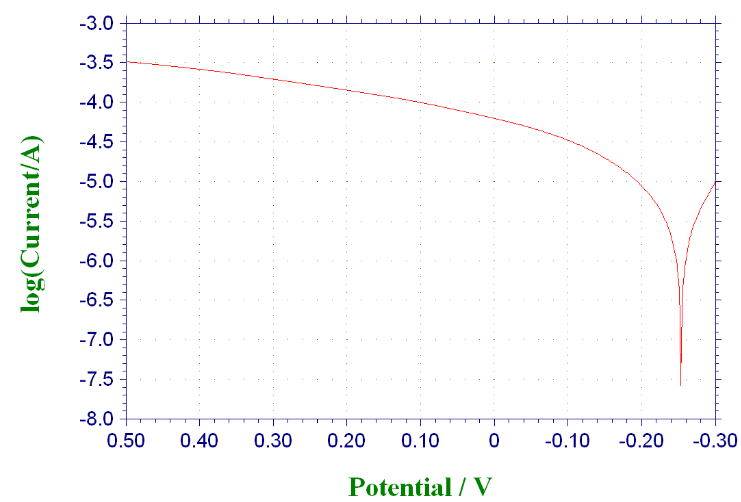
3.3.1 未添加缓蚀剂时316与304不锈钢的极化曲线·····································13
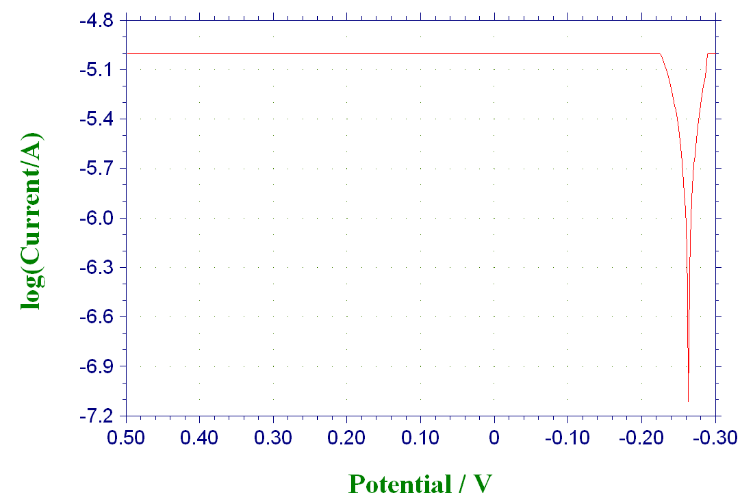
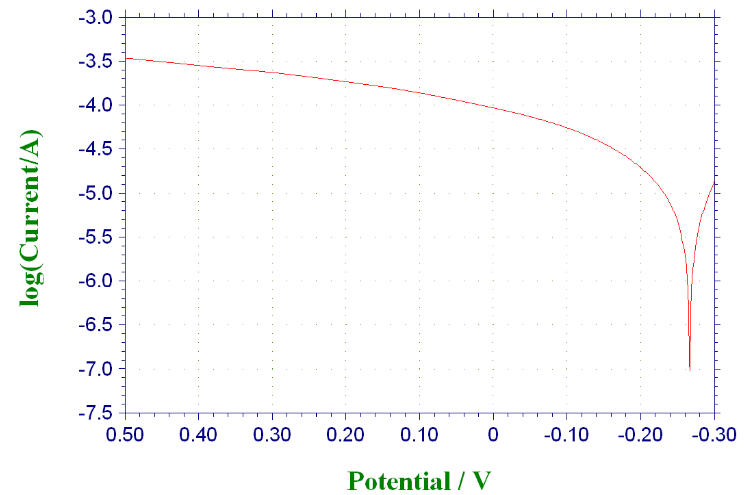
3.3.2 不同温度时316与304不锈钢的极化曲线···········································15
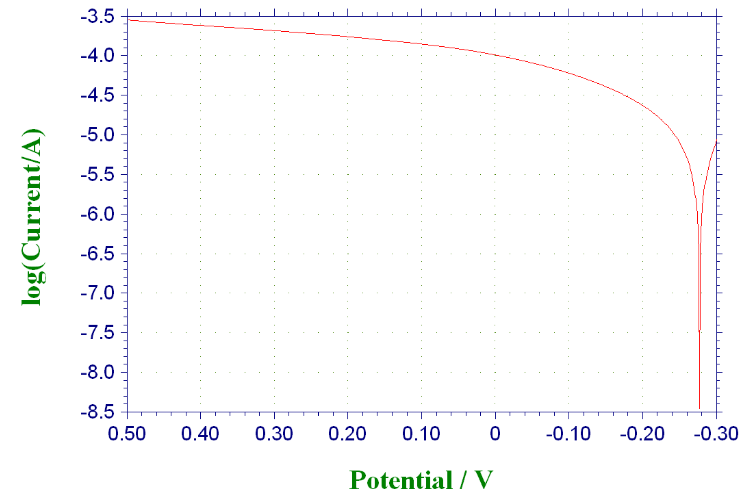
3.3.3 不同缓蚀剂浓度时316与304不锈钢的极化曲线··································19
第四章 总结与展望··························································································23
4.1 总结··································································································23
4.2 展望··································································································23
参考文献·······································································································24
第一章 绪论
1.1 研究背景
不锈钢在生活中应用极其广泛,因其良好的耐腐蚀性和外观,服务于各类生产活动和居家环境。然而在不锈钢平常的使用过程中,由于空气的缓慢氧化作用,不锈钢在经过长时间暴露在空气后容易在其表面生成一层黑色的氧化皮。这种情况的发生既影响了外观,又阻碍了后续的使用,增加了设备使用的风险。因此,对不锈钢进行酸洗处理,更有利于它的后续利用。在酸洗过程中,因只需除掉氧化层而不能够腐蚀到氧化层下的金属,一种针对减缓酸洗过程中金属腐蚀的试剂—缓蚀剂便应运而生。在这之后,缓蚀剂便成为了金属酸洗过程中不可缺少的一部分。通过缓蚀剂的保护,可以在不伤及金属本体的情况下除去氧化皮,在很大程度上保证了金属后续加工或使用时的优良性质。Lan-826作为我国自主研发的缓蚀剂,在盐酸、浓硝酸、硝酸-氢氟酸混酸等酸性条件下对金属都有着良好的保护作用。因此本课题着重研究Lan-826在有机酸条件下对不锈钢腐蚀行为的影响。通过研究在有机酸条件下304和316不锈钢的腐蚀行为以及添加Lan-826后304和316不锈钢的腐蚀行为,来探究在不同条件下缓蚀剂Lan-826对不锈钢腐蚀行为的影响。
1.2 Lan-826多功能缓蚀剂作用机理
相关图片展示: